AWS module
editAWS module
editThis functionality is in beta and is subject to change. The design and code is less mature than official GA features and is being provided as-is with no warranties. Beta features are not subject to the support SLA of official GA features.
This is a module for aws logs. It uses filebeat s3 input to get log files from
AWS S3 buckets with SQS notification. This module supports reading s3 server
access logs with s3access fileset, ELB access logs with elb fileset, VPC
flow logs with vpcflow fileset, and CloudTrail logs with cloudtrail fileset.
Access logs contain detailed information about the requests made to these services. VPC flow logs captures information about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in AWS VPC. ELB access logs captures detailed information about requests sent to the load balancer. CloudTrail logs contain events that represent actions taken by a user, role or AWS service.
The aws module requires AWS credentials configuration in order to make AWS API calls.
Users can either use access_key_id, secret_access_key and/or
session_token, or use shared AWS credentials file.
Please see AWS credentials options for more details.
Read the quick start to learn how to set up and run modules.
Module configuration
editExample config:
- module: aws
cloudtrail:
enabled: false
#var.queue_url: https://sqs.myregion.amazonaws.com/123456/myqueue
#var.shared_credential_file: /etc/filebeat/aws_credentials
#var.credential_profile_name: fb-aws
#var.access_key_id: access_key_id
#var.secret_access_key: secret_access_key
#var.session_token: session_token
#var.visibility_timeout: 300s
#var.api_timeout: 120s
#var.endpoint: amazonaws.com
cloudwatch:
enabled: false
#var.queue_url: https://sqs.myregion.amazonaws.com/123456/myqueue
#var.shared_credential_file: /etc/filebeat/aws_credentials
#var.credential_profile_name: fb-aws
#var.access_key_id: access_key_id
#var.secret_access_key: secret_access_key
#var.session_token: session_token
#var.visibility_timeout: 300s
#var.api_timeout: 120s
#var.endpoint: amazonaws.com
ec2:
enabled: false
#var.queue_url: https://sqs.myregion.amazonaws.com/123456/myqueue
#var.shared_credential_file: /etc/filebeat/aws_credentials
#var.credential_profile_name: fb-aws
#var.access_key_id: access_key_id
#var.secret_access_key: secret_access_key
#var.session_token: session_token
#var.visibility_timeout: 300s
#var.api_timeout: 120s
#var.endpoint: amazonaws.com
elb:
enabled: false
#var.queue_url: https://sqs.myregion.amazonaws.com/123456/myqueue
#var.shared_credential_file: /etc/filebeat/aws_credentials
#var.credential_profile_name: fb-aws
#var.access_key_id: access_key_id
#var.secret_access_key: secret_access_key
#var.session_token: session_token
#var.visibility_timeout: 300s
#var.api_timeout: 120s
#var.endpoint: amazonaws.com
s3access:
enabled: false
#var.queue_url: https://sqs.myregion.amazonaws.com/123456/myqueue
#var.shared_credential_file: /etc/filebeat/aws_credentials
#var.credential_profile_name: fb-aws
#var.access_key_id: access_key_id
#var.secret_access_key: secret_access_key
#var.session_token: session_token
#var.visibility_timeout: 300s
#var.api_timeout: 120s
#var.endpoint: amazonaws.com
vpcflow:
enabled: false
#var.queue_url: https://sqs.myregion.amazonaws.com/123456/myqueue
#var.shared_credential_file: /etc/filebeat/aws_credentials
#var.credential_profile_name: fb-aws
#var.access_key_id: access_key_id
#var.secret_access_key: secret_access_key
#var.session_token: session_token
#var.visibility_timeout: 300s
#var.api_timeout: 120s
#var.endpoint: amazonaws.com
-
var.queue_url - (Required) AWS SQS queue url.
-
var.visibility_timeout - The duration that the received messages are hidden from ReceiveMessage request. Default to be 300 seconds.
-
var.api_timeout - Maximum duration before AWS API request will be interrupted. Default to be 120 seconds.
-
var.endpoint - Custom endpoint used to access AWS APIs.
-
var.shared_credential_file - Filename of AWS credential file.
-
var.credential_profile_name - AWS credential profile name.
-
var.access_key_id - First part of access key.
-
var.secret_access_key - Second part of access key.
