Getting started
This page guides you through the installation process of the .NET client, shows you how to instantiate the client, and how to perform basic Elasticsearch operations with it.
- .NET Core, .NET 5+ or .NET Framework (4.6.1 and higher).
To install the latest version of the client for SDK style projects, run the following command:
dotnet add package Elastic.Clients.Elasticsearch
Refer to the Installation page to learn more.
You can connect to the Elastic Cloud using an API key and the Elasticsearch endpoint.
var client = new ElasticsearchClient("<CLOUD_ID>", new ApiKey("<API_KEY>"));
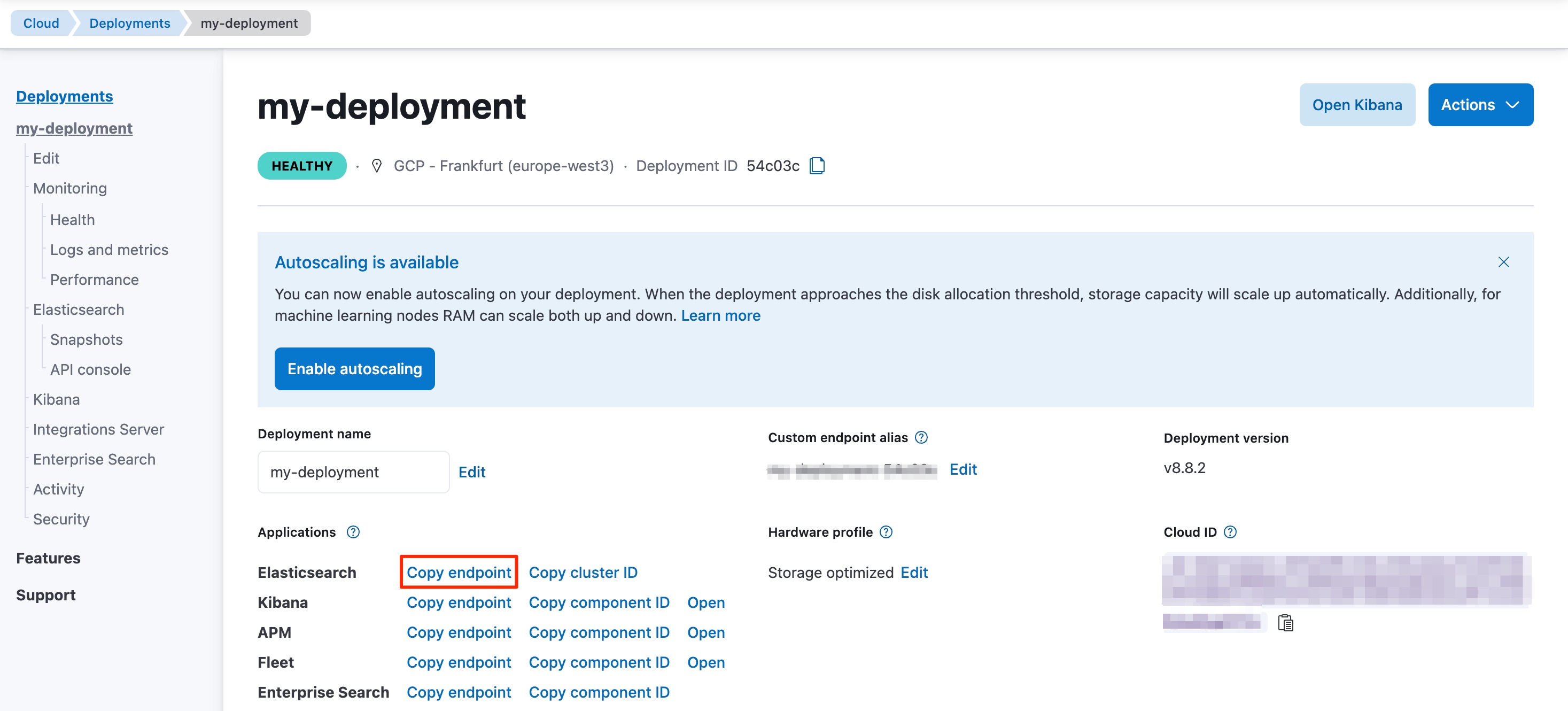
Your Elasticsearch endpoint can be found on the My deployment page of your deployment:
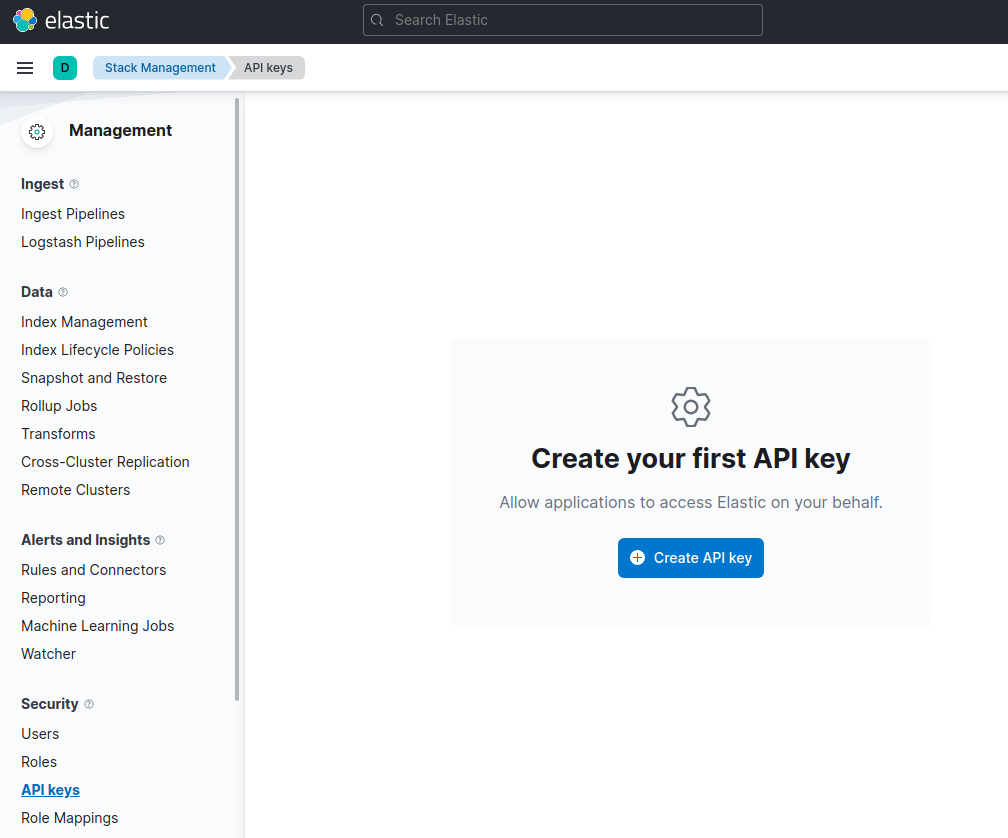
You can generate an API key on the Management page under Security.
For other connection options, refer to the Connecting section.
Time to use Elasticsearch! This section walks you through the basic, and most important, operations of Elasticsearch. For more operations and more advanced examples, refer to the CRUD usage examples page.
This is how you create the my_index index:
var response = await client.Indices.CreateAsync("my_index");
This is a simple way of indexing a document:
var doc = new MyDoc
{
Id = 1,
User = "flobernd",
Message = "Trying out the client, so far so good?"
};
var response = await client.IndexAsync(doc, x => x.Index("my_index"));
You can get documents by using the following code:
var response = await client.GetAsync<MyDoc>("my-index", id);
if (response.IsValidResponse)
{
var doc = response.Source;
}
This is how you can create a single match query with the .NET client:
var response = await client.SearchAsync<Person>(s => s
.Indices("my_index")
.From(0)
.Size(10)
.Query(q => q
.Term(t => t
.Field(x => x.User)
.Value("flobernd")
)
)
);
if (response.IsValidResponse)
{
var doc = response.Documents.FirstOrDefault();
}
This is how you can update a document, for example to add a new field:
doc.Message = "This is a new message";
var response = await client.UpdateAsync<MyDoc, MyDoc>("my_index", id, u => u
.Doc(doc)
);
var response = await client.DeleteAsync("my_index", id);
var response = await client.Indices.DeleteAsync("my_index");
- Refer to the Usage recommendations page to learn more about how to use the client the most efficiently.