Get hands-on with Elasticsearch: Dive into our sample notebooks, start a free cloud trial, or try Elastic on your local machine now.
In this article, we’ll walk through how to use the Google MCP Toolbox with Elasticsearch to build a simple tool for extracting information from an Elasticsearch index.
We recently contributed to the Google MCP Toolbox for Databases open-source project by adding support for Elasticsearch as a database.
With this new feature, you can now use the Google MCP Toolbox to connect to Elasticsearch and directly “converse” with your data.
Elasticsearch
We need to have an Elasticsearch instance running. You can activate a free trial on Elastic Cloud or install it locally using the start-local script:
This will install Elasticsearch and Kibana on your computer and generate an API key to be used for configuring Google MCP Toolbox.
The API key will be shown as output of the previous command and stored in a .env file in the elastic-start-local folder.
Install the example dataset
After the installation, you can log in to Kibana using the username elastic and the password generated by the start-local script (stored in a .env file).
You can install the eCommerce orders data set available from Kibana. It includes a single index named kibana_sample_data_ecommerce containing information about 4,675 orders from an ecommerce website. For each order, we have the following information:
- Customer information (name, ID, birth date, email, etc.)
- Order date
- Order ID
- Products (list of all the products with price, quantity, ID, category, discount, etc.)
- SKU
- Total price (taxless, taxed)
- Total quantity
- Geo information (city, country, continent, location, region)
To install the sample data, open the Integrations page in Kibana (search for “Integration” in the search top bar) and install the “Sample Data”. For more details, refer to the documentation here: https://www.elastic.co/docs/explore-analyze/#gs-get-data-into-kibana.
The goal of this article is to show how easy it is to configure Google MCP Toolbox to connect to Elasticsearch and interact with the kibana_sample_data_ecommerce index using natural language.
Google MCP Toolbox
The Google MCP Toolbox is an open-source MCP server designed to make it easy for applications and AI agents to interact with databases securely and efficiently. Previously known as the “GenAI Toolbox for Databases,” the project was renamed after adopting full compatibility with the Model Context Protocol (MCP). Its purpose is to remove the heavy lifting traditionally required when connecting agents to databases by handling connection pooling, authentication, observability, and other operational concerns behind the scenes.
At its core, the Toolbox allows developers to define reusable, high-level tools that encapsulate database interactions. These tools can then be invoked by any MCP-compatible client—such as an AI agent—without requiring the client to implement low-level SQL queries or manage database connections. This approach dramatically reduces the amount of boilerplate code needed to build database-aware agents, making it possible to integrate advanced data operations in only a few lines of application logic. Once a tool is defined, it can be shared across multiple agents, frameworks, or languages (Figure 1).
