Anomaly detection in Elastic Security
Serverless Security Stack
Machine learning functionality is available when you have the appropriate role, subscription, are using a cloud deployment, or are testing out a Free Trial. Refer to Machine learning job and rule requirements for more information.
Anomaly detection jobs identify anomalous events or patterns in your data. In a security context, they’re typically used with detection rules to trigger alerts when behavior deviates from baseline activity.
Refer to Machine learning: Anomaly detection and About detection rules for more background.
If you have the appropriate role, you can use the ML job settings interface on the Alerts, Rules, and Rule Exceptions pages to view, start, and stop Elastic Security machine learning jobs.
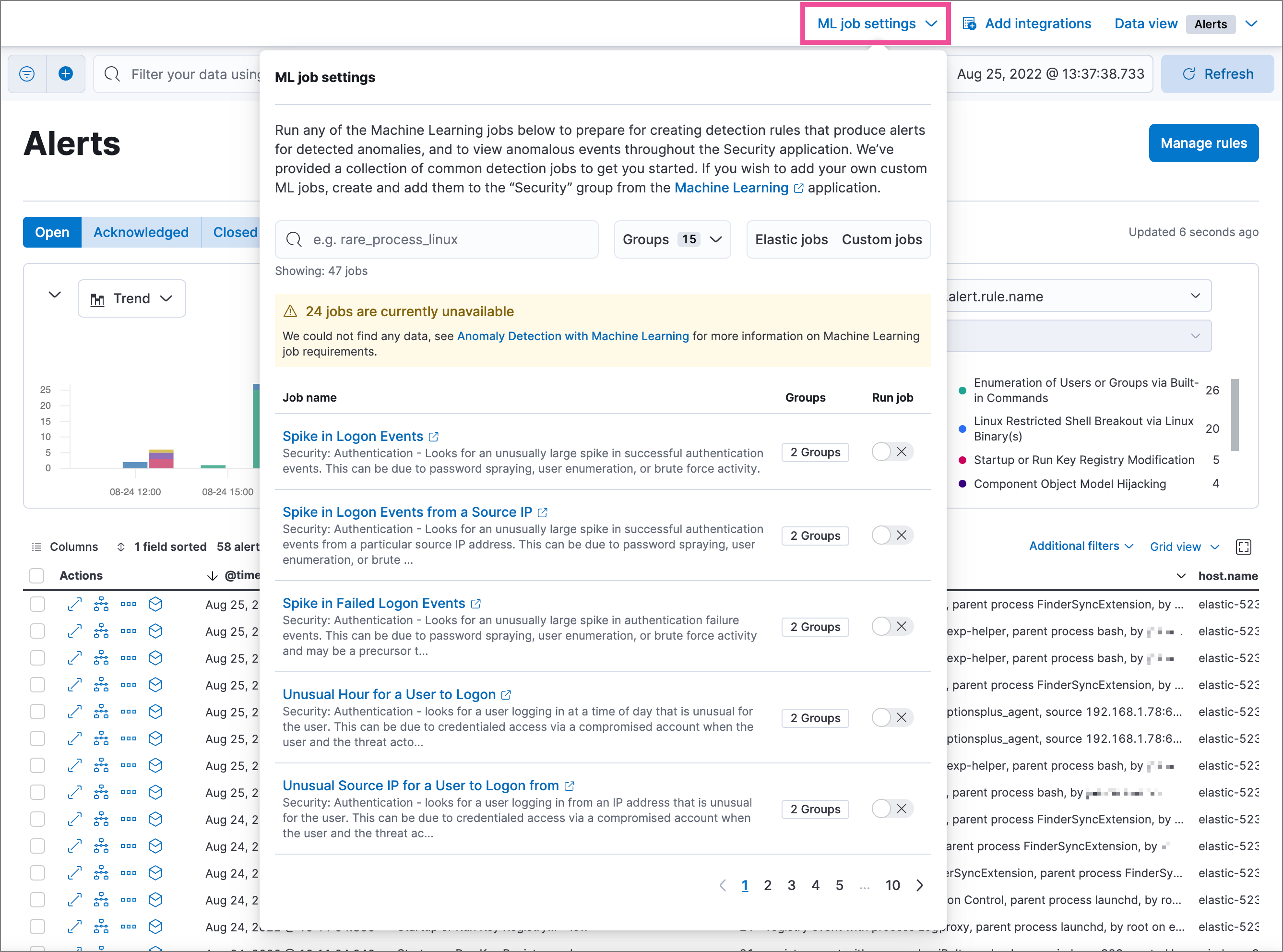
You can also check the status of machine learning detection rules, and start or stop their associated machine learning jobs:
On the Rules page, the Last response column displays the rule’s current status. An indicator icon (
 ) also appears if a required machine learning job isn’t running. Click the icon to list the affected jobs, then click Visit rule details page to investigate to open the rule’s details page.
