Create a deployment
An ECE deployment is a fully managed Elastic Stack environment running on Elastic Cloud Enterprise. It includes Elasticsearch, Kibana, and optional features like Machine Learning or an Integrations (Fleet & APM) Server.
Each deployment is based on a deployment template, which defines its resources, default topology, scaling policies, and available features. Deployments can be customized based on workload requirements, snapshot settings, and security configurations.
To create a deployment in ECE:
From the Cloud UI Deployments view, select Create deployment.
You can quickly create a deployment by setting the basic parameters shown in the UI. If you need more control, select Advanced settings to configure additional options, as detailed below.
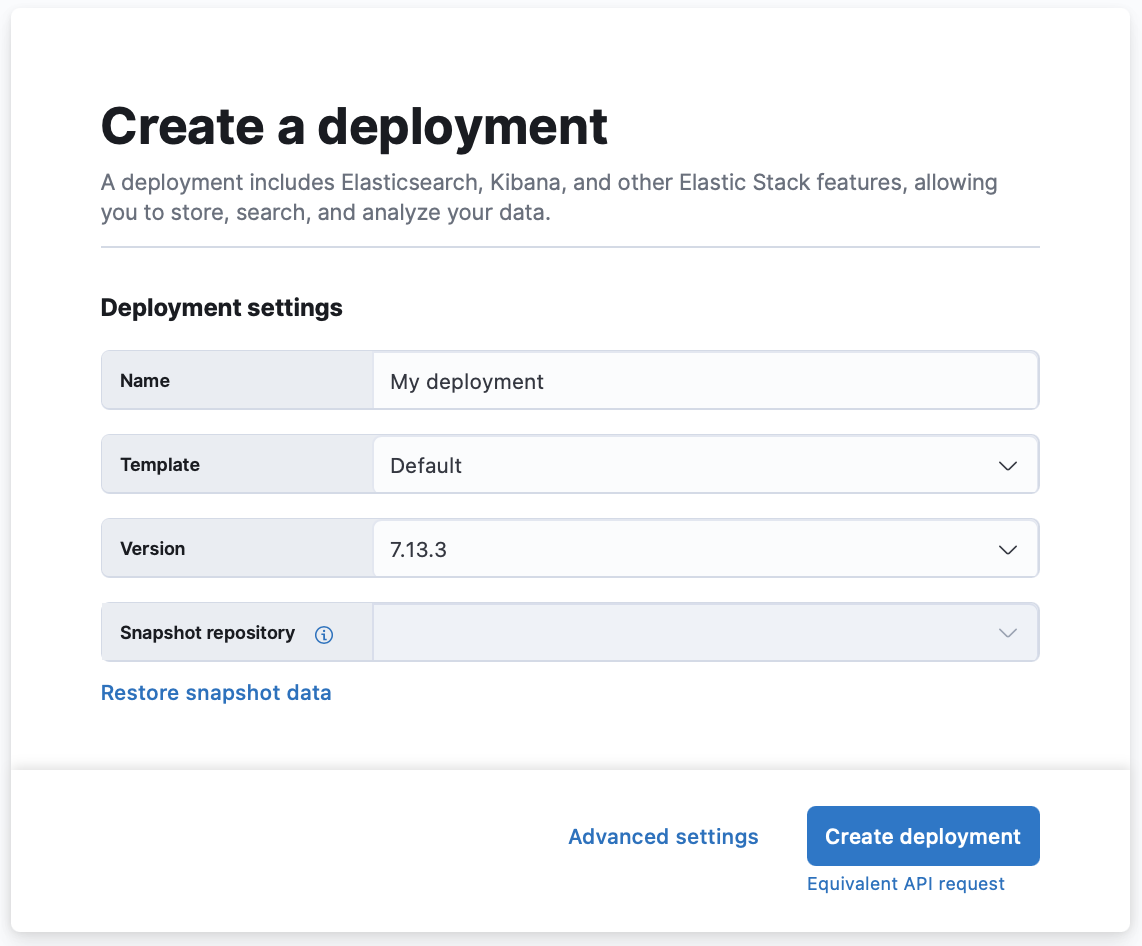
Set a name for your deployment.
Select a deployment template. For a description of the available system templates, refer to Deployment templates.
If the system templates do not meet your requirements, you can modify them or create your own custom templates.
Choose your Elastic Stack version. To manage available versions at platform level, refer to Manage Elastic Stack versions.
Optionally, use snapshots to back up your data, or restore data from another deployment.
TipRestoring a snapshot can help with major version upgrades by creating a separate, non-production deployment where you can test, for example. Or, make life easier for your developers by providing them with a development environment that is populated with real data.
Select Advanced settings if you want to configure autoscaling, adjust resources, select plugins, or customize data tiers. Refer to Customize your deployment for more details on the available options.
Select Create deployment. It takes a few minutes before your deployment gets created.
While you're waiting, you will be prompted to save the admin credentials for your deployment, which grant superuser access to Elasticsearch. Write down the password for the
elasticuser and keep it somewhere safe. These credentials also help you add data using Kibana. If you need to refresh these credentials, you can reset the password at any time.Once the deployment is ready, select Continue to open the deployment’s main page.
After a deployment is spun up, you can scale the size and add other features; however, the instance configuration and computing ratios cannot be changed. If you need to change an existing deployment to another template, we recommend migrating your data.
That’s it! Now that you are up and running, you may want to:
- Start exploring with Kibana, our open-source visualization tool. If you’re not familiar with adding data, yet, Kibana can show you how to index your data into Elasticsearch.
- Connect your applications to Elasticsearch to start ingesting data
- Learn how to configure and manage your deployment