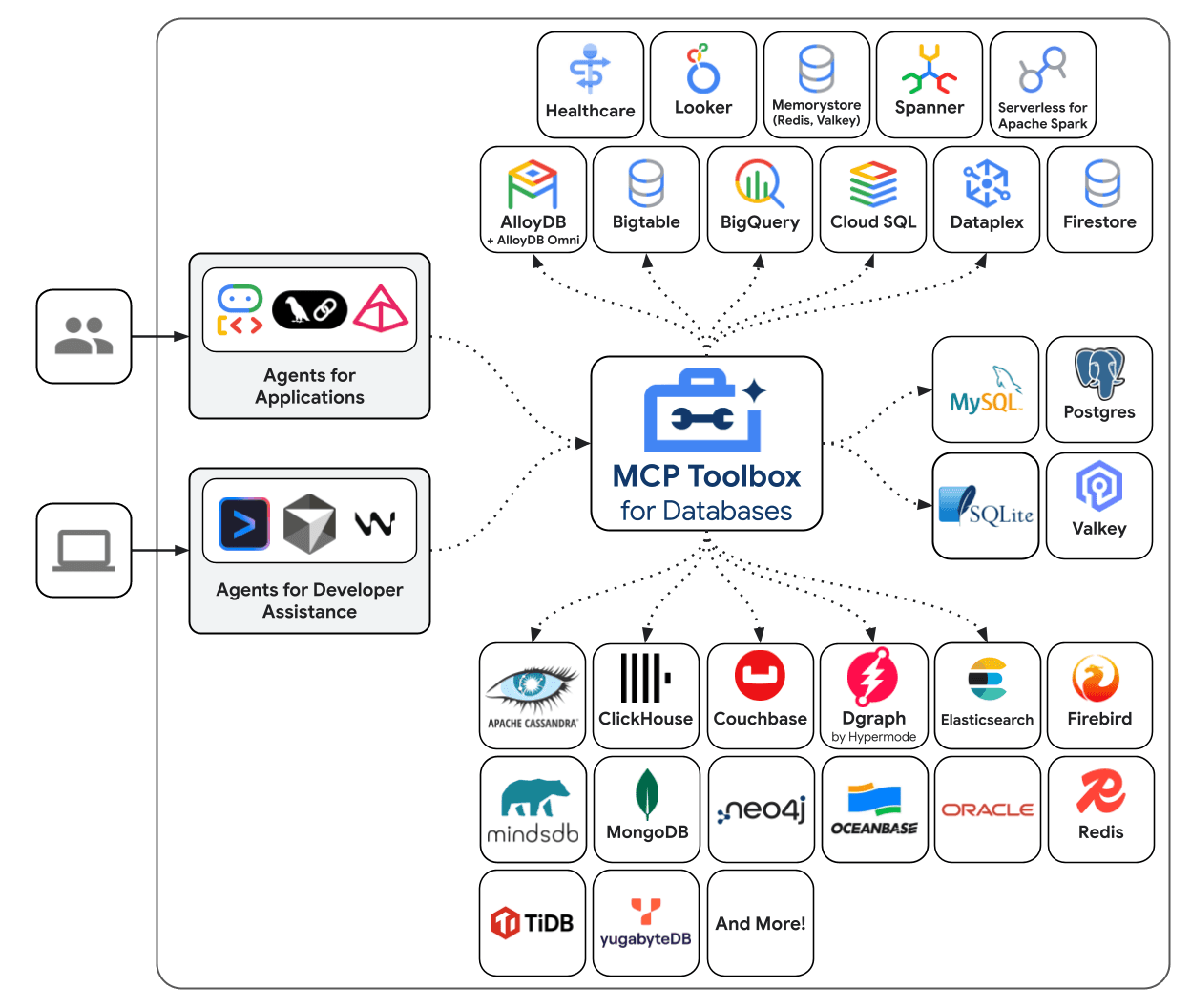
Figure 1: The general architecture of Google MCP Toolbox
A major advantage of using the Toolbox is the built-in security model. Authentication flows such as OAuth2 and OIDC are supported natively, allowing developers to avoid handling or storing sensitive database credentials in agents. The platform also provides observability features—including metrics and tracing—via OpenTelemetry, which is essential for debugging, monitoring, and production deployments. Altogether, MCP Toolbox serves as a unified, secure, and extensible interface for interacting with your data from any MCP-enabled system.
How to install MCP Toolbox
You can install the MCP Toolbox server on Linux using the following command:
If you want to install it on macOS or Windows, you can follow the instructions detailed here.
Configure Toolbox for Elasticsearch
To configure the MCP Toolbox for Elasticsearch, we need to create a tools.yaml file, as follows:
You need to replace the <insert-here-api-key> value with a valid Elasticsearch API key. If you are running Elasticsearch locally using start-local, you can find the API key in the .env file generated by start-local, under the ES_LOCAL_API_KEY variable. If you are using Elastic Cloud, you can generate an API key by following the procedure described here.
The previous tools contain the following ES|QL query for Elasticsearch:
If you are not familiar with ES|QL, it is a query language developed by Elastic, similar to SQL, that can be used to search across one or more indices. You can read more about ES|QL in the official documentation here.
The query above searches for all orders stored in the kibana_sample_data_ecommerce index that contain the specified customer’s name, using the ?name parameter (the question mark denotes a parameter).
The customer’s name is defined in the earlier YAML configuration using the type string and the description “The customer name.”
This tool can be used to answer questions about a customer’s orders—for example: How many orders did customer Foo place in October 2025?
The descriptions of the tools and their parameters are essential for extracting the relevant information from the user’s natural-language request. This extraction is performed using the function-calling capability of a Large Language Model (LLM). In practice, an LLM can determine which function (tool) needs to be executed to obtain the necessary information, along with the appropriate parameters for that function.
For more information about function calls, we suggest reading the OpenAI function calling with Elasticsearch article by Ashish Tiwari.
Run the Toolbox server
You can run the MCP Toolbox using the previous tools.yaml file with the following command:
The –ui parameter runs a web application at http://127.0.0.1:5000/ui (Figure 2).
Figure 2: The MCP Toolbox UI
You can select the Tools > customer-orders and insert a customer name in the parameter name (e.g. Gwen Sanders) and click on the Run Tool button. You should see a JSON response as reported in Figure 3.

