What is hybrid search?
Two or more retrieval methods. One ranked list.
Hybrid search is an information retrieval technique that blends two or more search methods (e.g., lexical search and semantic search) into a single ranked list to improve relevance and recall. The most common pairing combines full-text lexical search, which is great at matching exact words and phrases, with semantic vector search, which interprets the meaning behind a query. The lexical side adds precision, and the semantic side provides a deep understanding of the user's underlying intent.
These methods run together in a single query, and then their results are merged into one cohesive ranking using specialized fusion strategies. While lexical + semantic is the most popular combination, hybrid search can unite other approaches — like geospatial + semantic search or even text + image search — to fit different needs.
Why hybrid search matters
Hybrid search mitigates the weaknesses of individual retrieval methods while leveraging their strengths in a single pipeline. Modern AI must process diverse modalities, text, images, audio, logs, and more, and bridge intent to data. Relevance is becoming more critical than ever. In ecommerce, for example, a search experience can succeed if it helps users quickly filter and refine results, but an AI agent often requires a single highly relevant answer to respond to a question or take an action. That is why the ability to blend and optimize retrieval techniques matters today, powering not only traditional search results but also conversational agents that deliver precise, data-grounded responses.
Before diving further into hybrid search, let’s quickly look at how lexical and semantic search differ and why they complement each other.
Lexical search explained
Lexical search is ideal when you have well-structured data and users know what they are looking for. It matches exact terms, making it highly precise and explainable, relying on a relevance scoring algorithm (such as BM25F) to rank documents by the frequency and rarity of query terms. This approach offers transparent scoring and supports fine-tuned relevance through field boosts, synonyms, and analyzers. Because it has no model overhead, lexical search is fast and efficient, with filters and facets that perform reliably even at scale without slowdowns or full index scans. It's particularly effective for structured queries, rare terms, and domain-specific language.
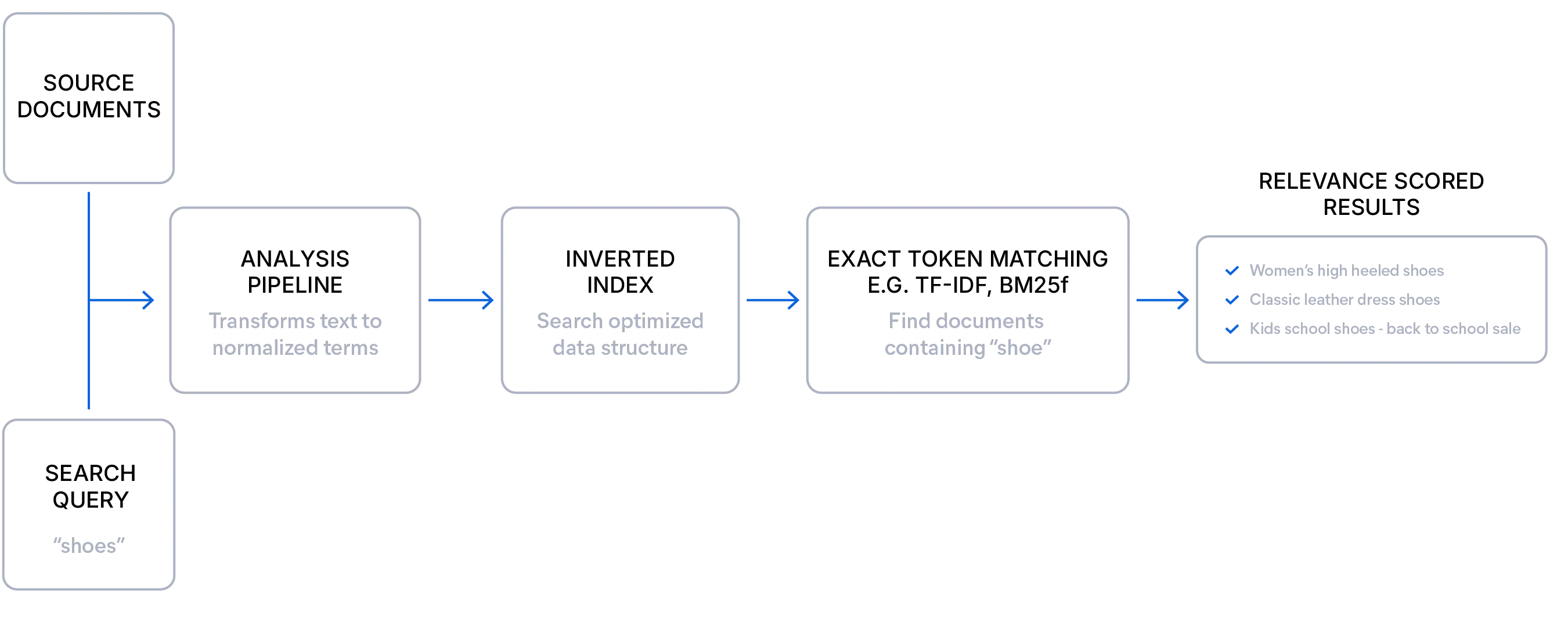
Here's a simple example of a lexical search query:
GET example-index/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"text": "blue shoes"
}
}
}
Let us also look at a similar lexical search example with Elasticsearch Query Language (ES|QL) for a cooking blog. The blog contains recipes with various attributes including textual content, categorical data, and numerical ratings.
