- Elastic Cloud Serverless
- Elasticsearch
- Elastic Observability
- Get started
- Observability overview
- Elastic Observability Serverless billing dimensions
- Create an Observability project
- Quickstart: Monitor hosts with Elastic Agent
- Quickstart: Monitor your Kubernetes cluster with Elastic Agent
- Quickstart: Monitor hosts with OpenTelemetry
- Quickstart: Unified Kubernetes Observability with Elastic Distributions of OpenTelemetry (EDOT)
- Quickstart: Collect data with AWS Firehose
- Get started with dashboards
- Applications and services
- Application performance monitoring (APM)
- Get started with traces and APM
- Learn about data types
- Collect application data
- View and analyze data
- Act on data
- Use APM securely
- Reduce storage
- Managed intake service event API
- Troubleshooting
- Synthetic monitoring
- Get started
- Scripting browser monitors
- Configure lightweight monitors
- Manage monitors
- Work with params and secrets
- Analyze monitor data
- Monitor resources on private networks
- Use the CLI
- Configure a Synthetics project
- Multifactor Authentication for browser monitors
- Configure Synthetics settings
- Grant users access to secured resources
- Manage data retention
- Scale and architect a deployment
- Synthetics Encryption and Security
- Troubleshooting
- Application performance monitoring (APM)
- Infrastructure and hosts
- Logs
- Inventory
- Incident management
- Data set quality
- Observability AI Assistant
- Machine learning
- Reference
- Get started
- Elastic Security
- Elastic Security overview
- Security billing dimensions
- Create a Security project
- Elastic Security requirements
- Elastic Security UI
- AI for Security
- Ingest data
- Configure endpoint protection with Elastic Defend
- Manage Elastic Defend
- Endpoints
- Policies
- Trusted applications
- Event filters
- Host isolation exceptions
- Blocklist
- Optimize Elastic Defend
- Event capture and Elastic Defend
- Endpoint protection rules
- Identify antivirus software on your hosts
- Allowlist Elastic Endpoint in third-party antivirus apps
- Elastic Endpoint self-protection features
- Elastic Endpoint command reference
- Endpoint response actions
- Cloud Security
- Explore your data
- Dashboards
- Detection engine overview
- Rules
- Alerts
- Advanced Entity Analytics
- Investigation tools
- Asset management
- Manage settings
- Troubleshooting
- Manage your project
- Changelog
Create an error count threshold rule
editCreate an error count threshold rule
editRequired role
The Editor role or higher is required to create error count threshold rules. To learn more, refer to Assign user roles and privileges.
Create an error count threshold rule to alert you when the number of errors in a service exceeds a defined threshold. Threshold rules can be set at different levels: environment, service, transaction type, and/or transaction name.
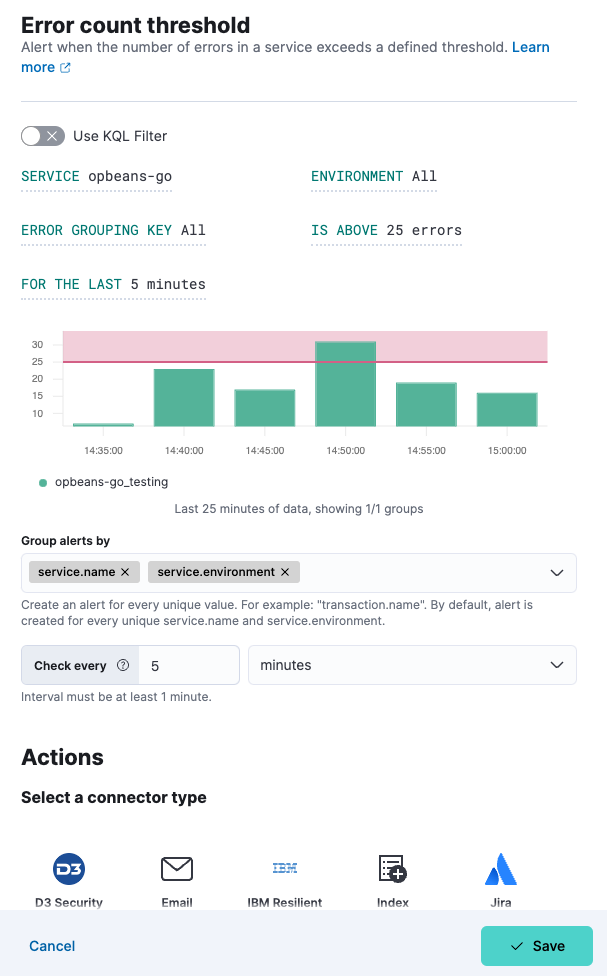
These steps show how to use the Alerts UI. You can also create an error count threshold rule directly from any page within Applications. Click the Alerts and rules button, and select Create error count rule. When you create a rule this way, the Name and Tags fields will be prepopulated but you can still change these.
To create your error count threshold rule:
- In your Elastic Observability Serverless project, go to Alerts.
- Select Manage Rules from the Alerts page, and select Create rule.
