WARNING: Version 2.1 of Elasticsearch has passed its EOL date.
This documentation is no longer being maintained and may be removed. If you are running this version, we strongly advise you to upgrade. For the latest information, see the current release documentation.
Running as a Service on Windows
editRunning as a Service on Windows
editWindows users can configure Elasticsearch to run as a service to run in the background or start automatically
at startup without any user interaction.
This can be achieved through service.bat script under bin/ folder which allows one to install,
remove, manage or configure the service and potentially start and stop the service, all from the command-line.
c:\elasticsearch-2.1.1\bin>service Usage: service.bat install|remove|start|stop|manager [SERVICE_ID]
The script requires one parameter (the command to execute) followed by an optional one indicating the service id (useful when installing multiple Elasticsearch services).
The commands available are:
|
|
Install Elasticsearch as a service |
|
|
Remove the installed Elasticsearch service (and stop the service if started) |
|
|
Start the Elasticsearch service (if installed) |
|
|
Stop the Elasticsearch service (if started) |
|
|
Start a GUI for managing the installed service |
Note that the environment configuration options available during the installation are copied and will be used during the service lifecycle. This means any changes made to them after the installation will not be picked up unless the service is reinstalled.
Based on the architecture of the available JDK/JRE (set through JAVA_HOME), the appropriate 64-bit(x64) or 32-bit(x86)
service will be installed. This information is made available during install:
c:\elasticsearch-2.1.1\bin>service install Installing service : "elasticsearch-service-x64" Using JAVA_HOME (64-bit): "c:\jvm\jdk1.8" The service 'elasticsearch-service-x64' has been installed.
While a JRE can be used for the Elasticsearch service, due to its use of a client VM (as oppose to a server JVM which offers better performance for long-running applications) its usage is discouraged and a warning will be issued.
Customizing service settings
editThere are two ways to customize the service settings:
- Manager GUI
-
accessible through
managercommand, the GUI offers insight into the installed service including its status, startup type, JVM, start and stop settings among other things. Simply invokingservice.batfrom the command-line with the aforementioned option will open up the manager window:
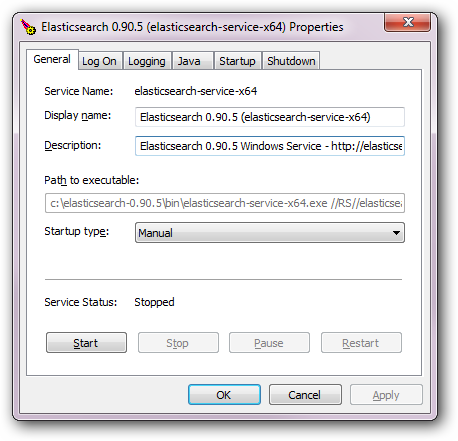
-
Customizing
service.bat -
at its core,
service.batrelies on Apache Commons Daemon project to install the services. For full flexibility such as customizing the user under which the service runs, one can modify the installation parameters to tweak all the parameters accordingly. Do note that this requires reinstalling the service for the new settings to be applied.
There is also a community supported customizable MSI installer available: https://github.com/salyh/elasticsearch-msi-installer (by Hendrik Saly).