-
var.session_token - Required when using temporary security credentials.
cloudtrail fileset
editCloudTrail monitors events for the account. If user creates a trail, it
delivers those events as log files to a specific Amazon S3 bucket.
The cloudtrail fileset does not read the CloudTrail Digest files
that are delivered to the S3 bucket when Log File Integrity is turned
on, it only reads the CloudTrail logs.
cloudwatch fileset
editUsers can use Amazon CloudWatch Logs to monitor, store, and access log files
from different sources. Export logs from log groups to an Amazon S3 bucket which
has SQS notification setup already. This fileset will parse these logs into
timestamp and message field.
ec2 fileset
editThis fileset is specifically for EC2 logs stored in AWS CloudWatch. Export logs
from log groups to Amazon S3 bucket which has SQS notification setup already.
With this fileset, EC2 logs will be parsed into fields like ip
and program_name. For logs from other services, please use cloudwatch fileset.
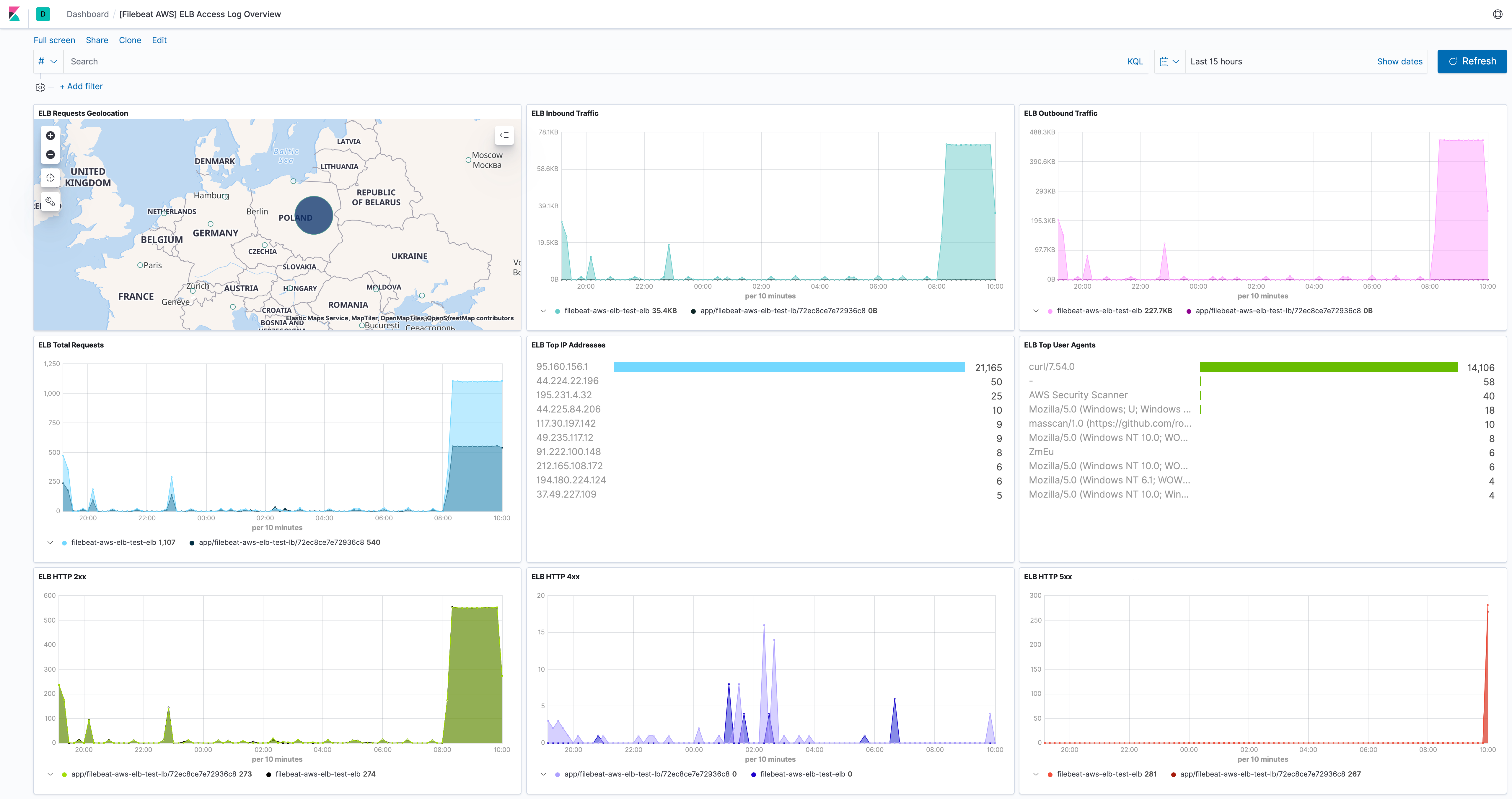
elb fileset
editElastic Load Balancing provides access logs that capture detailed information about requests sent to the load balancer. Each log contains information such as the time the request was received, the client’s IP address, latencies, request paths, and server responses. Users can use these access logs to analyze traffic patterns and to troubleshoot issues.
