Elasticsearch has native integrations with the industry-leading Gen AI tools and providers. Check out our webinars on going Beyond RAG Basics, or building prod-ready apps with the Elastic vector database.
To build the best search solutions for your use case, start a free cloud trial or try Elastic on your local machine now.
A few weeks ago, we had the incredible opportunity to sponsor Cal Hacks 12.0, one of the largest in-person hackathons with over 2000 participants coming from all over the world. We offered a dedicated prize track for the best use of Elastic Agent Builder on Serverless, and the response was phenomenal. In just 36 hours, we received 29 submissions that used Agent Builder in creative ways, from building wildfire intelligence tools to StackOverflow validators.
Beyond the impressive projects, the experience at Cal Hacks 12.0 also gave us something equally valuable: quick, unfiltered feedback from developers encountering our Stack for the first time. Hackathons are unique pressure tests with tight timelines, zero prior familiarity, and unpredictable obstacles (like the infamous WiFi outages). They expose exactly where the developer experience shines and where it still needs work. This matters even more now, as developers interact with the Elastic Stack in new ways, increasingly through LLM-driven workflows. In this blog post, we’ll dive deeper into what the participants built with Agent Builder and what we learned in the process.
The winning projects
First Place: AgentOverflow
Stack Overflow rebuilt for the LLM and agent era.
Read more about AgentOverflow here.
AgentOverflow addresses a problem most AI developers encounter: LLMs hallucinate, chat histories disappear, and developers waste time re-solving the same issues.
AgentOverflow captures, validates, and resurfaces real problem-solution pairs, so developers can break the hallucination spiral and ship faster.
How it works:
1. Share JSON - the “Solution Schema.”
One click from a Claude share will scrape, extract, and assemble a Share Solution JSON, which is a structured format containing:
- Problem
- Context
- Code
- Tags
- Verified solution steps.
A validator (LAVA) checks and enforces structure, the user adds a line of extra context, then it’s stored and indexed within Elasticsearch.
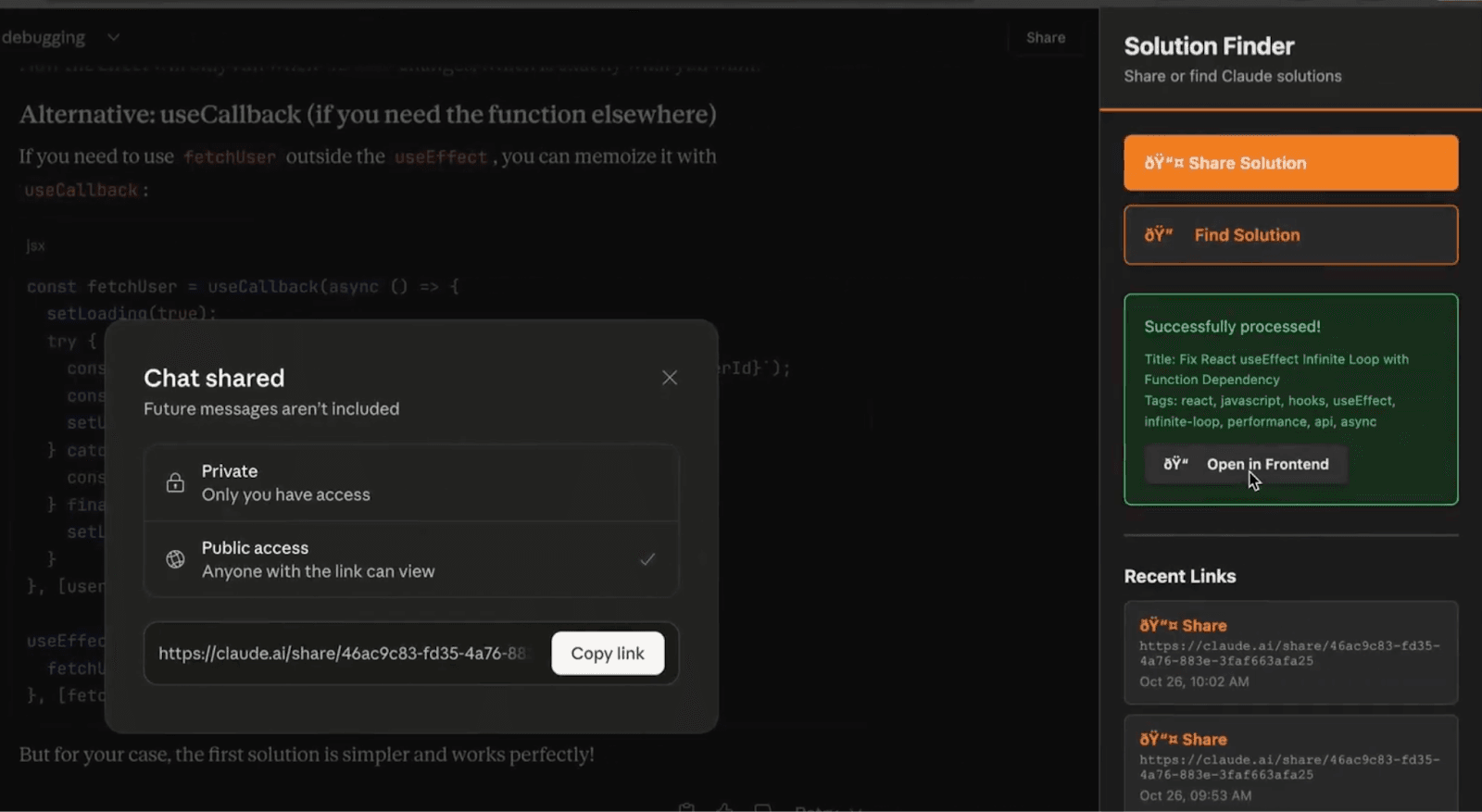
Clicking “Share Solution” will scrape the current session along with relevant metadata
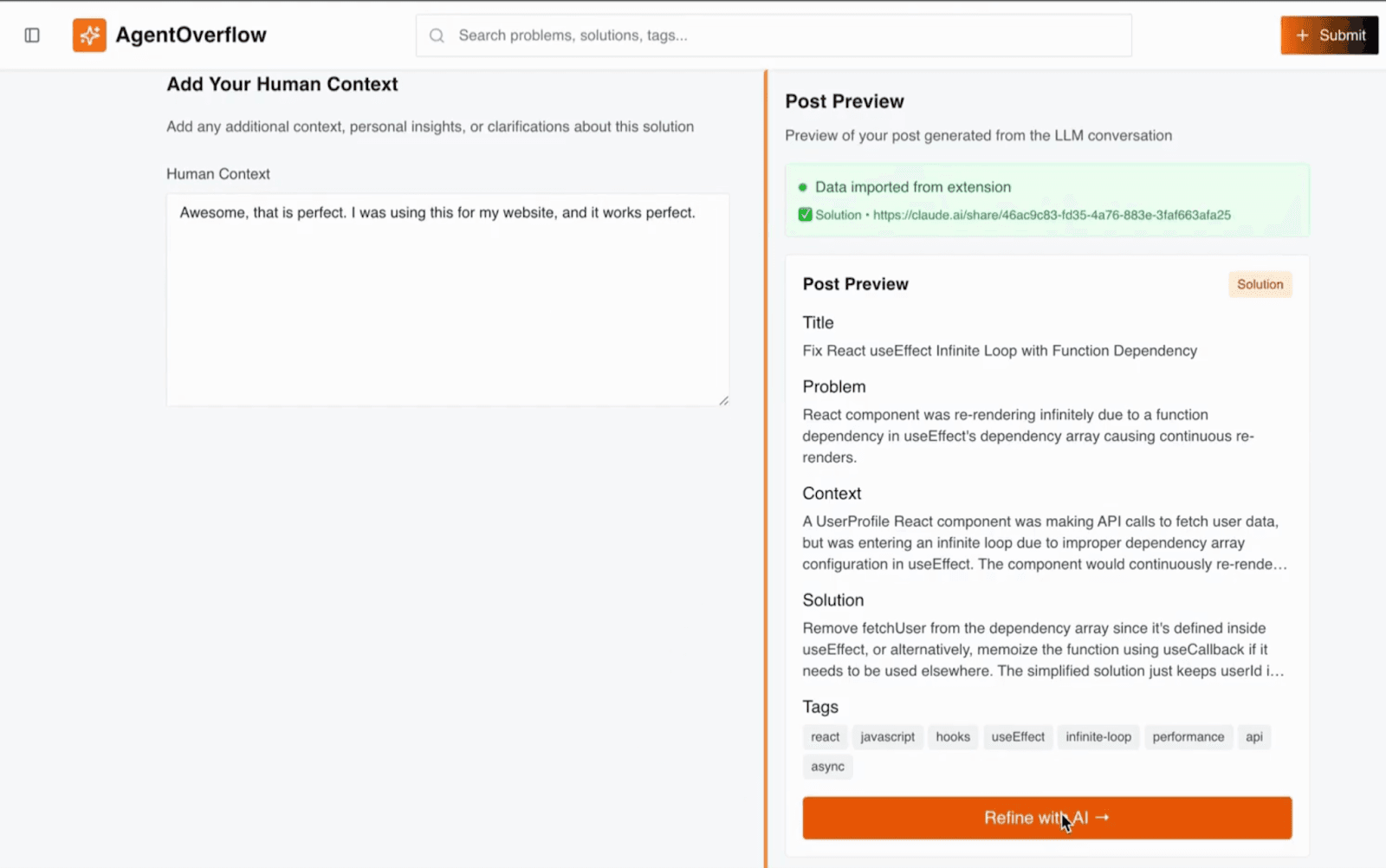
Users provide additional context through the web frontend, then the JSON is indexed in Elasticsearch
2. Find Solution
When you get stuck, click on Find Solution and AgentOverflow will scrape your current conversation, use it to build a query, and run a hybrid Elasticsearch search to surface:
- Ranked, community-validated fixes
- The exact prompts that originally solved the problem
This allows developers to copy, paste, and unblock their current session quickly.