) also appears if a required machine learning job isn’t running. Click the icon to list the affected jobs, then click Visit rule details page to investigate to open the rule’s details page.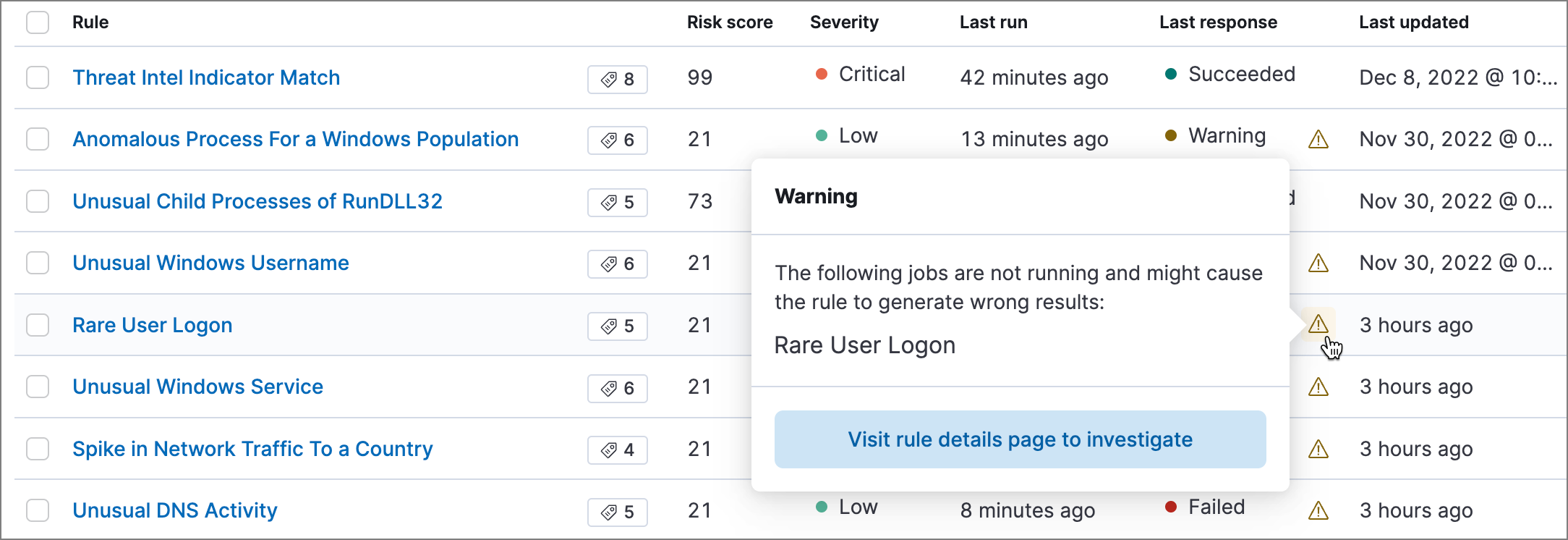
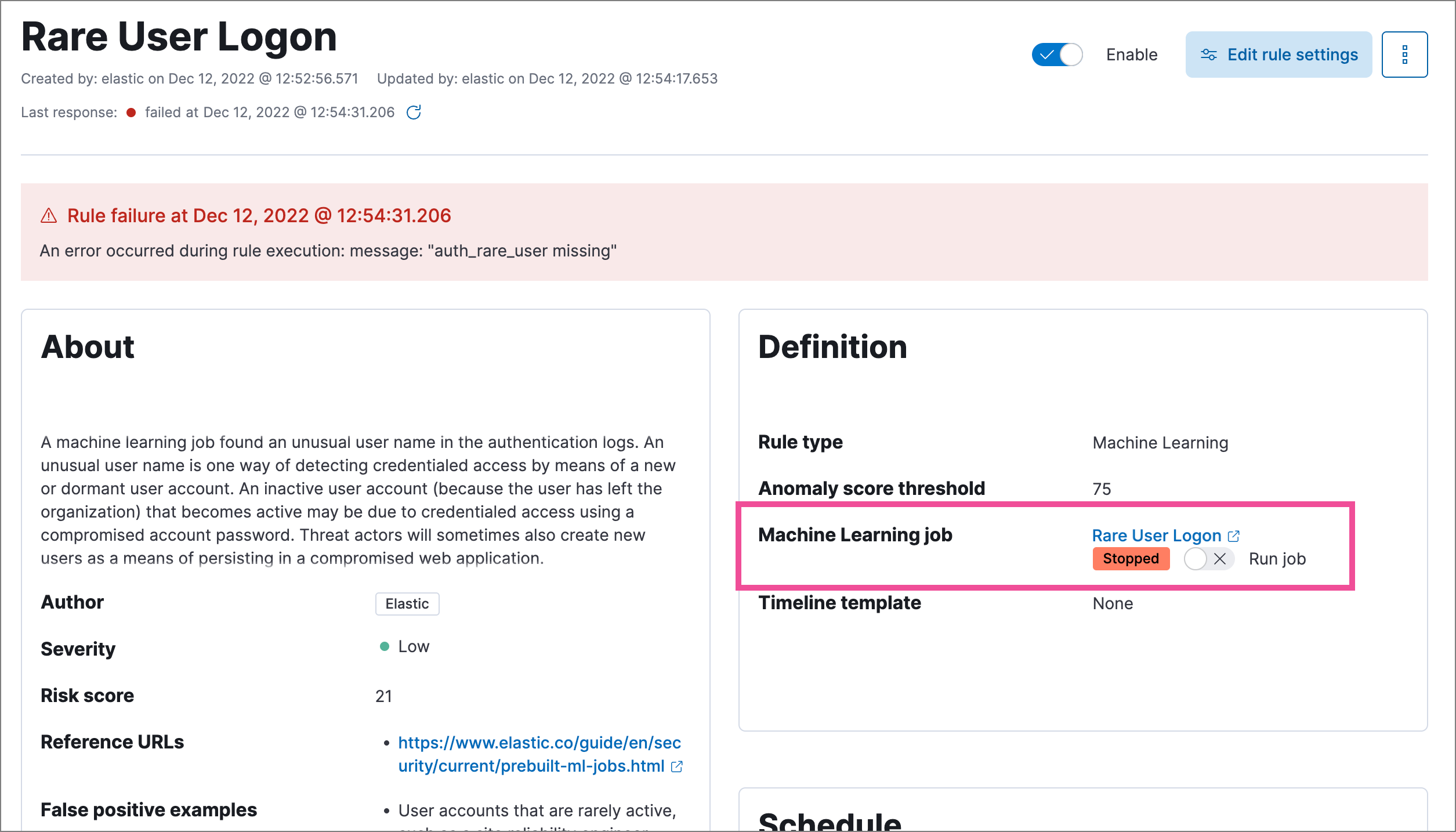
On a rule’s details page, check the Definition section to confirm whether the required machine learning jobs are running. Switch the toggles on or off to run or stop each job.
- For instructions on creating machine learning rules, refer to Create a machine learning rule.
- Alerts generated by machine learning rules are displayed on the Alerts page. For more information, refer to Manage detection alerts.
Elastic Security comes with prebuilt machine learning anomaly detection jobs for automatically detecting host and network anomalies. The jobs are displayed in the Anomaly Detection interface. They are available when either:
- You ship data using Beats or the Elastic Agent, and Kibana is configured with the required index patterns (such as
auditbeat-*,filebeat-*,packetbeat-*, orwinlogbeat-*) on the Data Views page. To find this page, navigate to Data Views in the navigation menu or by using the global search field.
Or
- Your shipped data is ECS-compliant, and Kibana is configured with the shipped data’s index patterns on the Data Views page.
Or
- You install one or more of the Advanced Analytics integrations.
Security anomaly detection configurations describes all available machine learning jobs and lists their requirements. For information on tuning anomaly results to reduce the number of false positives, see Optimizing anomaly results.
Machine learning jobs look back and analyze two weeks of historical data prior to the time they are enabled. After jobs are enabled, they continuously analyze incoming data. When jobs are stopped and restarted within the two-week time frame, previously analyzed data is not processed again.
