What’s new in 8.7
editWhat’s new in 8.7
editHere are the highlights of what’s new and improved in Elasticsearch 8.7!
Other versions:
8.6 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 8.3 | 8.2 | 8.1 | 8.0
Time series (TSDS) GA
editTime Series Data Stream (TSDS) is a feature for optimizing Elasticsearch indices for time series data. This involves sorting the indices to achieve better compression and using synthetic _source to reduce index size. As a result, TSDS indices are significantly smaller than non-time_series indices that contain the same data. TSDS is particularly useful for managing time series data with high volume.
Downsampling GA
editDownsampling is a feature that reduces the number of stored documents in Elasticsearch time series indices, resulting in smaller indices and improved query latency. This optimization is achieved by pre-aggregating time series indices, using the time_series index schema to identify the time series. Downsampling is configured as an action in ILM, making it a useful tool for managing large volumes of time series data in Elasticsearch.
Geohex aggregations on both geo_point and geo_shape fields
editPreviously Elasticsearch 8.1.0 expanded geo_grid aggregation support from rectangular tiles (geotile and geohash)
to include hexagonal tiles, but for geo_point only. Now Elasticsearch 8.7.0 will support
Geohex aggregations over geo_shape as well,
which completes the long desired need to perform hexagonal aggregations on spatial data.
In 2018 Uber announced they had open sourced their H3 library, enabling hexagonal tiling of the planet for much better analytics of their traffic and regional pricing models. The use of hexagonal tiles for analytics has become increasingly popular, due to the fact that each tile represents a very similar geographic area on the planet, as well as the fact that the distance between tile centers is very similar in all directions, and consistent across the map. These benefits are now available to all Elasticsearch users.
Allow more than one KNN search clause
editSome vector search scenarios require relevance ranking using a few kNN clauses, e.g. when ranking based on several fields, each with its own vector, or when a document includes a vector for the image and another vector for the text. The user may want to obtain relevance ranking based on a combination of all of these kNN clauses.
Make natural language processing GA
editFrom 8.7, NLP model management, model allocation, and support for inference against third party models are generally available. (The new text_embedding extension to knn search is still in technical preview.)
Speed up ingest geoip processors
editThe geoip ingest processor is significantly faster.
Previous versions of the geoip library needed special permission to execute
databinding code, requiring an expensive permissions check and
AccessController.doPrivileged call. The current version of the geoip
library no longer requires that, however, so the expensive code has been
removed, resulting in better performance for the ingest geoip processor.
Speed up ingest set and append processors
editThe set and append ingest processors that use mustache templates are
significantly faster.
Improved downsampling performance
editSeveral improvements were made to the performance of downsampling. All hashmap lookups were removed. Also metrics/label producers were modified so that they extract the doc_values directly from the leaves. This allows for extra optimizations for cases such as labels/counters that do not extract doc_values unless they are consumed. Those changes yielded a 3x-4x performance improvement of the downsampling operation, as measured by our benchmarks.
The Health API is now generally available
editElasticsearch introduces a new Health API designed to report the health of the cluster. The new API provides both a high level overview of the cluster health, and a very detailed report that can include a precise diagnosis and a resolution.
Improved performance for get, mget and indexing with explicit `_id`s
editThe false positive rate for the bloom filter on the _id field was reduced from ~10% to ~1%,
reducing the I/O load if a term is not present in a segment.
This improves performance when retrieving documents by _id, which happens when performing
get or mget requests, or when issuing _bulk requests that provide explicit `_id`s.
Speed up ingest processing with multiple pipelines
editProcessing documents with both a request/default and a final pipeline is significantly faster.
Rather than marshalling a document from and to json once per pipeline, a document is now marshalled from json before any pipelines execute and then back to json after all pipelines have executed.
