Connect to Elastic Maps Service
editConnect to Elastic Maps Service
editElastic Maps Service (EMS) is a service that hosts tile layers and vector shapes of administrative boundaries. If you are using Kibana’s out-of-the-box settings, Maps is already configured to use EMS.
EMS requests are made to the following domains:
- tiles.maps.elastic.co
- vector.maps.elastic.co
Maps makes requests directly from the browser to EMS.
Disable Elastic Maps Service
editYou might experience EMS connection issues if your Kibana server or browser are on a private network or behind a firewall. If this happens, you can disable the EMS connection to avoid unnecessary EMS requests.
To disable EMS, change your kibana.yml file.
-
Set
map.includeElasticMapsServicetofalseto turn off the EMS connection. -
Set
map.tilemap.urlto the URL of your tile server. This configures the default tile layer of Maps.
Host Elastic Maps Service locally
editIf you cannot connect to Elastic Maps Service from the Kibana server or browser clients, and your cluster has the appropriate license level, you can opt to host the service on your own infrastructure.
Elastic Maps Server is a self-managed version of Elastic Maps Service offered as a Docker image that provides both the EMS basemaps and EMS boundaries. The image is bundled with basemaps up to zoom level 8. After connecting it to your Elasticsearch cluster for license validation, you have the option to download and configure a more detailed basemaps database.
Elastic Maps Server does not serve raster tiles, needed by Vega, coordinate, and region map visualizations.
You can use docker pull to download the Elastic Maps Server image from the Elastic Docker registry.
docker pull docker.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service/elastic-maps-server-ubi8:8.7.1
Start Elastic Maps Server and expose the default port 8080:
docker run --rm --init --publish 8080:8080 \ docker.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service/elastic-maps-server-ubi8:8.7.1
Once Elastic Maps Server is running, follow instructions from the webpage at localhost:8080 to define a configuration file and optionally download a more detailed basemaps database.
Configuration
editElastic Maps Server reads properties from a configuration file in YAML format that is validated on startup. The location of this file is provided by the EMS_PATH_CONF container environment variable and defaults to /usr/src/app/server/config/elastic-maps-server.yml. This environment variable can be changed by making use of the -e docker flag of the start command.
General settings
Specifies the host of the backend server. To allow remote users to connect, set the value to the IP address or DNS name of the Elastic Maps Server container. Default: your-hostname. Equivalent Kibana setting. |
|
|
Specifies the port used by the backend server. Default: |
|
Specify a path at which to mount the server if you are running behind a proxy. This setting cannot end in a slash ( |
|
Controls the display of the status page and the layer preview. Default: |
|
Verbosity of Elastic Maps Server logs. Valid values are |
|
Path of the basemaps database. Default: |
Elasticsearch connection and security settings
|
URL of the Elasticsearch instance to use for license validation. |
|
Credentials of a user with at least the |
|
Paths to one or more PEM-encoded X.509 certificate authority (CA) certificates that make up a trusted certificate chain for Elastic Maps Server. This chain is used by Elastic Maps Server to establish trust when connecting to your Elasticsearch cluster. Equivalent Kibana setting. |
|
Optional settings that provide the paths to the PEM-format SSL certificate and key files and the key password. These files are used to verify the identity of Elastic Maps Server to Elasticsearch and are required when |
|
Controls the verification of the server certificate that Elastic Maps Server receives when making an outbound SSL/TLS connection to Elasticsearch. Valid values are " |
Server security settings
|
Enables SSL/TLS for inbound connections to Elastic Maps Server. When set to |
|
Paths to one or more PEM-encoded X.509 certificate authority (CA) certificates that make up a trusted certificate chain for Elastic Maps Server. This chain is used by the Elastic Maps Server to establish trust when receiving inbound SSL/TLS connections from end users. Equivalent Kibana setting. |
|
Location of yor SSL key and certificate files and the password that decrypts the private key that is specified via |
|
An array of supported protocols with versions.
Valid protocols: |
|
Details on the format, and the valid options, are available via the
OpenSSL cipher list format documentation.
Default: |
Bind-mounted configuration
editOne way to configure Elastic Maps Server is to provide elastic-maps-server.yml via bind-mounting. With docker-compose, the bind-mount can be specified like this:
version: '2'
services:
Elastic Maps Server:
image: docker.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service/elastic-maps-server-ubi8:8.7.1
volumes:
- ./elastic-maps-server.yml:/usr/src/app/server/config/elastic-maps-server.yml
Environment variable configuration
editAll configuration settings can be overridden by environment variables that are named with all uppercase letters and by replacing YAML periods with underscores. For example elasticsearch.ssl.certificate could be overridden by the environment variable ELASTICSEARCH_SSL_CERTIFICATE. Boolean variables must use the true or false strings.
All information that you include in environment variables is visible through the ps command, including sensitive information.