Figure 3: execution of the customer-orders tool with name value “Gwen”
The setup is completed, and the MCP Toolbox can execute the customer-orders tool to communicate with Elasticsearch, running the ES|QL query.
Using the MCP Toolbox with Gemini CLI
We can use any MCP client to communicate with the MCP Toolbox for Databases. For instance, we can use Gemini CLI, a command-line tool to use Gemini. You can install Gemini CLI following the instructions reported here.
Gemini CLI offers a pre-configured extension for MCP Toolbox, available at gemini-cli-extensions/mcp-toolbox. You can install this extension by running the following command:
After the installation, you need to go into the directory where you stored the tools.yaml configuration file for MCP Toolbox and execute Gemini CLI as follows (this step is required for the Gemini CLI to be automatically configured with MCP Toolbox):
You should see an output ad reported in Figure 4.

Figure 4: The Gemini CLI terminal
You can check if the MCP Toolbox is connected using the following command:
You should see the mcp_toolbox with the customer-orders tools listed (Figure 5).
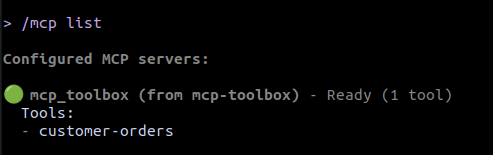
Figure 5: The output of the /mcp list command
If the MCP Toolbox is connected to the Gemini CLI, we can now try asking some questions, such as: “Give me the orders for the customer Gwen Sanders.” The Gemini CLI will then request permission to execute the customer-orders tool from the mcp_toolbox server (see Figure 6).
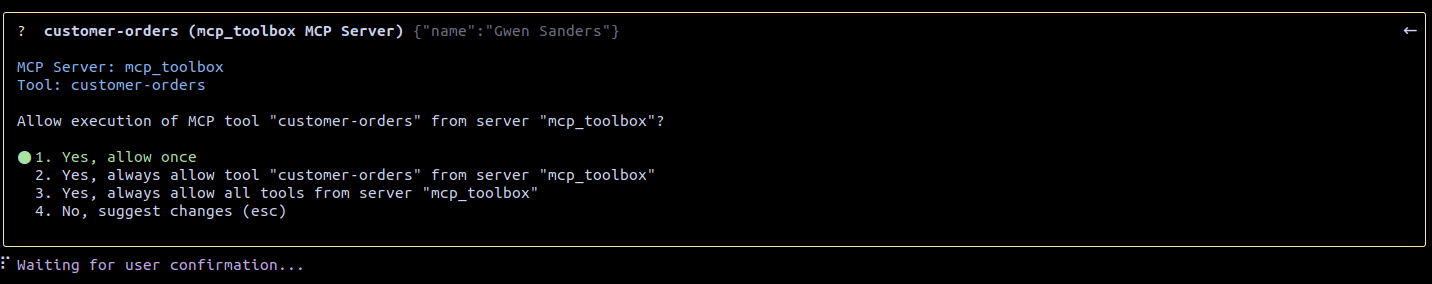
Figure 6: The permission to execute the customer-orders tool
After the confirmation, Gemini CLI will execute the request to the MCP Toolbox, getting a JSON response as a result and using it to format the response (Figure 7).