FROM cooking_blog METADATA _score | WHERE description:"fluffy pancakes" | KEEP title, description, _score | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 1000
This query searches the description field for documents containing either "fluffy" OR "pancakes" (or both). By default, ES|QL uses OR logic between search terms, so it matches documents that contain any of the specified words. You can specify exactly which fields to include in your results using the KEEP command and request the _score metadata to rank search results by how well they match your query.
Learn more about lexical search with this hands-on tutorial.
Semantic search explained
Semantic search retrieves results based on the similarity of meaning between a query and documents, rather than just matching exact terms as in lexical search.
An embedding model converts the meaning of your text or other media into a numerical representation called a vector. These vectors — a list of numbers — capture the text's underlying context and topic and are stored in a vector database like Elasticsearch.
This allows the search engine to find conceptually similar results even when they share no exact words with the query.
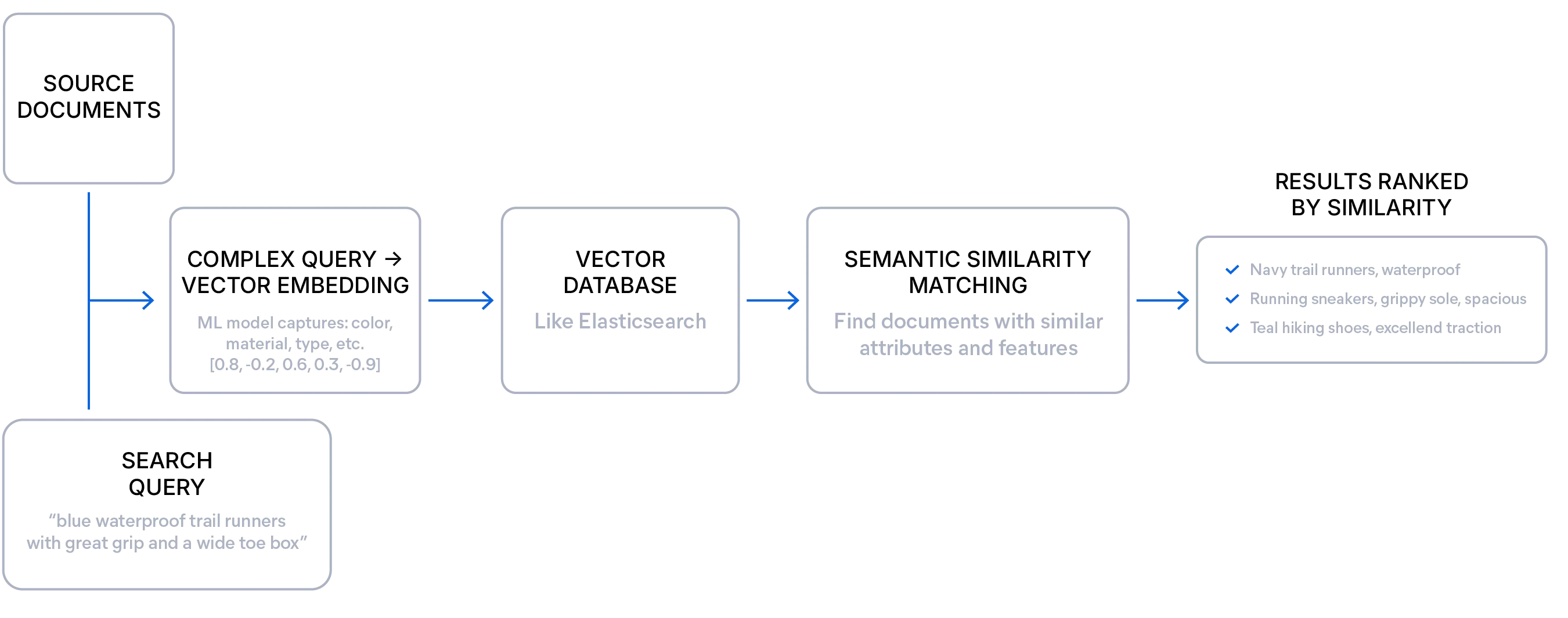
This approach is especially useful for unstructured data, exploratory queries, and cases where users may not know the exact terms to use. Developers can take advantage of semantic search to deliver more relevant results and handle vague, verbose, or ambiguous phrasing while still surfacing the right answers.