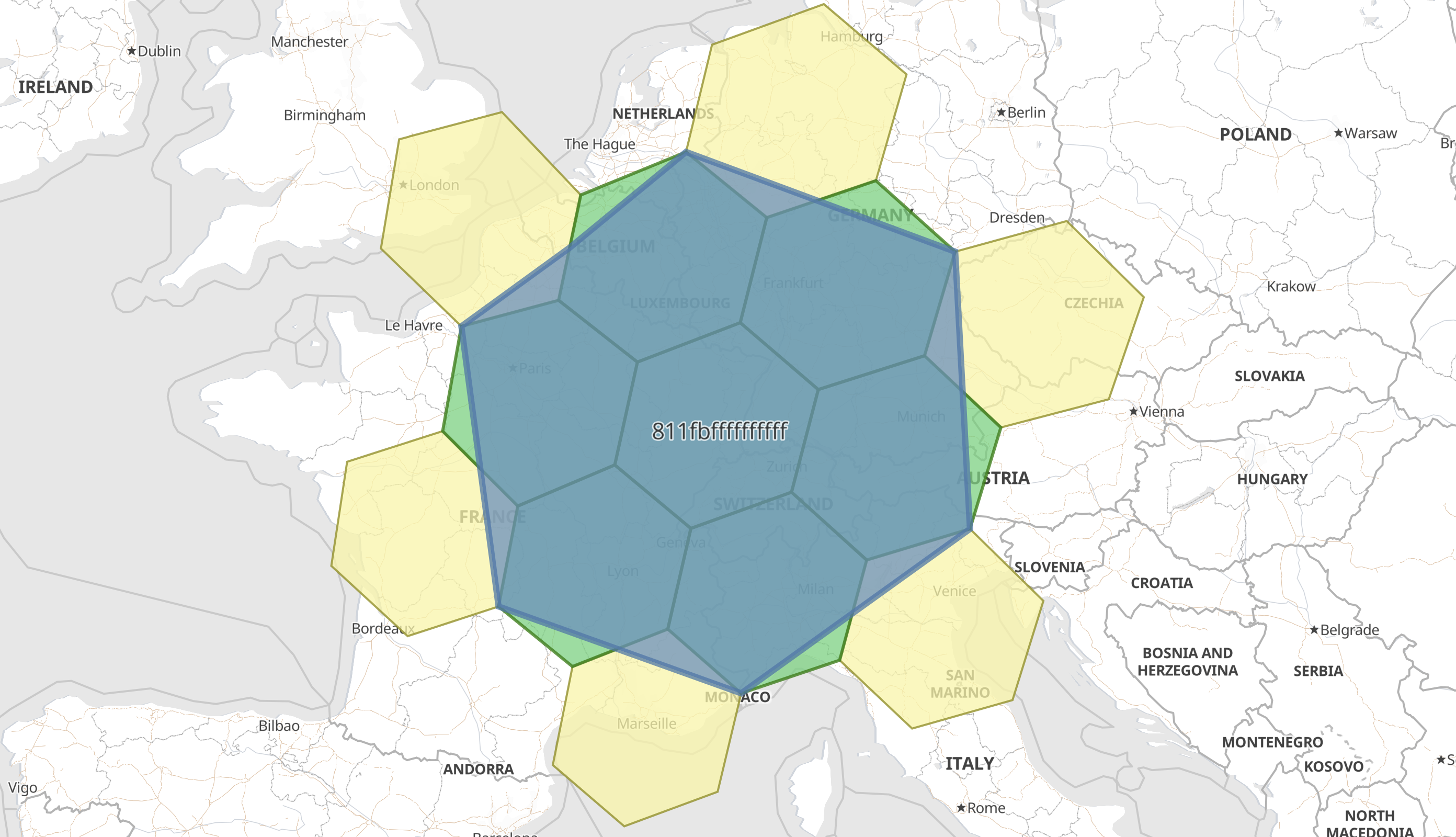
Support geo_grid ingest processor
editThe geo_grid ingest processor supports creating indexable geometries
from geohash, geotile and H3 cells.
There already exists a circle ingest processor that creates a polygon from a point and radius definition.
This concept is useful when there is need to use spatial operations that work with indexable geometries on
geometric objects that are not defined spatially (or at least not indexable by lucene).
In this case, the string 4/8/5 does not have spatial meaning, until we interpret it as the address
of a rectangular geotile, and save the bounding box defining its border for further use.
Likewise we can interpret geohash strings like u0 as a tile, and H3 strings like 811fbffffffffff
as an hexagonal cell, saving the cell border as a polygon.
Make frequent_item_sets aggregation GA
editThe frequent_item_sets aggregation has been moved from technical preview to general availability.
Release time_series and rate (on counter fields) aggegations as tech preview
editMake time_series aggregation and rate aggregation (on counter
fields) available without using the time series feature flag. This
change makes these aggregations available as tech preview.
Currently there is no documentation about the time_series aggregation.
This will be added in a followup change.