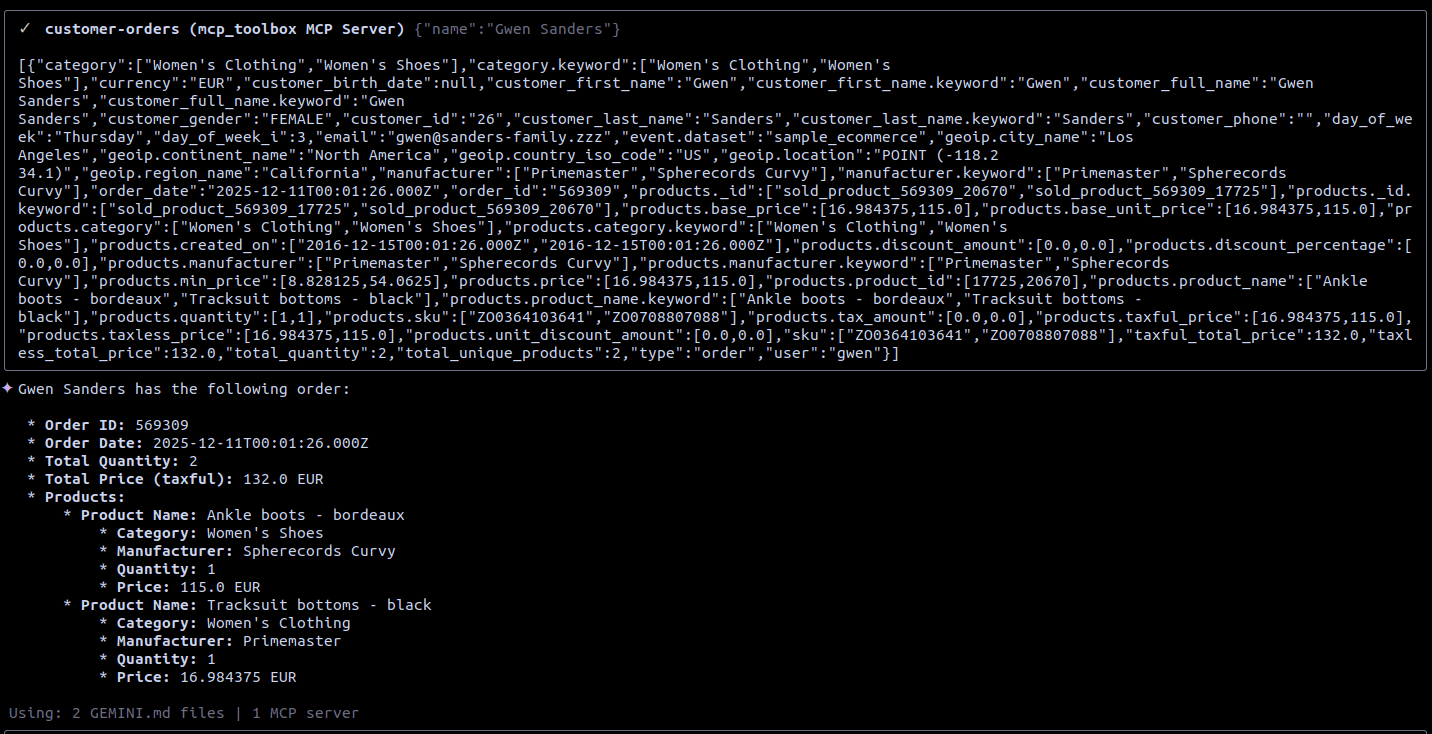
Figure 7: The response from MCP Toolbox and the final response from Gemini CLI
The response from Gemini CLI will report that Gewn Sanders did just one order of 2 products, for a total price of 132 euros.
MCP Toolbox SDKs
Google MCP Toolbox also offers an SDK to access all the functionalities from a program written in Go, Python and Javascript.
For instance, the Python SDK is available on Github at the following page: https://github.com/googleapis/mcp-toolbox-sdk-python.
We need to create a simple agent to connect to the MCP Toolbox. We need to install the following packages:
And create a new agent project using the following command:
This will create a new directory named my_agent with a file agent.py.
Update my_agent/agent.py with the following content to connect to Toolbox:
Create a .env file with your Google API key:
Finally, we can run the agent and observe the results. To execute the agent, you can run the following command:
Or, you can serve it via a web interface:
In both cases, you can interact with the MCP Toolbox using a Q&A interface. For instance, you can ask the previous question: Give me the orders of the customer Gwen Sanders.
For more information about the different SDKs, you can refer to this documentation page.
Conclusion
In this article, we demonstrated the Elasticsearch integration for the Google MCP Toolbox for Databases. Using a simple YAML configuration file, we can define a set of tools that translate natural-language questions into Elasticsearch queries using the ES|QL language.
We showed how to interact with the kibana_sample_data_ecommerce dataset, which contains orders from an e-commerce website. With this configuration file, we can simply run the MCP Toolbox server and connect to it from any MCP client.
Finally, we demonstrated how to use the Gemini CLI as a client to connect to the MCP Toolbox for Databases and query the e-commerce data stored in Elasticsearch. We executed a natural-language query to retrieve information about orders for a specific customer identified by name.
As the MCP ecosystem continues to grow, this pattern—lightweight tool definitions backed by secure, production-ready infrastructure—creates new opportunities for building increasingly capable, data-aware agents with minimal effort. Whether you're experimenting locally with Elastic’s sample datasets or integrating search capabilities into a larger application, MCP Toolbox provides a reliable, extensible foundation for interacting with your Elasticsearch data using natural language.
For more information about the development of agentic AI applications, you can read the Building AI Agentic workflows with Elasticsearch article by Anish Mathur and Dana Juratoni.
For more information about the Google MCP Toolbox, you can visit https://googleapis.github.io/genai-toolbox/getting-started/introduction/.