Get started with Synthetics in Elastic Observability
Serverless Stack
To set up a synthetic monitor, you need to configure the monitor, run it, and send data back to Elastic. After setup is complete, the data will be available in your serverless Observability project or in Kibana to view, analyze, and alert on.
There are two ways to set up a synthetic monitor:
- Synthetics project
- The Synthetics UI
Read more about each option below, and choose the approach that works best for you.
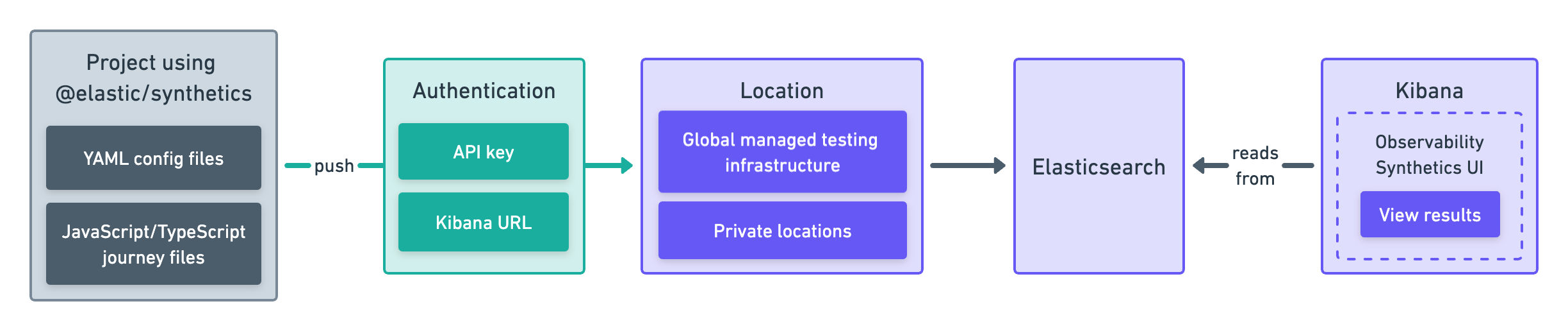
With a Synthetics project, you write tests in an external version-controlled Node.js project using YAML for lightweight monitors and JavaScript or TypeScript for browser monitors. Then, you use the @elastic/synthetics NPM library’s push command to create monitors.
This approach works well if you want to create both browser monitors and lightweight monitors. It also allows you to configure and update monitors using a GitOps workflow.
Get started in Create monitors in a Synthetics project.
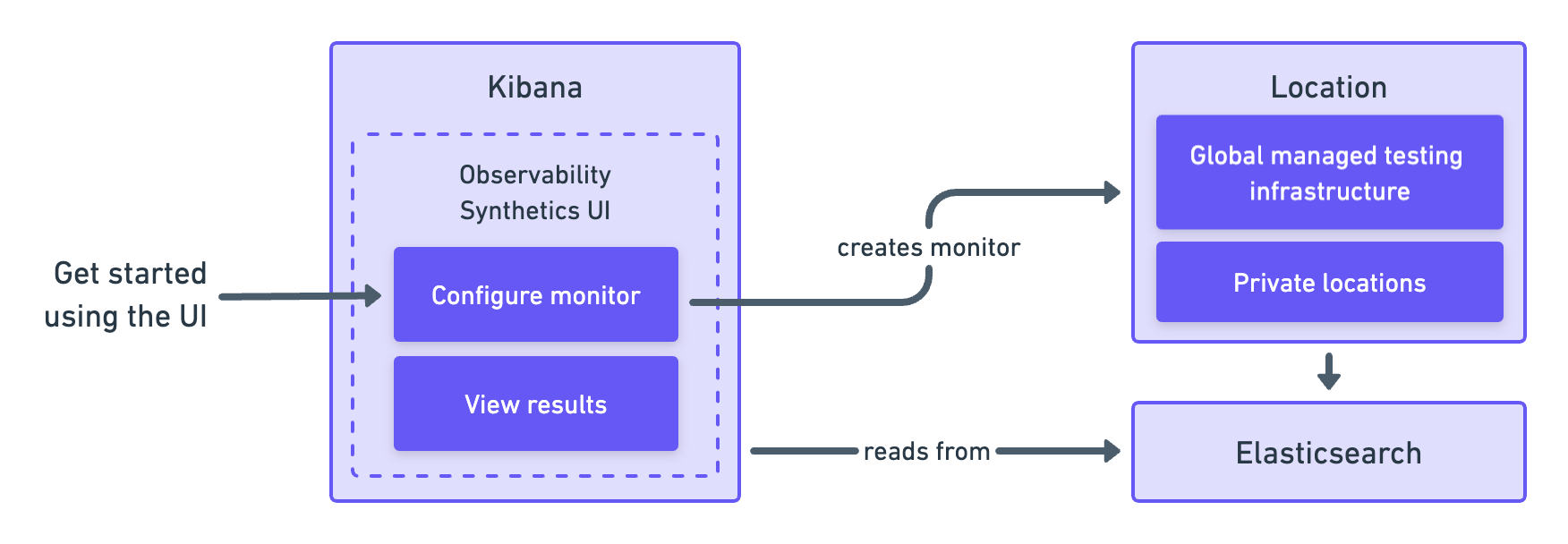
You can create monitors directly in the user interface. This approach works well if you want to create and manage your monitors in the browser.
Get started in Create monitors in the Synthetics UI.
The Elastic Synthetics integration is a method for creating synthetic monitors that is no longer recommended. Do not use the Elastic Synthetics integration to set up new monitors.
For details on how to migrate from Elastic Synthetics integration to project monitors or the Synthetics app, refer to Migrate from the Elastic Synthetics integration.
If you’ve used the Elastic Synthetics integration to create monitors in the past and need to reference documentation about the integration, go to the 8.3 documentation.