3. MCP - context injection for LLMs
By connecting to the stored structured solutions within Elasticsearch through MCP (Model Context Protocol), LLMs are fed high signal context (code, logs, configs, prior fixes) at runtime without extra noise.
AgentOverflow uses Agent Builder with Elasticsearch as a structured memory layer that injects relevant context into LLMs. This transforms them from passive chatbots into context-aware problem solvers.
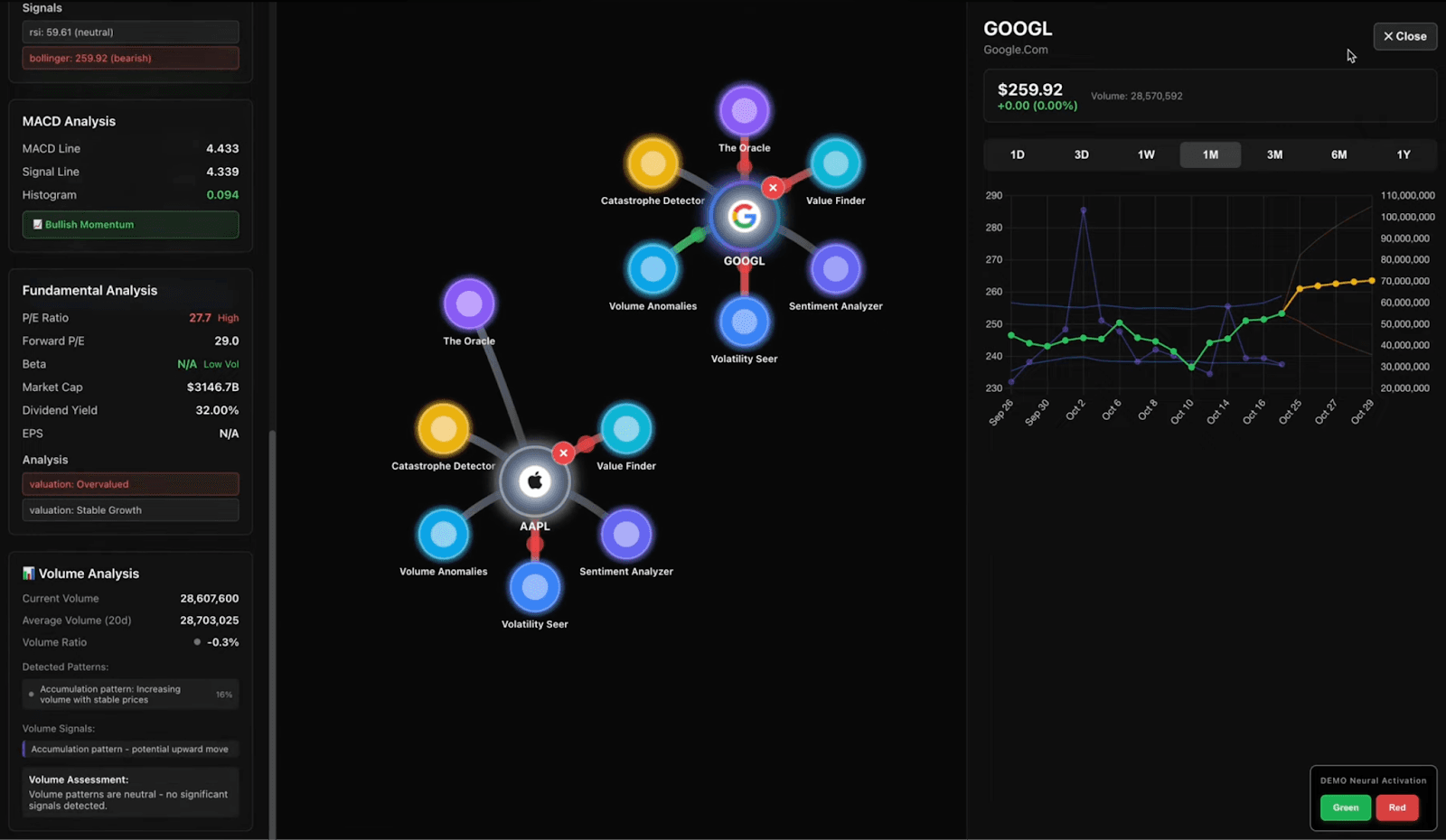
Runner-up: MarketMind
A real-time interpretable view of market energy, powered by six Elastic Agents.