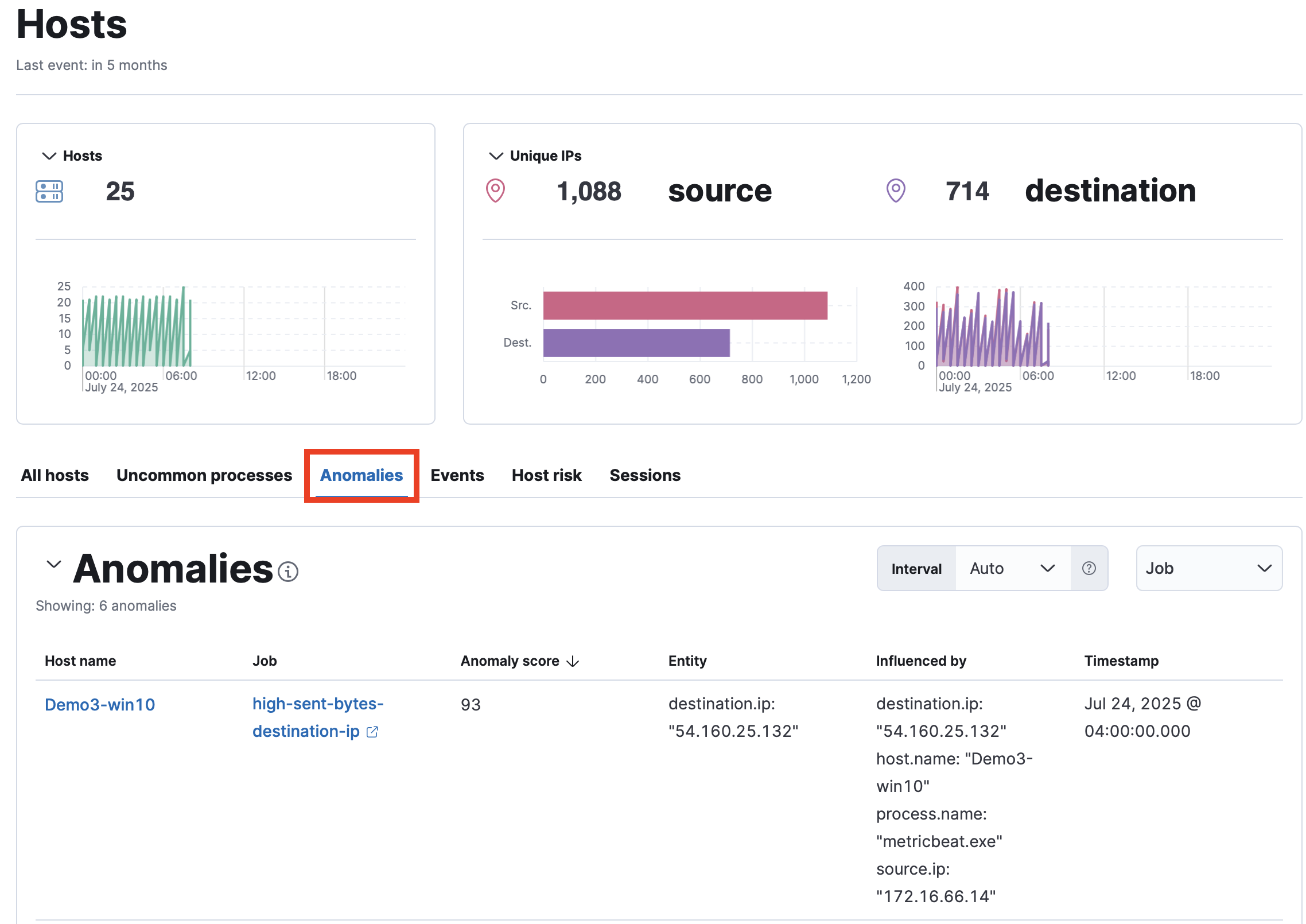
View details of detected anomalies in the Anomalies data tables, available on the Hosts, Network, or Users pages. You can access these pages from the navigation menu or with the global search field.
