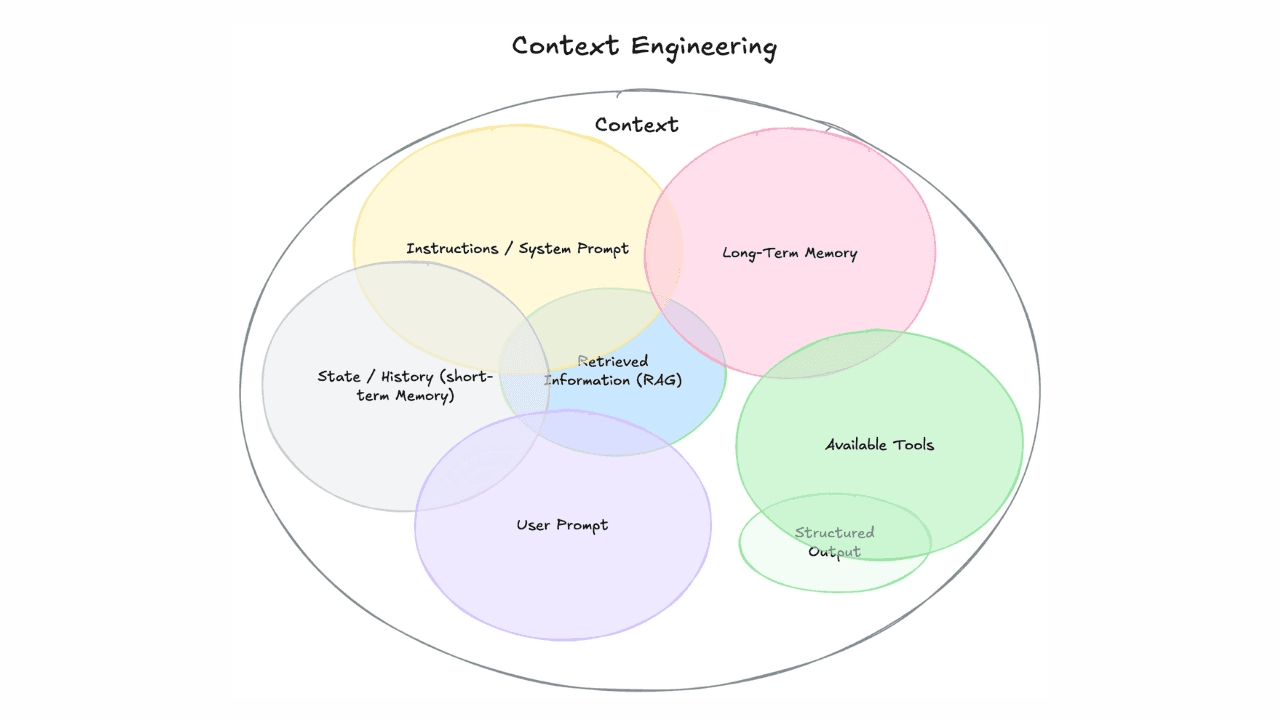
Elasticsearch has native integrations with the industry-leading Gen AI tools and providers. Check out our webinars on going Beyond RAG Basics, or building prod-ready apps with the Elastic vector database.
To build the best search solutions for your use case, start a free cloud trial or try Elastic on your local machine now.
We are excited to announce our latest addition to the Elasticsearch open inference API: the integration of Google’s Gemini models through Google Cloud’s Vertex AI platform!
Elasticsearch open inference chat completion API provides a standardized, feature-rich, and familiar way to access large language models. With this, Elasticsearch developers can use large language models, such as Gemini 2.5 Pro, to build GenAI applications with use cases including question answering, summarization, and text generation.
Now, they can use their Google Cloud account for chat completion tasks, store summarizations, utilize Google’s Gemini models in ES|QL or directly through the inference API, and take advantage of Elasticsearch’s comprehensive AI search tooling and proven vector database capabilities.
Using Google’s Gemini models to answer questions and generate tool calls
In this blog, we’ll demonstrate how to use Google’s Gemini models to answer questions about data stored in Elasticsearch using ES|QL. Before we start interacting with Elasticsearch, ensure you have a Google Cloud Vertex AI account and the necessary keys handy. We’ll need them when configuring the Inference Endpoint.
Creating a Vertex AI Service Account and retrieving the keys
1. Go to https://console.cloud.google.com/iam-admin/serviceaccounts
2. Click the button Create service account.
- Write a name that is suitable for you.
- Click Create and continue.
- Grant the role to the Vertex AI User.
- Click Add another role and then grant the role Service account token creator. This role is needed to allow the SA to generate the necessary access tokens.
- Click Done.
3. Go to https://console.cloud.google.com/iam-admin/serviceaccounts and click on the SA just created.
4. Go to the keys tab and click Add key -> Create new key -> JSON -> Click on Create.
- If you get an error message Service account key creation is disabled your administrator needs to change the organization policy
iam.disableServiceAccountKeyCreationor grant an exception.
5. The service account keys should be downloaded automatically.
Now that we’ve downloaded the service account key, let’s format it before we use it to create the Inference Endpoint. The following sed command will escape the quotes and remove newlines.
sed 's/"/\\"/g' <path to your service account file> | tr -d "\n"
Setting up the Inference Endpoint and interacting with Google’s Gemini models
We’ll use Kibana’s Console to execute these next steps in Elasticsearch without needing to set up an IDE.
First, we configure an inference endpoint, which will interact with Gemini:
We’ll get back a response similar to the following with status code 200 OK on successful inference endpoint creation:
We can now call the configured endpoint to perform chat completion on any text input and receive the response in real-time. Let’s ask Gemini for a short description of ES|QL:
We should get a streamed response back with a status code 200 OK providing a short description of ES|QL:
The Inference Chat Completion API supports tool calling, allowing us to interact with Google’s Gemini models hosted on the Vertex AI platform in a robust manner to retrieve information about our data.
We’ll ask Gemini to write an ES|QL query to retrieve documents that contain a failure status code in the response field and summarize the results. The response field may not be mapped as an integer, so we’ll need Gemini to retrieve the mapping for us and adjust the query appropriately.
We’ll pretend we have a tool implemented that Gemini can interact with. For this demonstration, we’ll perform the tool call ourselves in the Dev Console.
Initial request:
Gemini responds with a tool call to retrieve the mapping of the index kibana_sample_data_logs:
To simulate the tool call, we’ll retrieve the mapping using the following command:
To finish simulating the tool call, we’ll include the response in the next request to Gemini:
Request with mapping result:
Now that Gemini has the mapping, it responds with a tool call to execute a query to retrieve the last two web logs:
If you look closely, you’ll notice that the syntax is missing pipe characters before the different clauses. Our pretend tool call will simulate Kibana and return an error, allowing us to see how Gemini handles the issue. Kibana’s ES|QL query console would respond with this error:
Let’s include that in the response for the execute_esql_query.
Request with error:
Gemini is able to identify the mistake and produce the correct query:
Our next message will include the results from executing the correctly formatted query in Kibana. To retrieve the documents, we can either execute the query directly in Discover and copy the document contents or execute the query in Dev Tools. Let’s pretend our tool implementation used Discover and retrieved the full source for the documents.
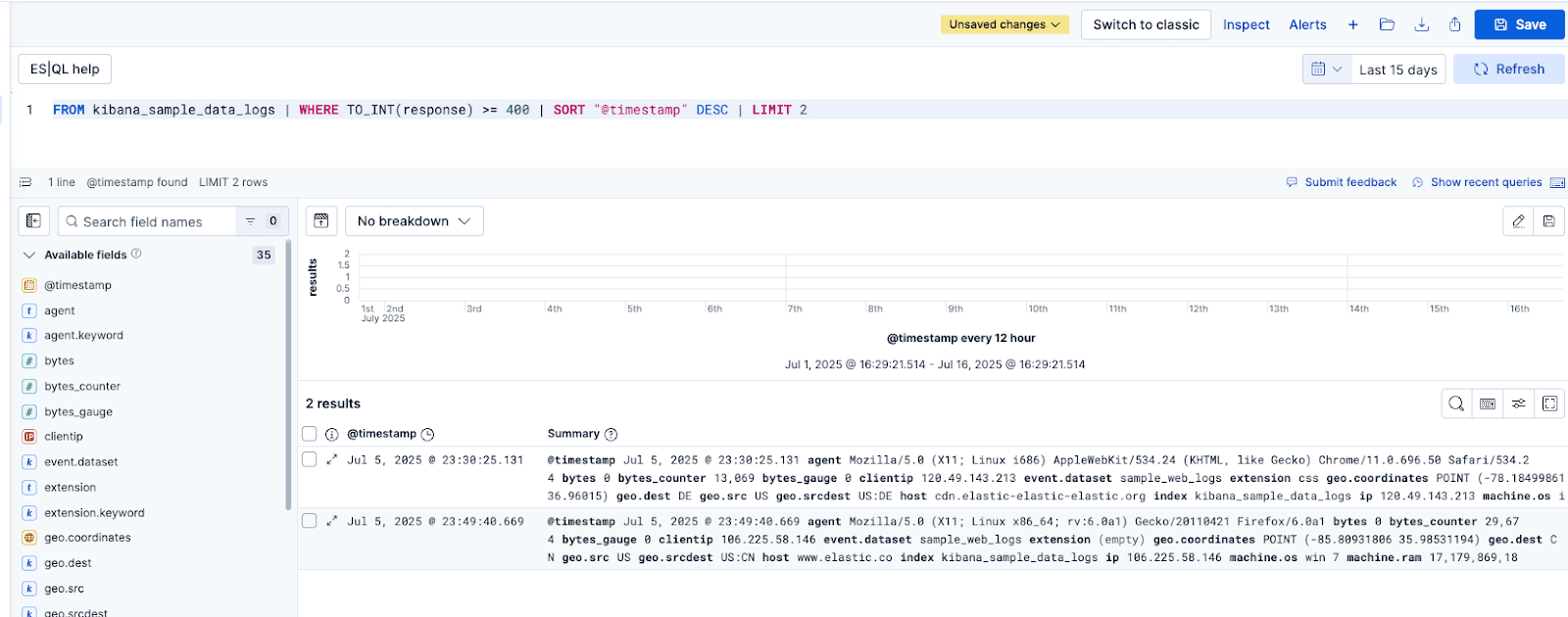
Request with document results:
Gemini’s last response reiterates what the conversation has covered so far and summarizes the two retrieved documents, just like we asked:
Here is the response summarizing the results:
Using ES|QL’s Completion command to summarize results
In the previous workflow, we used Google’s Gemini models to summarize the two failure web logs. We can also leverage the power of ES|QL’s Completion command to summarize the results directly in Kibana. First we need to create a new inference endpoint that uses the completion task type.