These variables can be set with docker-compose like this:
version: '2'
services:
Elastic Maps Server:
image: docker.elastic.co/elastic-maps-service/elastic-maps-server-ubi8:8.7.1
environment:
ELASTICSEARCH_HOST: <ELASTICSEARCH_HOST_URL>
ELASTICSEARCH_USERNAME: 'ems'
ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD: 'changeme'
Data
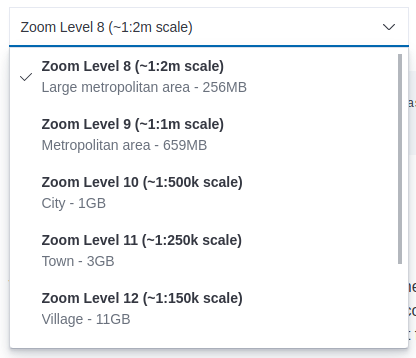
editElastic Maps Server hosts vector layer boundaries and vector tile basemaps for the entire planet. Boundaries include world countries, global administrative regions, and specific country regions. Basemaps up to zoom level 8 are bundled in the Docker image. These basemaps are sufficient for maps and dashboards at the country level. To present maps with higher detail, follow the instructions of the front page to download and configure the appropriate basemaps database. The most detailed basemaps at zoom level 14 are good for street level maps, but require ~90GB of disk space.
The available basemaps and boundaries can be explored from the /maps endpoint in a web page that is your self-managed equivalent to https://maps.elastic.co.
Kibana configuration
editWith Elastic Maps Server running, add the map.emsUrl configuration key in your kibana.yml file pointing to the root of the service. This setting will point Kibana to request EMS basemaps and boundaries from Elastic Maps Server. Typically this will be the URL to the host and port of Elastic Maps Server. For example, map.emsUrl: <BASE_URL>:8080.
Status check
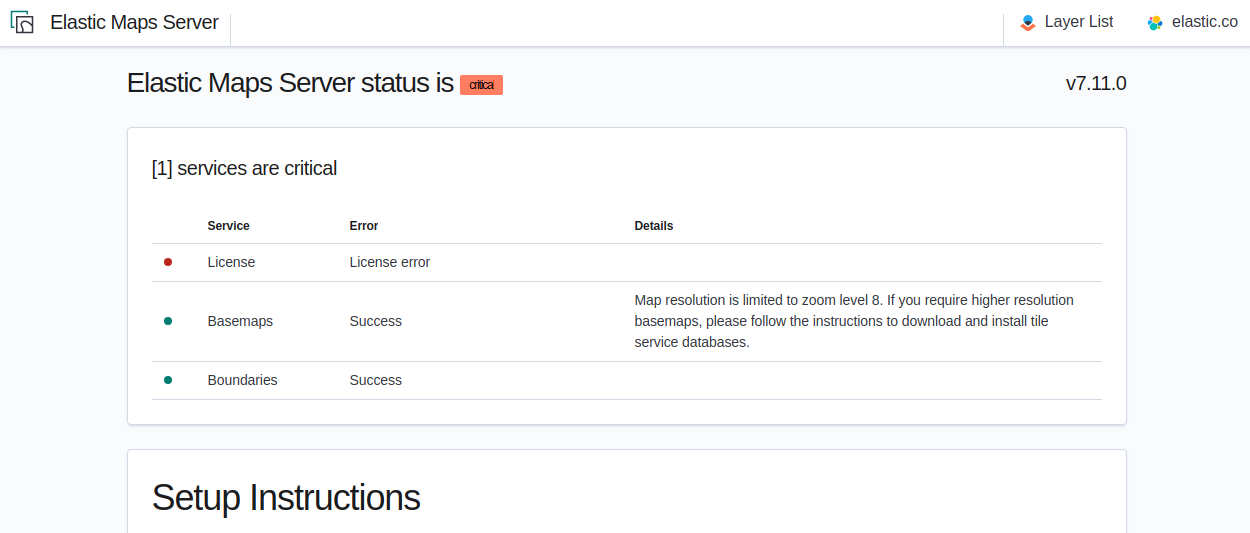
editElastic Maps Server periodically runs a status check that is exposed in three different forms:
- At the root of Elastic Maps Server, a web page will render the status of the different services.
-
A JSON representation of Elastic Maps Server status is available at the
/statusendpoint. -
The Docker
HEALTHCHECKinstruction is run by default and will inform about the health of the service, running a process equivalent to the/statusendpoint.
Elastic Maps Server won’t respond to any data request if the license validation is not fulfilled.
Logging
editLogs are generated in ECS JSON format and emitted to the standard output and to /var/log/elastic-maps-server/elastic-maps-server.log. The server won’t rotate the logs automatically but the logrotate tool is installed in the image. Mount /dev/null to the default log path if you want to disable the output to that file.