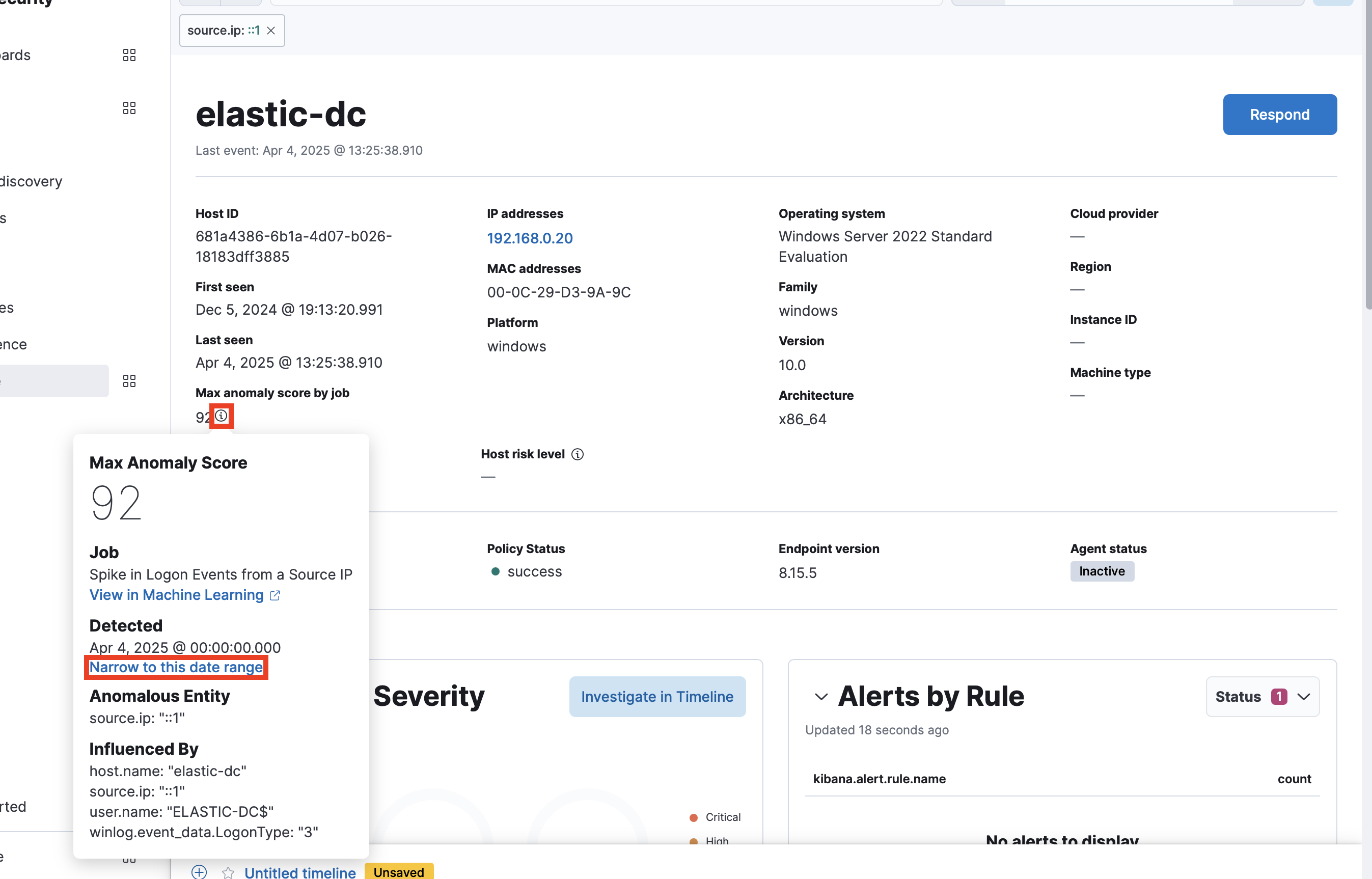
To view the Anomalies table and Max Anomaly Score By Job details, the user must have the machine_learning_admin or machine_learning_user role.
To adjust the score threshold that determines which anomalies are shown, you can modify the securitySolution:defaultAnomalyScore advanced setting.
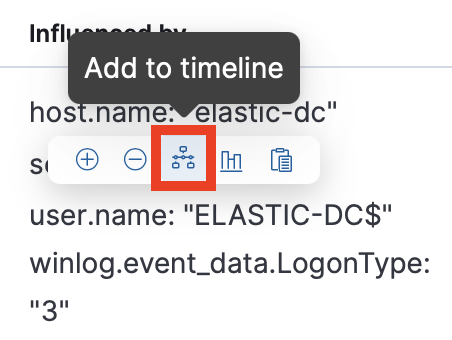
In the Anomalies table, you can add entity details, like the entity or any associated influencers, into Timeline.
When you click into a specific host, IP, or user name (depending on the page), you can narrow the time range to a specific anomaly. To do this, click the info icon next to a maximum anomaly score and select Narrow to this date range.
On this page, you can also add fields to Timeline by hovering over a field name and selecting the Add to timeline icon.
