Getting started with cross-cluster replication
editGetting started with cross-cluster replication
editThis functionality is in beta and is subject to change. The design and code is less mature than official GA features and is being provided as-is with no warranties. Beta features are not subject to the support SLA of official GA features.
This getting-started guide for cross-cluster replication shows you how to:
- Connect a local cluster to a remote cluster
- Create a leader index in a remote cluster
- Create a follower index that replicates a leader index
- Automatically create follower indices
Before you begin
edit- Install Elasticsearch on your local and remote clusters.
- Obtain a license that includes the cross-cluster replication features. See subscriptions and License-management.
-
If the Elastic security features are enabled in your local and remote clusters, you need a user that has appropriate authority to perform the steps in this tutorial.
The cross-cluster replication features use cluster privileges and built-in roles to make it easier to control which users have authority to manage cross-cluster replication.
By default, you can perform all of the steps in this tutorial by using the built-in
elasticuser. However, a password must be set for this user before the user can do anything. For information about how to set that password, see Tutorial: Getting started with security.If you are performing these steps in a production environment, take extra care because the
elasticuser has thesuperuserrole and you could inadvertently make significant changes.Alternatively, you can assign the appropriate privileges to a user ID of your choice. On the remote cluster that contains the leader index, a user will need the
read_ccrcluster privilege andmonitorandreadprivileges on the leader index.ccr_user: cluster: - read_ccr indices: - names: [ 'leader-index' ] privileges: - monitor - readOn the local cluster that contains the follower index, the same user will need the
manage_ccrcluster privilege andmonitor,read,writeandmanage_follow_indexprivileges on the follower index.ccr_user: cluster: - manage_ccr indices: - names: [ 'follower-index' ] privileges: - monitor - read - write - manage_follow_indexIf you are managing connecting to the remote cluster via the cluster update settings API, you will also need a user with the
allcluster privilege.
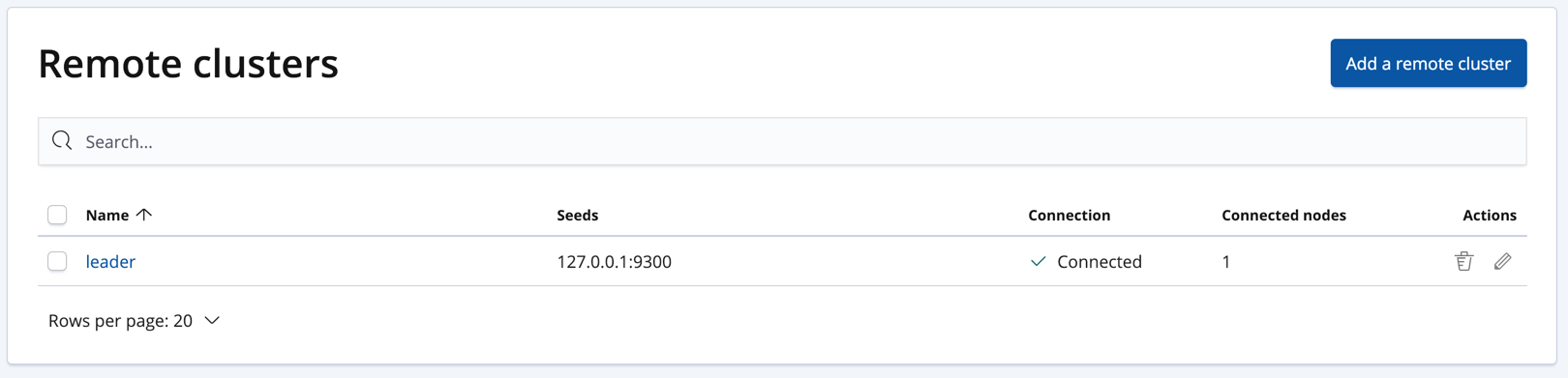
Connecting to a remote cluster
editThe cross-cluster replication features require that you
connect your local cluster to a remote
cluster. In this tutorial, we will connect our local cluster to a remote
cluster with the cluster alias leader.
PUT /_cluster/settings
{
"persistent" : {
"cluster" : {
"remote" : {
"leader" : {
"seeds" : [
"127.0.0.1:9300"
]
}
}
}
}
}
You can verify that the local cluster is successfully connected to the remote cluster.
GET /_remote/info
The API will respond by showing that the local cluster is connected to the remote cluster.