Please follow enable access logs for classic load balancer for sending Classic ELB access logs to S3 bucket. For application load balancer, please follow enable access log for application load balancer. For network load balancer, please follow enable access log for network load balancer.
This fileset comes with a predefined dashboard:
s3access fileset
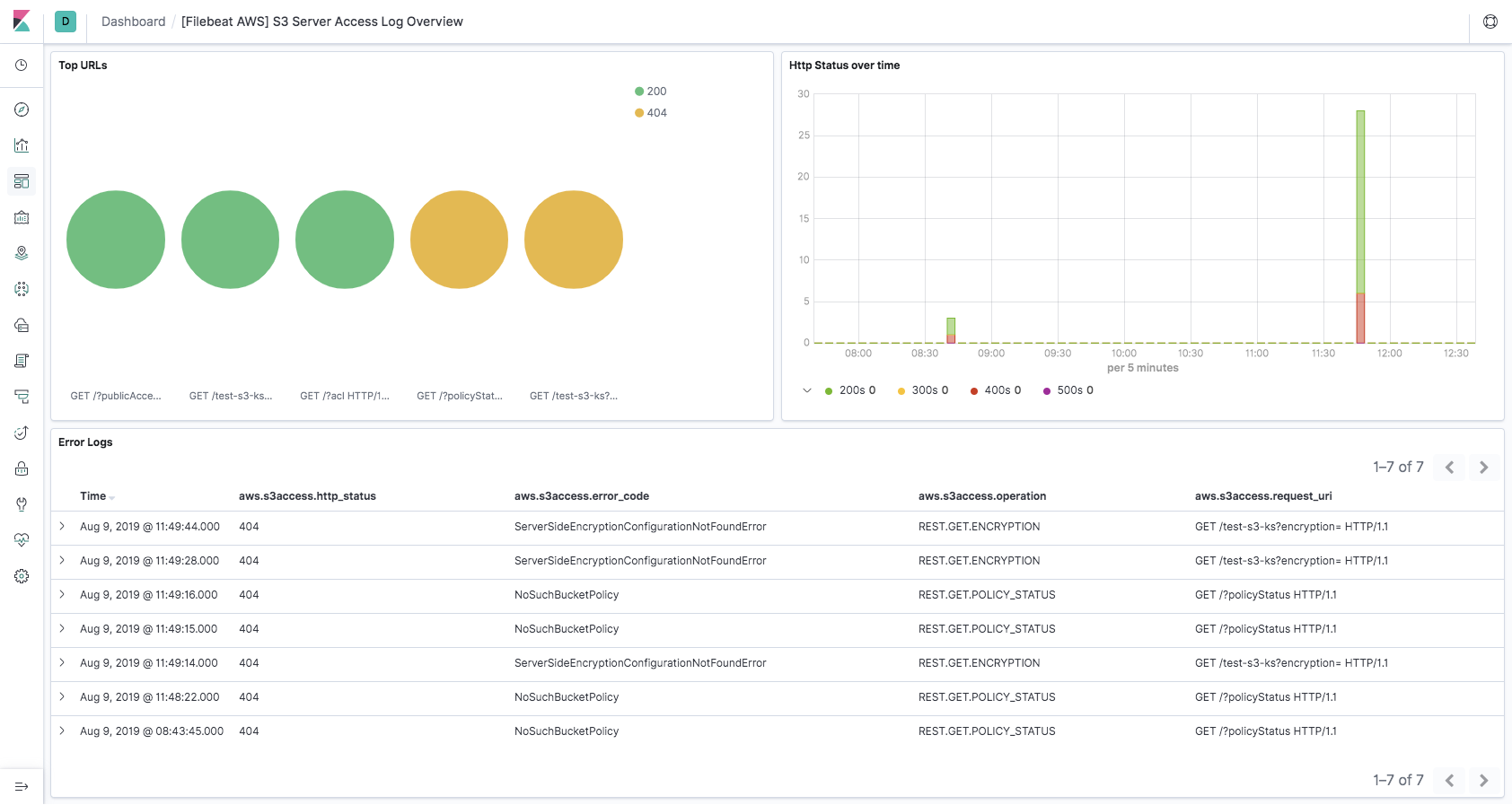
editServer access logging provides detailed records for the requests that are made to a bucket. Server access logs are useful for many applications. For example, access log information can be useful in security and access audits. It can also help you learn about customer base and understand Amazon S3 bill.
Please follow how to enable server access logging for sending server access logs to S3 bucket.
This fileset comes with a predefined dashboard:
vpcflow fileset
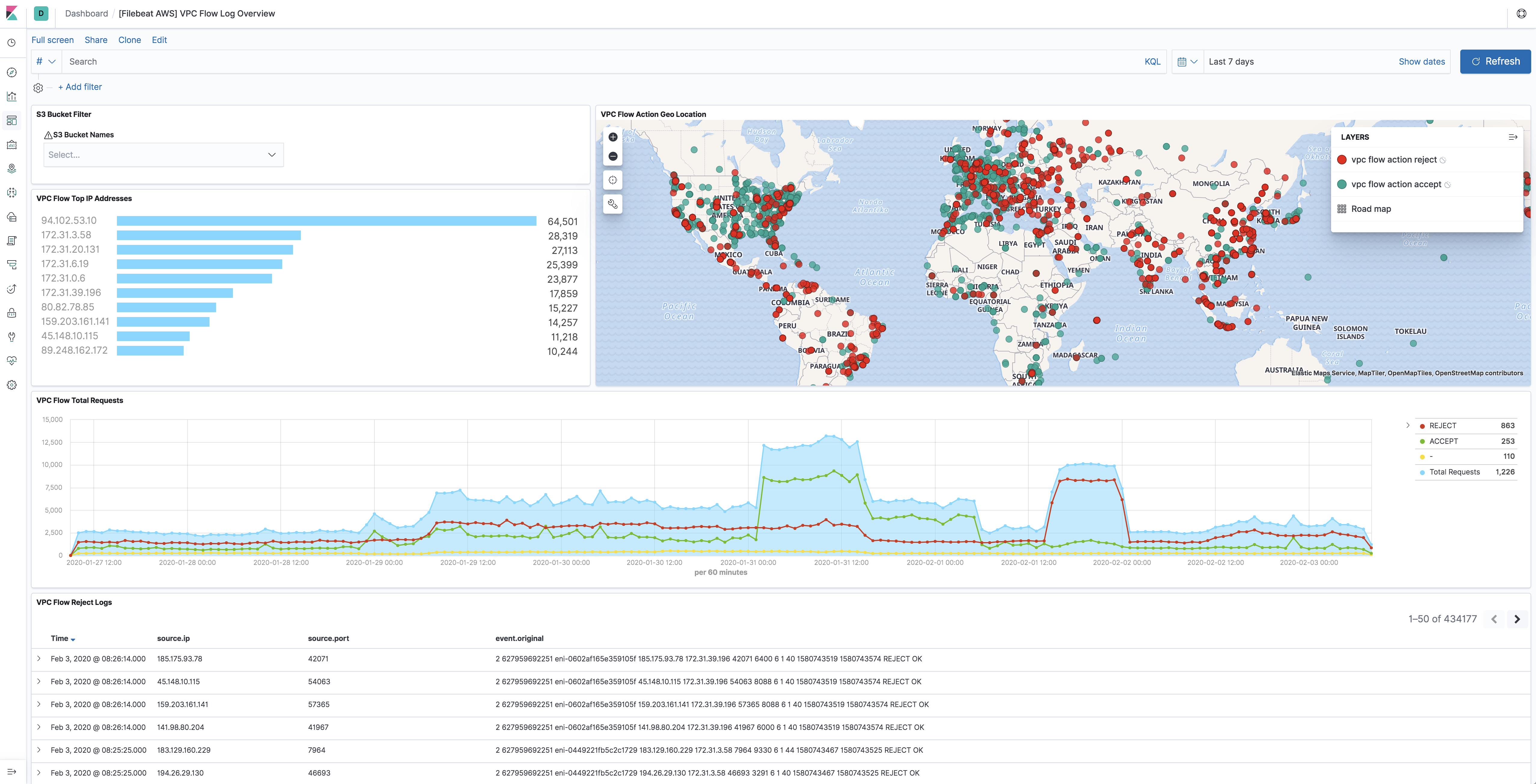
editVPC Flow Logs is a feature in AWS that enables users to capture information
about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in VPC. Flow log data
needs to be published to Amazon S3 in order for vpcflow fileset to retrieve.
