APM Agent central configuration
editAPM Agent central configuration
editAPM Agent configuration allows you to fine-tune your APM agent configuration from within the APM UI. Changes are automatically propagated to your APM agents, so there’s no need to redeploy.
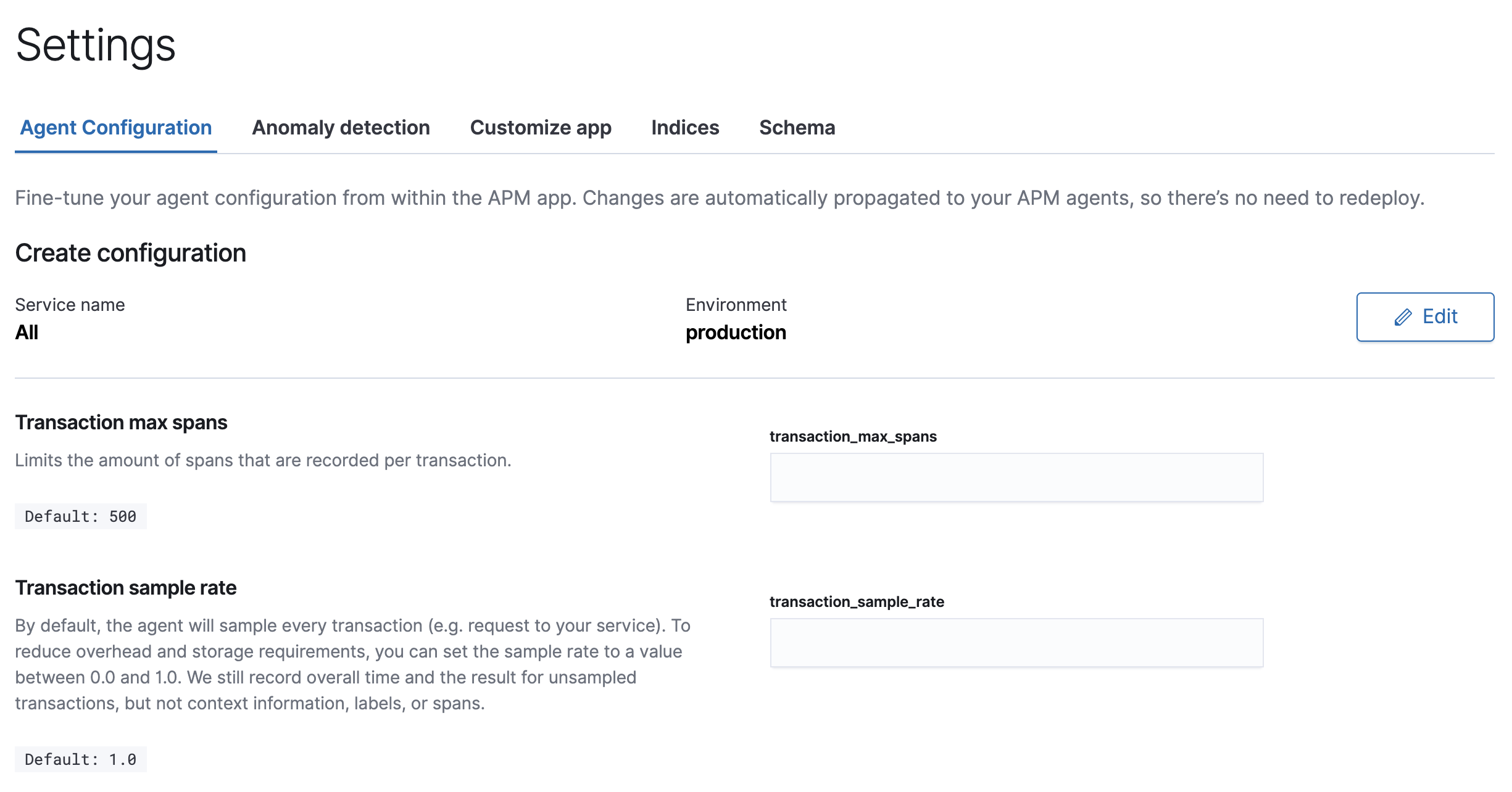
To get started, choose the services and environments you wish to configure. The APM UI will let you know when your APM agents have applied your configurations.
Precedence
editConfigurations set from the APM UI take precedence over configurations set locally in each APM agent. However, if APM Server is slow to respond, is offline, reports an error, etc., APM agents will use local defaults until they’re able to update the configuration. For this reason, it is still essential to set custom default configurations locally in each of your APM agents.
Supported configurations
editEach APM agent has a list of supported configurations. After selecting a Service name and environment in the APM UI, a list of all supported configuration options, including descriptions and default values, will be displayed.
Supported configurations are also tagged with the 
|
Android agent |
|
|
Go agent |
|
|
iOS agent |
|
|
Java agent |
|
|
.NET agent |
|
|
Node.js agent |
|
|
PHP agent |
|
|
Python agent |
|
|
Ruby agent |
|
|
Real User Monitoring (RUM) agent |
APM Server configuration
editFor most users, APM agent configuration should work out-of-the-box. If you run into trouble, it may be because you’re not using the Elasticsearch output, or because your Elasticsearch credentials don’t have sufficient privileges.
See configure APM agent configuration to learn how to configure APM Server to avoid these problems.