Get started with dashboards
Serverless
Elastic provides a wide range of pre-built dashboards for visualizing observability data from a variety of sources. These dashboards are loaded automatically when you install Elastic integrations.
You can also create new dashboards and visualizations based on your data views to get a full picture of your data.
In your Observability project, go to Dashboards to see installed dashboards or create your own. This example shows dashboards loaded by the System integration:
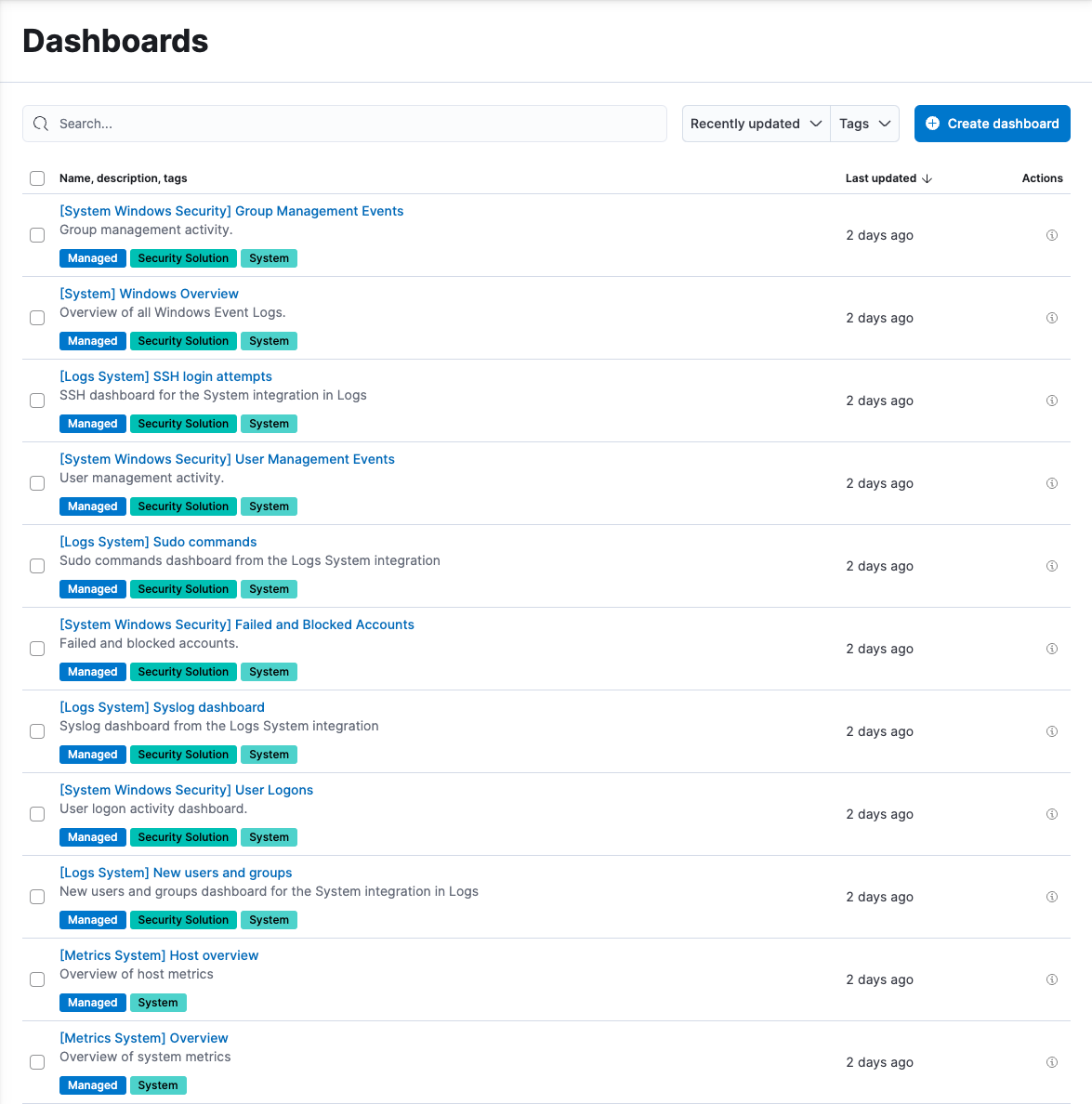
Notice you can filter the list of dashboards:
- Use the text search field to filter by name or description.
- Use the Tags menu to filter by tag. To create a new tag or edit existing tags, click Manage tags.
- Click a dashboard’s tags to toggle filtering for each tag.
To create a new dashboard, click Create Dashboard and begin adding visualizations. You can create charts, graphs, maps, tables, and other types of visualizations from your data, or you can add visualizations from the library.
You can also add other types of panels — such as filters, links, and text — and add controls like time sliders.
For more information about creating dashboards, refer to Create your first dashboard.
The tutorial about creating your first dashboard is written for Kibana users, but the steps for serverless are very similar. To load the sample data in serverless, go to Project Settings → Integrations in the navigation pane, then search for "sample data".