{
"leader" : {
"seeds" : [
"127.0.0.1:9300"
],
"http_addresses" : [
"127.0.0.1:9200"
],
"connected" : true,
"num_nodes_connected" : 1,
"max_connections_per_cluster" : 3,
"initial_connect_timeout" : "30s",
"skip_unavailable" : false
}
}
|
This shows the local cluster is connected to the remote cluster with cluster
alias |
|
|
This shows the number of nodes in the remote cluster the local cluster is connected to. |
Alternatively, you can manage remote clusters on the Management / Elasticsearch / Remote Clusters page in Kibana:
Creating a leader index
editLeader indices require special index settings to ensure that the operations that need to be replicated are available when the follower requests them from the leader. These settings are used to enable soft deletes on the leader index and to control how many soft deletes are retained. A soft delete occurs whenever a document is deleted or updated. Soft deletes can be enabled only on new indices created on or after Elasticsearch 6.5.0.
In the following example, we will create a leader index in the remote cluster:
PUT /server-metrics
{
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"number_of_shards" : 1,
"number_of_replicas" : 0,
"soft_deletes" : {
"enabled" : true,
"retention" : {
"operations" : 1024
}
}
}
},
"mappings" : {
"metric" : {
"properties" : {
"@timestamp" : {
"type" : "date"
},
"accept" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"deny" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"host" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"response" : {
"type" : "float"
},
"service" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"total" : {
"type" : "long"
}
}
}
}
}
Creating a follower index
editFollower indices are created with the create follower API. When you create a follower index, you must reference the remote cluster and the leader index that you created in the remote cluster.
PUT /server-metrics-copy/_ccr/follow
{
"remote_cluster" : "leader",
"leader_index" : "server-metrics"
}
Now when you index documents into your leader index, you will see these documents replicated in the follower index. You can inspect the status of replication using the get follower stats API.
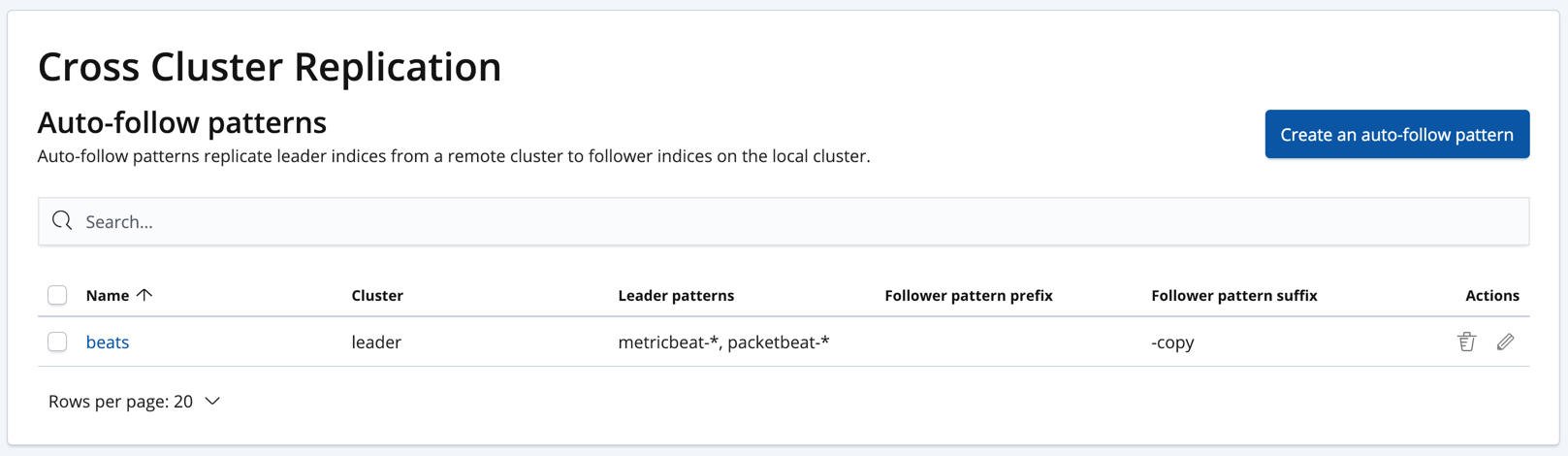
Automatically create follower indices
editThe auto-follow feature in cross-cluster replication helps for time series use cases where you want to follow new indices that are periodically created in the remote cluster (such as daily Beats indices). Auto-following is configured using the create auto-follow pattern API. With an auto-follow pattern, you reference the remote cluster that you connected your local cluster to. You must also specify a collection of patterns that match the indices you want to automatically follow.
For example:
PUT /_ccr/auto_follow/beats
{
"remote_cluster" : "leader",
"leader_index_patterns" :
[
"metricbeat-*",
"packetbeat-*"
],
"follow_index_pattern" : "{{leader_index}}-copy"
}
|
Automatically follow new Metricbeat indices. |
|
|
Automatically follow new Packetbeat indices. |
|
|
The name of the follower index is derived from the name of the leader index
by adding the suffix |
Alternatively, you can manage auto-follow patterns on the Management / Elasticsearch / Cross Cluster Replication page in Kibana: