Monitoring AWS Lambda Functions
Serverless Stack
Elastic APM lets you monitor your AWS Lambda functions. The natural integration of distributed tracing into your AWS Lambda functions provides insights into the function’s execution and runtime behavior as well as its relationships and dependencies to other services.
AWS Lambda uses a special execution model to provide a scalable, on-demand compute service for code execution. In particular, AWS freezes the execution environment of a lambda function when no active requests are being processed. This execution model poses additional requirements on APM in the context of AWS Lambda functions:
- To avoid data loss, APM data collected by APM agents needs to be flushed before the execution environment of a lambda function is frozen.
- Flushing APM data must be fast so as not to impact the response times of lambda function requests.
To accomplish the above, Elastic APM agents instrument AWS Lambda functions and dispatch APM data via an AWS Lambda extension.
Normally, during the execution of a Lambda function, there’s only a single language process running in the AWS Lambda execution environment. With an AWS Lambda extension, Lambda users run a second process alongside their main service/application process.
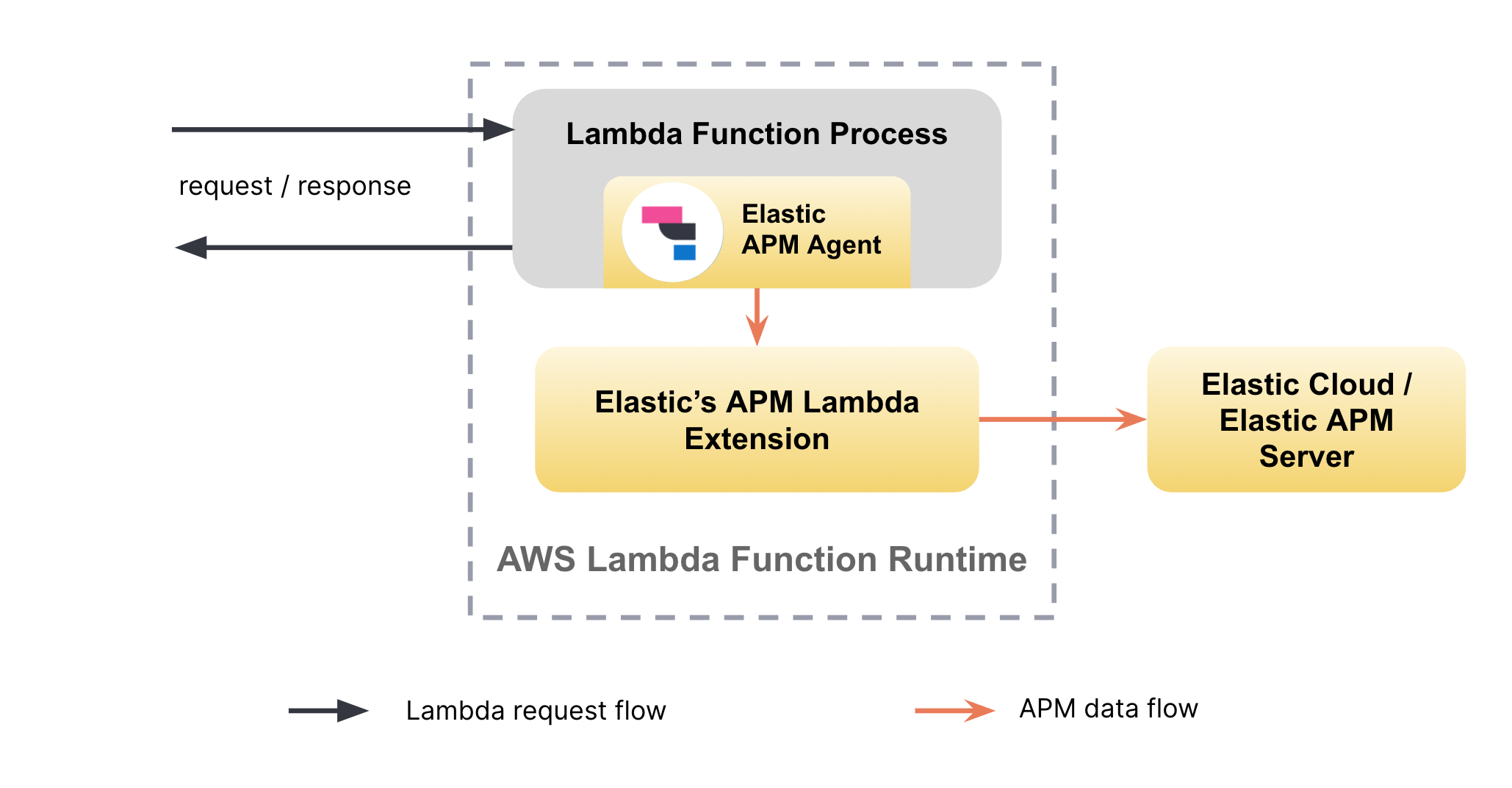
By using an AWS Lambda extension, Elastic APM agents can send data to a local Lambda extension process, and that process will forward data on to the managed intake service asynchronously. The Lambda extension ensures that any potential latency between the Lambda function and the managed intake service instance will not cause latency in the request flow of the Lambda function itself.
To get started with the setup of Elastic APM for your Lambda functions, checkout the language-specific guides:
- Quick Start with APM on AWS Lambda - Node.js
- Quick Start with APM on AWS Lambda - Python
- Quick Start with APM on AWS Lambda - Java
Or, see the architecture guide to learn more about how the extension works, performance impacts, and more.