- Enter a Name for your rule, and any optional Tags for more granular reporting (leave blank if unsure).
- Select the Error count threshold rule type from the APM use case.
- Select the appropriate Service, Environment, and Error Grouping Key (or leave ALL to include all options). Alternatively, you can select Use KQL Filter and enter a KQL expression to limit the scope of your rule.
- Enter the error threshold in Is Above (defaults to 25 errors).
- Define the period to be assessed in For the last (defaults to last 5 minutes).
- Choose how to Group alerts by. Every unique value will create an alert.
- Define the interval to check the rule (for example, check every 1 minute).
- (Optional) Set up Actions.
- Save your rule.
Add actions
editYou can extend your rules with actions that interact with third-party systems, write to logs or indices, or send user notifications. You can add an action to a rule at any time. You can create rules without adding actions, and you can also define multiple actions for a single rule.
To add actions to rules, you must first create a connector for that service (for example, an email or external incident management system), which you can then use for different rules, each with their own action frequency.
Connector types
Connectors provide a central place to store connection information for services and integrations with third party systems. The following connectors are available when defining actions for alerting rules:
Some connector types are paid commercial features, while others are free. For a comparison of the Elastic subscription levels, go to the subscription page.
For more information on creating connectors, refer to Connectors.
Action frequency
After you select a connector, you must set the action frequency. You can choose to create a Summary of alerts on each check interval or on a custom interval. For example, you can send email notifications that summarize the new, ongoing, and recovered alerts every twelve hours.
Alternatively, you can set the action frequency to For each alert and specify the conditions each alert must meet for the action to run. For example, you can send an email only when the alert status changes to critical.
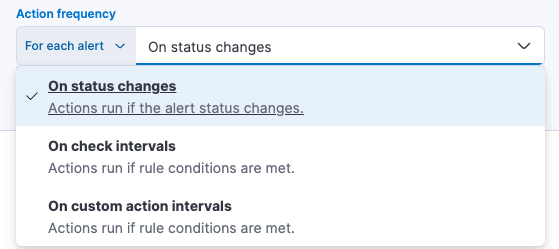
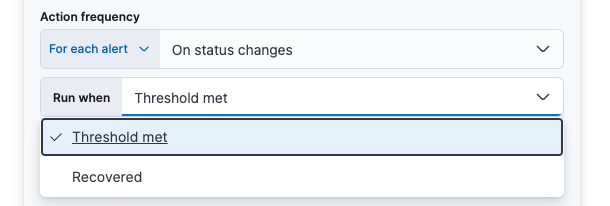
With the Run when menu you can choose if an action runs when the threshold for an alert is reached, or when the alert is recovered. For example, you can add a corresponding action for each state to ensure you are alerted when the rule is triggered and also when it recovers.
Action variables
Use the default notification message or customize it.
You can add more context to the message by clicking the Add variable icon and selecting from a list of available variables.
The following variables are specific to this rule type. You can also specify variables common to all rules.
-
context.alertDetailsUrl -
Link to the alert troubleshooting view for further context and details. This will be an empty string if the
server.publicBaseUrlis not configured. -
context.environment - The transaction type the alert is created for.
-
context.errorGroupingKey - The error grouping key the alert is created for.
-
context.errorGroupingName - The error grouping name the alert is created for.
-
context.interval - The length and unit of time period where the alert conditions were met.
-
context.reason - A concise description of the reason for the alert.
-
context.serviceName - The service the alert is created for.
-
context.threshold - Any trigger value above this value will cause the alert to fire.
-
context.transactionName - The transaction name the alert is created for.
-
context.triggerValue - The value that breached the threshold and triggered the alert.
-
context.viewInAppUrl - Link to the alert source.
Example
editThe error count threshold alert triggers when the number of errors in a service exceeds a defined threshold. Because some errors are more important than others, this guide will focus a specific error group ID.
Before continuing, identify the service name, environment name, and error group ID that you’d like to create an error count threshold rule for.
This guide will create an alert for an error group ID based on the following criteria:
-
Service:
{your_service.name} -
Environment:
{your_service.environment} -
Error Grouping Key:
{your_error.ID} - Error count is above 25 errors for the last five minutes
-
Group alerts by
service.nameandservice.environment - Check every 1 minute
- Send the alert via email to the site reliability team
From any page in Applications, select Alerts and rules → Create threshold rule → Error count rule. Change the name of the alert (if you wish), but do not edit the tags.
Based on the criteria above, define the following rule details:
-
Service:
{your_service.name} -
Environment:
{your_service.environment} -
Error Grouping Key:
{your_error.ID} -
Is above:
25 errors -
For the last:
5 minutes -
Group alerts by:
service.nameservice.environment -
Check every:
1 minute
Next, select the Email connector and click Create a connector. Fill out the required details: sender, host, port, etc., and select Save.
A default message is provided as a starting point for your alert. You can use the Mustache template syntax ({{variable}}) to pass additional alert values at the time a condition is detected to an action. A list of available variables can be accessed by clicking the Add variable icon .
Select Save. The alert has been created and is now active!
On this page