Flow logs can help users to monitor traffic that is reaching each instance and
determine the direction of the traffic to and from the network interfaces.
This fileset comes with a predefined dashboard:
AWS Credentials Configuration
editTo configure AWS credentials, either put the credentials into the Filebeat configuration, or use a shared credentials file, as shown in the following examples.
Configuration parameters
edit- access_key_id: first part of access key.
- secret_access_key: second part of access key.
- session_token: required when using temporary security credentials.
- credential_profile_name: profile name in shared credentials file.
- shared_credential_file: directory of the shared credentials file.
- endpoint: URL of the entry point for an AWS web service.
Supported Formats
edit-
Use
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYand/orAWS_SESSION_TOKEN
Users can either put the credentials into metricbeat module configuration or use
environment variable AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY and/or
AWS_SESSION_TOKEN instead.
-
Use AWS credentials in Filebeat configuration
filebeat.inputs: - type: s3 queue_url: https://sqs.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/123/test-queue access_key_id: '<access_key_id>' secret_access_key: '<secret_access_key>' session_token: '<session_token>'
or
filebeat.inputs: - type: s3 queue_url: https://sqs.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/123/test-queue access_key_id: '${AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID:""}' secret_access_key: '${AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY:""}' session_token: '${AWS_SESSION_TOKEN:""}' -
Use shared AWS credentials file
filebeat.inputs: - type: s3 queue_url: https://sqs.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/123/test-queue credential_profile_name: test-fb
credential_profile_name is optional. If you use different credentials for
different tools or applications, you can use profiles to configure multiple
access keys in the same configuration file. If there is no credential_profile_name
given, the default profile will be used.
shared_credential_file is optional to specify the directory of your shared
credentials file. If it’s empty, the default directory will be used.
In Windows, shared credentials file is at C:\Users\<yourUserName>\.aws\credentials.
For Linux, macOS or Unix, the file is located at ~/.aws/credentials. Please see
Create Shared Credentials File
for more details.
AWS Credentials Types
editThere are two different types of AWS credentials can be used: access keys and temporary security credentials.
- Access keys
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY are the two parts of access keys.
They are long-term credentials for an IAM user or the AWS account root user.
Please see
AWS Access Keys
and Secret Access Keys
for more details.
- Temporary security credentials
temporary security credentials has a limited lifetime and consists of an
access key ID, a secret access key, and a security token which typically returned
from GetSessionToken. MFA-enabled IAM users would need to submit an MFA code
while calling GetSessionToken. default_region identifies the AWS Region
whose servers you want to send your first API request to by default. This is
typically the Region closest to you, but it can be any Region. Please see
Temporary Security Credentials
for more details.
sts get-session-token AWS CLI can be used to generate temporary credentials. For example. with MFA-enabled:
aws> sts get-session-token --serial-number arn:aws:iam::1234:mfa/[email protected] --token-code 456789 --duration-seconds 129600
Because temporary security credentials are short term, after they expire, the user needs to generate new ones and modify the aws.yml config file with the new credentials. Unless live reloading feature is enabled for Metricbeat, the user needs to manually restart Metricbeat after updating the config file in order to continue collecting Cloudwatch metrics. This will cause data loss if the config file is not updated with new credentials before the old ones expire. For Metricbeat, we recommend users to use access keys in config file to enable aws module making AWS api calls without have to generate new temporary credentials and update the config frequently.
IAM policy is an entity that defines permissions to an object within your AWS environment. Specific permissions needs to be added into the IAM user’s policy to authorize Metricbeat to collect AWS monitoring metrics. Please see documentation under each metricset for required permissions.
Fields
editFor a description of each field in the module, see the exported fields section.