Below is an example semantic search query:
GET example-index/_search
{
"query": {
"semantic": {
"field": "inference_field",
"query": "blue waterproof trail runners with great grip and a wide toe box"
}
}
}
ES|QL supports semantic search when your mappings include fields of the semantic_text type. Once the document has been processed by the underlying model running on the inference endpoint, you can perform semantic search. Here’s an example natural language query against the semantic_description field:
FROM cooking_blog METADATA _score | WHERE semantic_description:"What are some easy to prepare but nutritious plant-based meals?" | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 5
Learn more about semantic search or try this hands-on tutorial to dive deeper.
Lexical algorithms like BM25F excel at precision when query terms match document terms but fail when relevant content is expressed differently. (For example, a query for "athletic footwear" might miss documents that only say "shoes" or "trail runner.") Semantic vector search, using high-dimensional embeddings and approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) algorithms (e.g., HNSW), retrieves conceptually similar documents regardless of exact term overlap — but it can introduce noise if context is ambiguous.
How hybrid search works
What if you could get the best of both worlds? Enter hybrid search. When done right, hybrid search is more than the sum of its parts; it can produce far better results than lexical or semantic search alone. Hybrid gives you both, with balanced relevance, better normalized discounted cumulative gain (NDCG), and higher recall without bolting on a second search system.
Below is an example hybrid search query:
GET example-index/_search
{
"retriever": {
"rrf": {
"retrievers": [
{
"standard": {
"query": {
"term": {
"description": "shoes"
}
}
}
},
{
"knn": {
"field": "vector",
"query_vector": [1.25, 2, 3.5],
"k": 50,
"num_candidates": 100
}
}
],
"rank_constant": 20,
"rank_window_size": 50
}
}
}
You can also combine full-text and semantic queries in ES|QL. In this example, we combine full-text and semantic search with custom weights:
FROM my-index METADATA _score
| FORK ( WHERE match(text_field:"shoes") | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 50)
( WHERE knn(vector, [1.25, 2, 3.5], { "min_candidates" : 100 }) | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 50 ) // k for knn is derived from LIMIT
| FUSE RRF WITH { "rank_constant": 20 }
| SORT _score DESC
| LIMIT 50
Running a hybrid search query typically involves executing at least one lexical search and one semantic search and then combining their results. The main challenge lies in merging multiple ranked lists into a single, coherent ranking.
Lexical search scores, generated by algorithms like BM25F or TF-IDF, can be unbounded, with maximum values influenced by term frequency and document distribution. In contrast, semantic search scores usually fall within a fixed range, determined by the similarity function (e.g., [0, 2] for cosine similarity).
To merge them, you need a fusion method that maintains the relative relevance of retrieved documents.
