API Authentication Reference
editAPI Authentication Reference
editWorkplace Search APIs support multiple authentication methods:
Workplace Search admin user access tokens
editEach admin user has an access token that acts like a private API key. Access tokens are unique to every admin user. Access tokens must be used as bearer in the authorization header for every API call.
curl -X POST http://localhost:3002/api/ws/v1/sources/[ID]/documents/bulk_create \ -H "Authorization: Bearer [ACCESS_TOKEN]" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d ' ... '
To locate the access token for the logged-in admin user, navigate to the Details area of an existing Content Source that uses document-level permissions, such as Custom API Sources:
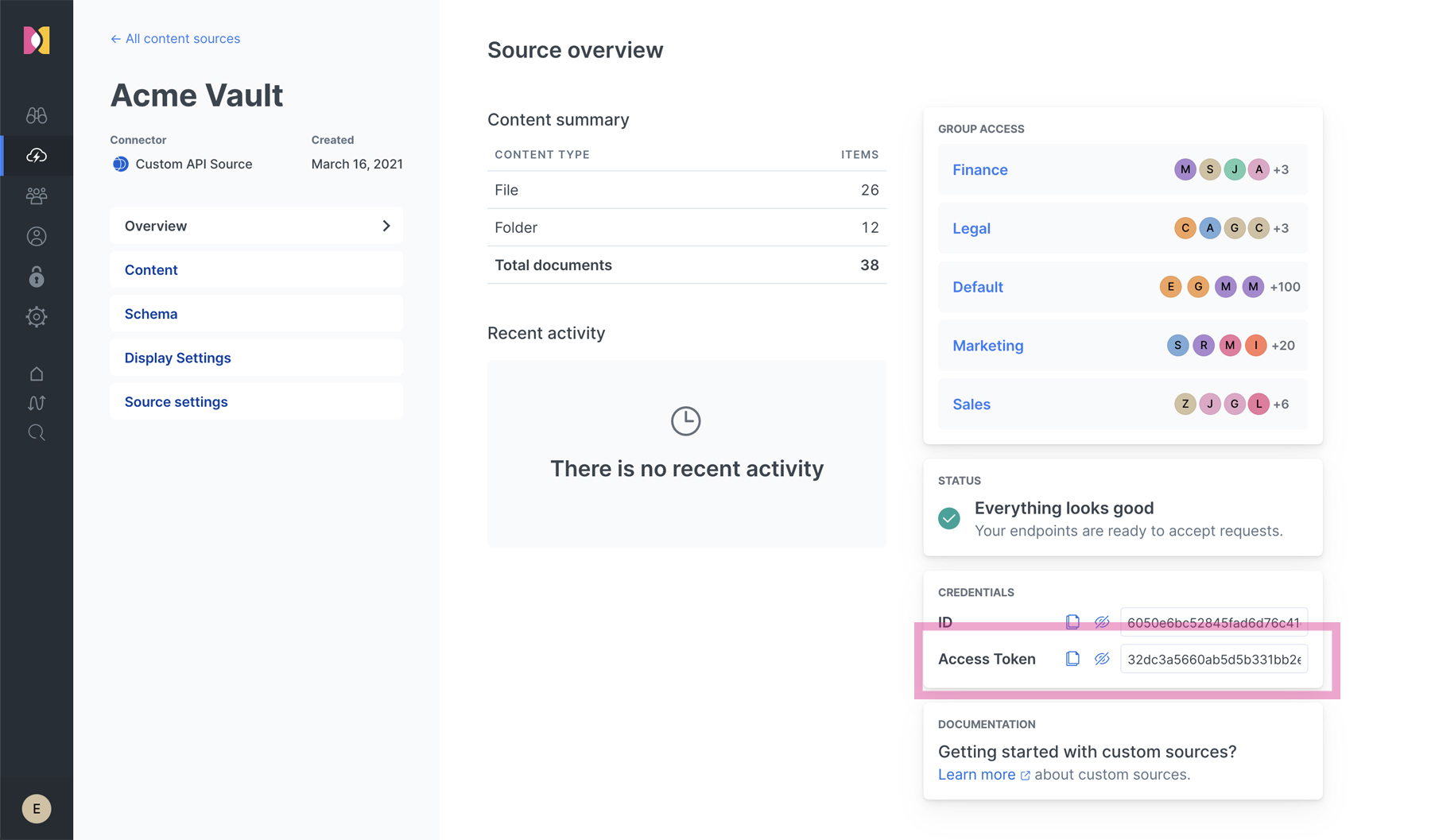
The admin access token cannot be used with the Search API and the Analytics Events API. For these endpoints, the authentication mechanisms follow the Search API OAuth flow, basic authentication or Elasticsearch bearer token strategies.
Basic authentication
editWorkplace Search APIs support basic authentication headers to authenticate users.
Consult your HTTP client’s documentation for its support of the basic authentication scheme. For example, cURL provides the -u and --user arguments to provide a username and password for each request.
curl -X POST http://localhost:3002/api/ws/v1/search \
-u "[USERNAME]:[PASSWORD]" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"query": "denali"
}'
All Workplace Search APIs support basic authentication.
Basic authentication cannot be used with Elasticsearch SAML user management mode.
Elasticsearch tokens
editWorkplace Search APIs support Elasticsearch tokens generated by the Elasticsearch Token Service.
curl -X POST http://localhost:3002/api/ws/v1/search \
-H "Authorization: Bearer [TOKEN]" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"query": "denali"
}'
All Workplace Search APIs support Elasticsearch tokens as an authentication method.
Workplace Search OAuth access tokens
editThe Search API and the Analytics Events API support user access tokens generated by the Workplace Search OAuth Service.
The token is acquired via an OAuth authorization flow.
User access tokens are meant to be used for Custom Search Experiences.
curl -X POST http://localhost:3002/api/ws/v1/search \
-H "Authorization: Bearer [TOKEN]" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"query": "denali"
}'
Only the Search API and the Analytics Events API support user access tokens.
Who Am I? Current User API
editWith token authentication mechanisms, it is easy to get confused about exactly who is authenticated. To remove all doubt, you can check who the authenticated user is with the below API.
GET /api/ws/v1/whoami
Request headers
edit-
Authorization -
Bearer token permitting API access, or basic auth.
Query parameters
edit-
get_token(optional) -
The boolean for whether or not the response should include an admin user access token. This can be particularly useful for programmatically exchanging Basic authentication or Elasticsearch tokens credentials for an admin user access token.
Request examples
editcurl \ --request 'GET' \ --url "https://f3fae9ab3e4f423d9d345979331ef3a1.ent-search.us-east-1.aws.cloud.es.io/api/ws/v1/whoami?get_token=true" \ --header "Authorization: Bearer $ACCESS_TOKEN"
curl \ --request 'GET' \ --url "http://localhost:3002/api/ws/v1/whoami?get_token=true" \ --header "Authorization: Bearer $ACCESS_TOKEN"
Responses
edit-
200 OK -
The current user is returned, optionally including an access token.
{ "email": "[email protected]", "username": "enterprise_search", "access_token": "3adbcba70c69402d9c7706648d88e595f533ce77e7df4399142f23085986ed4c" } -
401 Unauthorized -
The authorization header was missing from the request or authentication failed.
-
404 Not Found -
The authenticated user is not an Admin user, and therefore does not have permission.