Again, we’ll get back a response similar to the following with status code 200 OK on successful inference endpoint creation:
We can now execute a modified version of the ES|QL query that Gemini generated for us.
These are the modifications to the query:
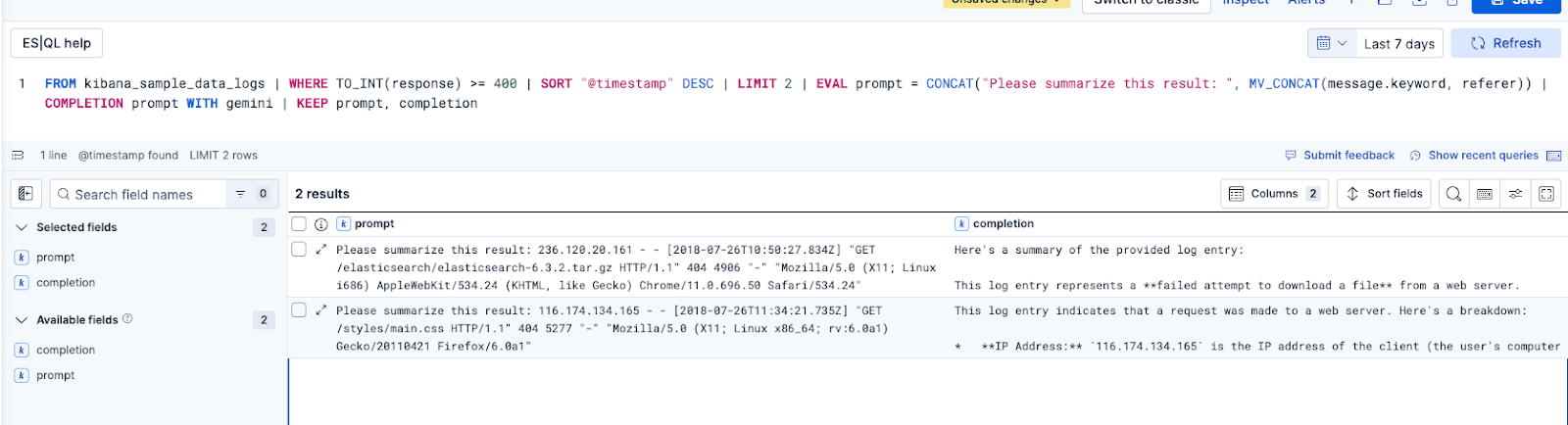
EVAL prompt- This command creates a field that is sent with the text to Gemini to provide specific fields and instructions on what to do with those fields. In our example, it will ask Gemini to summarize the contents of the message and the referer fieldsCOMPLETION- This command will pass each result to the LLM to perform the task we’ve instructed it to doWITH gemini_completion- This is the inference endpoint ID we created earlier
KEEP prompt, completion- This instructs ES|QL to generate a table with the prompt we sent to Gemini and the results we received
The results should look like the image below.
Wrap-up
We continue to bring state-of-the-art AI tools and providers to Elasticsearch, and we hope that you are as excited as we are about our integration with Google Cloud’s Vertex AI platform and Google’s Gemini models! Combine Google Cloud’s generative AI capabilities with Elasticsearch vector database and AI search tooling to deliver high-relevance, production-ready search and analytics experiences.
Visit Google Cloud’s Vertex AI page on Elasticsearch Labs, or try other sample notebooks on Search Labs GitHub.
To run Elasticsearch for local testing, use Docker to install and start both Elasticsearch and Kibana on your local machine with start-local:
curl -fsSL https://elastic.co/start-local | sh
Get started with your free Elastic Cloud trial or by subscribing through Google Cloud Marketplace.