Hybrid search with Elasticsearch
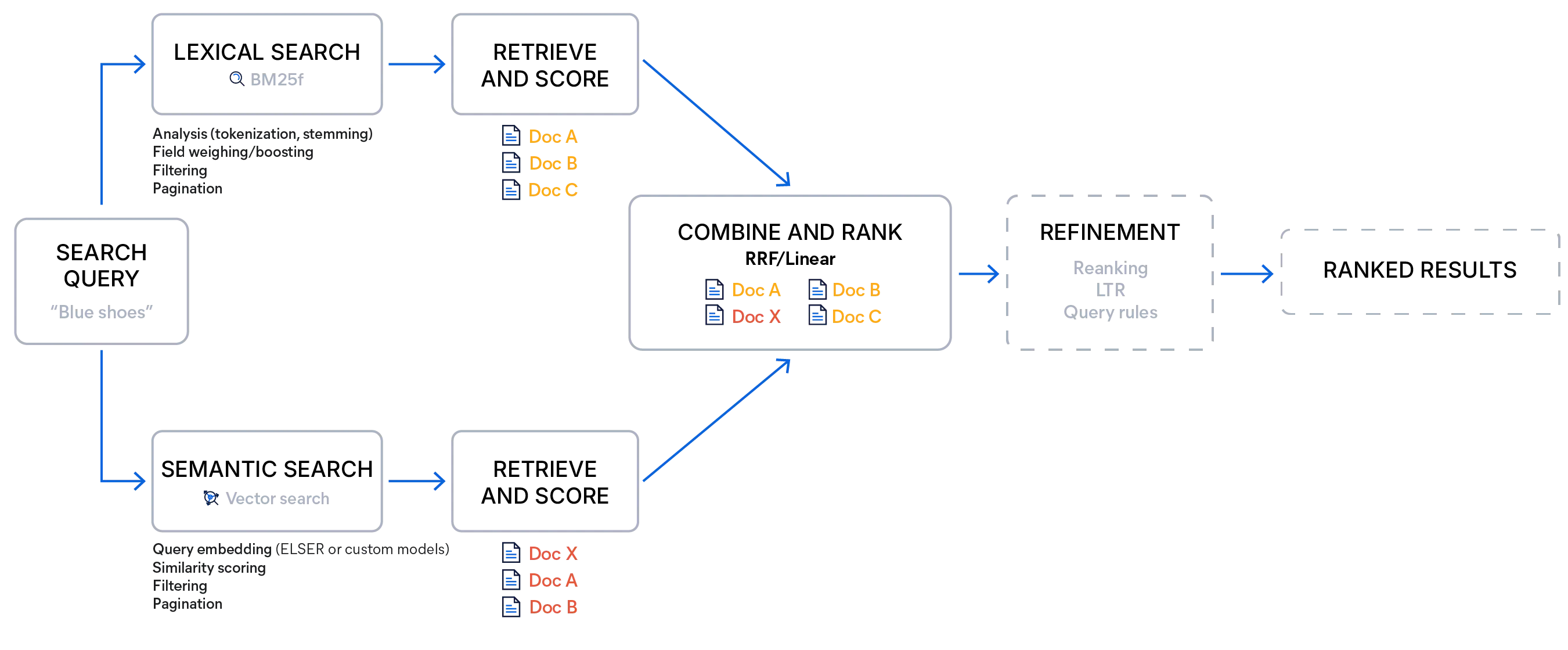
Hybrid search with Elasticsearch can be implemented by pairing a standard keyword query with a vector query or by using a retriever — a search option that runs multiple queries of different types and merges their results into a single ranked list using a chosen scoring method. This enables multistage retrieval pipelines within a single search call, removing the need for multiple requests or extra client-side logic to combine results.
Elasticsearch provides two built-in fusion methods: reciprocal rank fusion (RRF) and linear combination (often called linear retriever in the APIs). Both aim to produce a unified ranking that preserves the strengths of each retriever, but they differ in how they treat scores and when they are most effective.
Reciprocal rank fusion ignores raw scores entirely and focuses on how high a document appears in each list. Documents ranked near the top of any list are rewarded strongly, and documents appearing in multiple lists receive additive boosts. The method is robust because it sidesteps issues with incompatible score ranges, requires almost no tuning beyond the rank constant, and naturally promotes diversity in the top results.
RRF scores the documents according to their rank in the result set using the following formula, where k is an arbitrary constant meant to adjust the importance of lowly ranked documents:
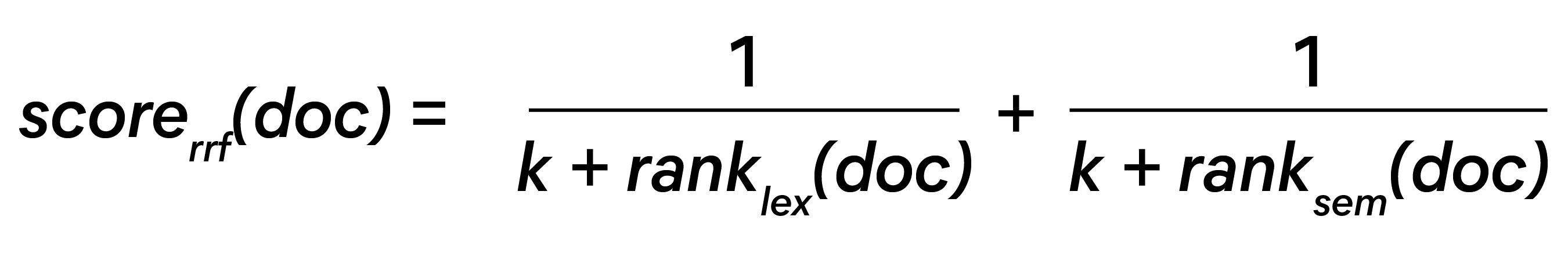
RRF is especially useful when retrievers share some overlap in their top results and when developers need a plug-and-play solution without labeled training data or complex calibration.
Linear combination, by contrast, directly merges the actual scores from each retriever. Because lexical and semantic scores operate on very different scales, linear requires normalization, such as min-max scaling, to bring the scores into a comparable range.
Once normalized, scores are blended using weights that represent the relative importance of each retriever. A weight greater than 1 boosts a retriever’s influence, while a weight less than 1 reduces it.
This approach allows for fine-grained control: Developers can emphasize BM25F when keyword precision matters, tilt toward semantic similarity when intent and context are critical, or integrate additional business or personalization signals alongside retrieval scores. When weights are carefully calibrated, linear combination can outperform RRF by producing more accurate and predictable rankings, but it does require experimentation and is sensitive to dataset-specific tuning.
Linear combination combines lexical search results and semantic search results with respective weights and β (where 0 ≤α, β), such that:
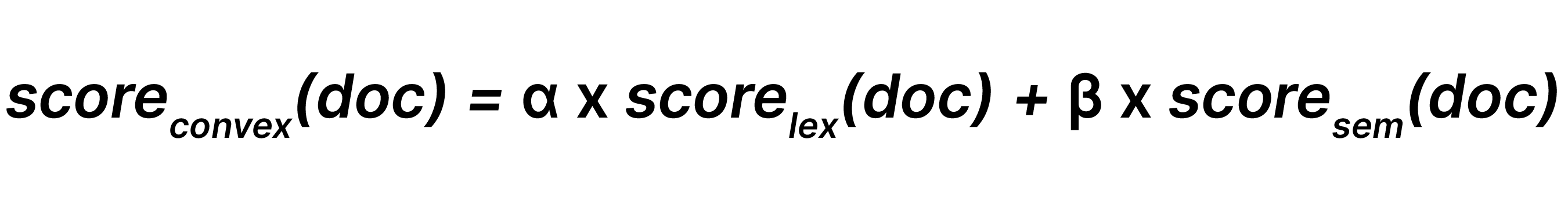
In practice, RRF is the best starting point for hybrid search because of its simplicity and resilience to mismatched score scales. It produces strong results without extensive tuning, making it ideal for prototyping or when retrievers overlap. Linear combination is better suited when different retrieval methods return disjoint results or when there is a need to carefully balance lexical, semantic, and external signals. In short, RRF provides fast, reliable hybridization out of the box, while linear offers higher potential accuracy once weights and normalizers are tuned to the application and data.
To summarize:
| Reciprocal rank fusion | Linear combination |
|---|---|
Start with RRF to get robust hybrid results quickly. |
Graduate to linear when you are ready to fine tune relevance. |
In short, linear combination offers higher potential accuracy when tuned, while RRF is easier to implement and works well without labeled training data.
Try this tutorial to learn more about hybrid search.
How hybrid search retrieval works
- Lexical retrieval: BM25F matches query terms against indexed tokens — great for precision, structured filters, and explainable scoring.
- Semantic retrieval: Vectors (dense or sparse) represent text meaning; similarity search finds related content even without shared words.
- Fusion: Combine scores with RRF, weighted blending, or a linear retriever. Filters and boosts apply consistently across both retrievals.
| Search type | How it works | What happens | Ideal for when |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lexical search Query: "red running shoes size 10" | Matches exact words in the query with words in documents (BM25F, TF-IDF, analyzers, synonyms). | Finds products with those exact tokens in the title/description (e.g., "Nike Men's Red Running Shoes, Size 10"). | The shopper knows exactly what they want. Precise, explainable, and efficient. |
| Semantic search Query : "lightweight shoes for jogging" | Uses embeddings to capture meaning and context, not just keywords. Finds results conceptually related even if terms don't match. | Returns "Adidas Cloudfoam Running Sneakers, Size 10" even if "lightweight" and "jogging" don't appear verbatim. | Shoppers describe intent or use natural language. Handles vague or descriptive queries. |
| Hybrid search Query: "comfortable dress shoes for office" | Combines lexical and semantic results and then fuses rankings (e.g., via RRF). | Retrieves exact matches like "Black Leather Dress Shoes, Comfort Fit" and semantically related items like "Loafers with cushioned insoles." Both appear together, ranked by relevance. | Queries mix precise terms and intent. Balances accuracy with discovery. |
Inside hybrid search: Dense and sparse vectors explained
Semantic search with Elasticsearch works by transforming queries and documents into vector representations that capture meaning. Hybrid search combines lexical and semantic retrieval, whether using dense or sparse models.
Dense vectors
Dense vectors are fixed-length arrays of numbers produced by models like BERT, where similar inputs (such as cat and kitten) appear close in vector space, making them powerful for semantic matching, recommendations, and similarity search.
When text is embedded as a dense vector, it looks like this:
[ 0.13586345314979553, -0.6291824579238892, 0.32779985666275024, 0.36690405011177063, ... ]
Every dimension contains meaningful information, making the vectors dense with data. Similar content produces embeddings that are close together in vector space.
In Elasticsearch, dense vectors are stored in a dense_vector field and queried with approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) algorithms like HNSW. This is ideal for capturing the overall semantic meaning of text, images, or other content.
POST my-index/_search
{
"retriever": {
"rrf": {
"retrievers": [
{
"standard": {
"query": {
"match": {
"text_field": "fox"
}
}
}
},
{
"knn": {
"field": "title_vector",
"query_vector": [0.1, 3.2, 2.1],
"k": 5,
"num_candidates": 100
}
}
]
}
}
}
Here is an ES|QL example:
FROM my-index METADATA _score
| FORK ( WHERE match(text_field:"fox") | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 5)
( WHERE knn(image_vector, [0.1, 3.2, 2.1], { "min_candidates" : 100 }) | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 5 )
| FUSE
| SORT _score DESCAs we can see above, a hybrid search query simply leverages the rrf retriever that combines a lexical search query (e.g., a match query) made with a standard retriever and a vector search query specified in the knn retriever. What this query does is first retrieve the top five vector matches at the global level, then combine them with the lexical matches, and finally return the 10 best matching hits. The rrf retriever uses RRF ranking in order to combine vector and lexical matches.
Understanding sparse vectors and ELSER
Dense embeddings aren't the only way to do semantic search.
Sparse vectors contain mostly zeros with a few weighted values tied to interpretable terms, making them resource-efficient, explainable, and effective in zero-shot scenarios.
A sparse vector representation looks like this:
{"f1":1.2,"f2":0.3,… }
In Elasticsearch, Elastic Learned Sparse EncodeR (ELSER) is an out-of-domain sparse natural language processing (NLP) model that expands text into semantically related terms and assigns weights, enabling matches beyond exact keywords while preserving interpretability.
Additionally, the semantic_text field makes semantic search as easy as traditional text search by handling embedding generation and inference automatically at ingest. You can index documents like a text field and run a simple match query — even across indices where the field type differs — to get both lexical and semantic matches without extra query logic. For advanced control, use knn or sparse_vector queries on the same field.
Example with ELSER:
- Pretrained on ~30,000 term vocabulary
- Stored as sparse_vector (term/weight pairs)
- Generated automatically at ingest with semantic_text or at index time with the inference ingest processor
- Queried via an inverted index (like lexical search), making them efficient, filter-friendly, and explainable
POST my-index/_search
{
"retriever": {
"rrf": {
"retrievers": [
{
"standard": {
"query": {
"match": {
"text_field": "fox"
}
}
}
},
{
"standard": {
"query": {
"sparse_vector": {
"field": "ml.tokens",
"inference_id": ".elser_model_1",
"query": "a quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog"
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
Together, dense and sparse vectors provide flexibility: Dense vectors excel at capturing nuanced meaning, while sparse vectors offer transparency and scalability for real-world search.
Sparse vs. dense vectors in practice
| Sparse vectors (ELSER) | Dense vectors | |
|---|---|---|
| How it works | Expands text into semantically related, weighted terms. Each dimension corresponds to a token with an associated weight. | Encodes content (text, images, etc.) into fixed-length floating-point vectors. Similar meaning = nearby positions in vector space. |
| Strengths |
|
|
| Example use cases |
|
|
| Ideal for | When you need semantic improvement and transparency, or when domain-specific terms matter most | When you want discovery and similarity based on meaning, not exact words, across varied data types |
Hybrid search with dense and sparse models
So far, we have seen two different ways of running a hybrid search, depending on whether a dense or sparse vector space was being searched. We can mix both dense and sparse data inside the same index.
POST my-index/_search
{
"_source": false,
"fields": [ "text_field" ],
"retriever": {
"rrf": {
"retrievers": [
{
"knn": {
"field": "image_vector",
"query_vector": [0.1, 3.2, ..., 2.1],
"k": 5,
"num_candidates": 100
}
},
{
"standard": {
"query": {
"sparse_vector": {
"field": "ml.tokens",
"inference_id": ".elser_model_1",
"query": "a quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog"
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
Going further: Hybrid search with dense, sparse, and BM25F
This example combines three retrievers and fuses their ranked lists with RRF:
- BM25F (match on text): Precise keyword/phrase matches ("snowy mountain")
- kNN (image_vector): Visual similarity using the provided image embedding (k results from num_candidates)
- Semantic (semantic_text): Concept matches via semantic expansion of the query
rank_window_size controls how many results are fused; rank_constant balances contributions from each list.
GET my-index/_search
{
"retriever": {
"rrf": {
"retrievers": [
{
"standard": {
"query": {
"match": {
"text": {
"query": "snowy mountain"
}
}
}
}
},
{
"knn": {
"field": "image_vector",
"query_vector": [
0.01,
0.3,
-0.4
],
"k": 10,
"num_candidates": 100
}
},
{
"standard": {
"query": {
"semantic": {
"field": "semantic_text",
"query": "snowy mountain"
}
}
}
}
],
"rank_window_size": 50,
"rank_constant": 60
}
}
}
Let us also look at a similar example with ES|QL:
FROM my-index METADATA _score
| FORK (WHERE match(text, "snowy mountain") | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 50)
(WHERE knn(image_vector, [0.01, 0.3, -0.4], {"min_candidates": 100 }) | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 50)
(WHERE match(semantic_text, "snowy mountain") | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 50)
| FUSE RRF WITH {"rank_constant": 60 } // 60 is the default anyway?
| SORT _score DESC
| LIMIT 50Conclusion
Hybrid search brings together the precision of full-text search and the contextual reach of semantic search, delivering more accurate and relevant results across diverse content. By supporting both dense and sparse models and offering flexible fusion methods like linear combination and reciprocal rank fusion, you can tailor retrieval to your use case — whether pairing queries and vectors directly or streamlining multistage retrieval with a retriever. This flexibility makes hybrid search a powerful approach for complex queries, varied data, and demanding relevance requirements.
Explore this blog to learn what hybrid search is, the query types Elasticsearch supports, and how to build them.
Want to go beyond vectors? Check out intelligent hybrid search with LLM agents in Elasticsearch.
Ready to get hands-on? Follow our hybrid search tutorial to combine full-text and kNN results, or try the ES|QL tutorial to search and filter using ES|QL.