Read more about MarketMind here.
MarketMind earned their spot by giving novice traders a platform that converts fragmented market data into clear, real-time signals. Instead of juggling price action, fundamentals, sentiment, and volatility across different tools, MarketMind consolidates all this information into one platform, helping traders gain actionable insights. This project also used some complex ES|QL queries when building their agents.
How it works:
1. Collect real-time market data
MarketMind pulls price-action, fundamentals, sentiment, volatility and risk metrics from Yahoo Finance. This data is ingested and organized into multiple Elasticsearch indices.
2. Six specialized agents analyze the market
Each agent, built with Agent Builder, focuses on a different layer of the market. They read from an Elasticsearch index, compute their own domain-specific metrics, and generate a standardized JSON output with scores and reasoning.
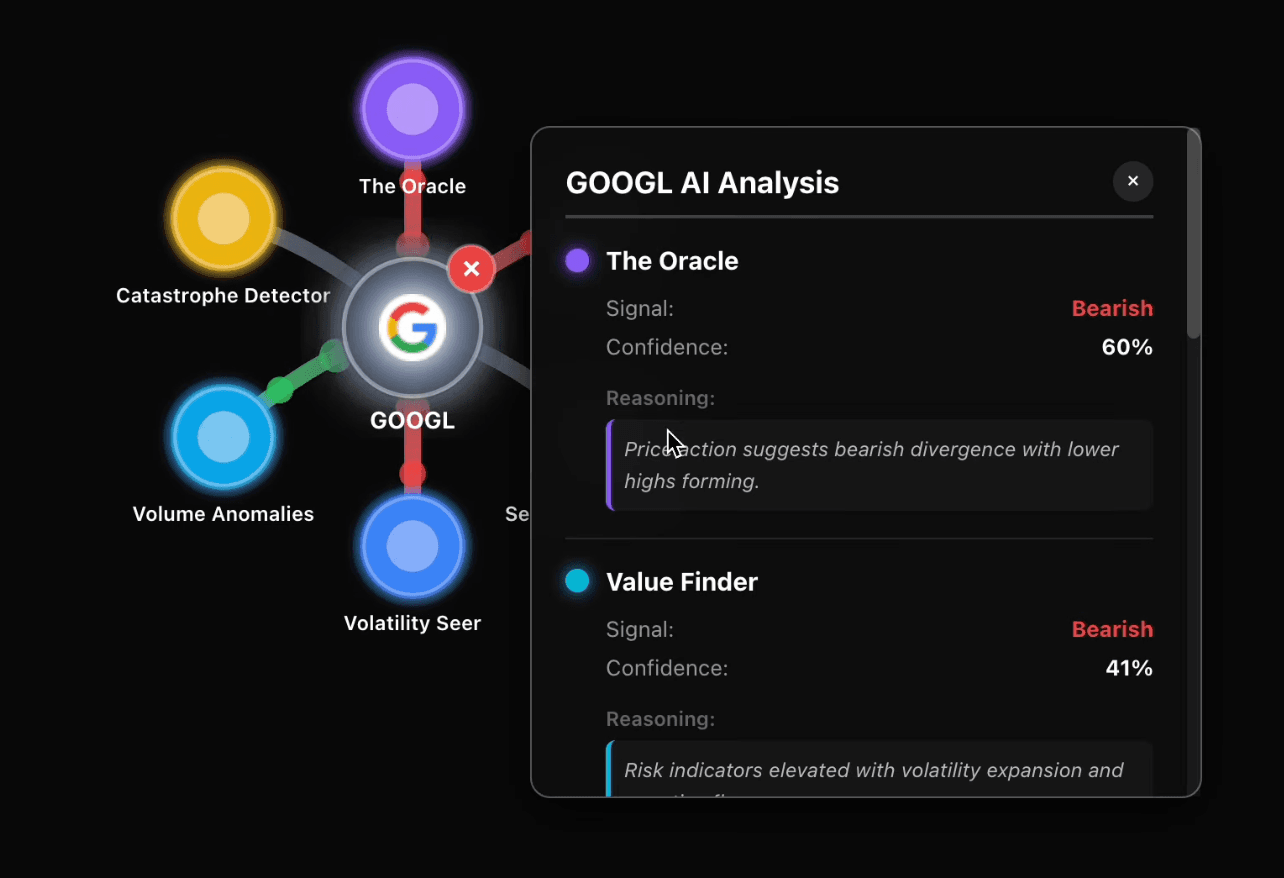
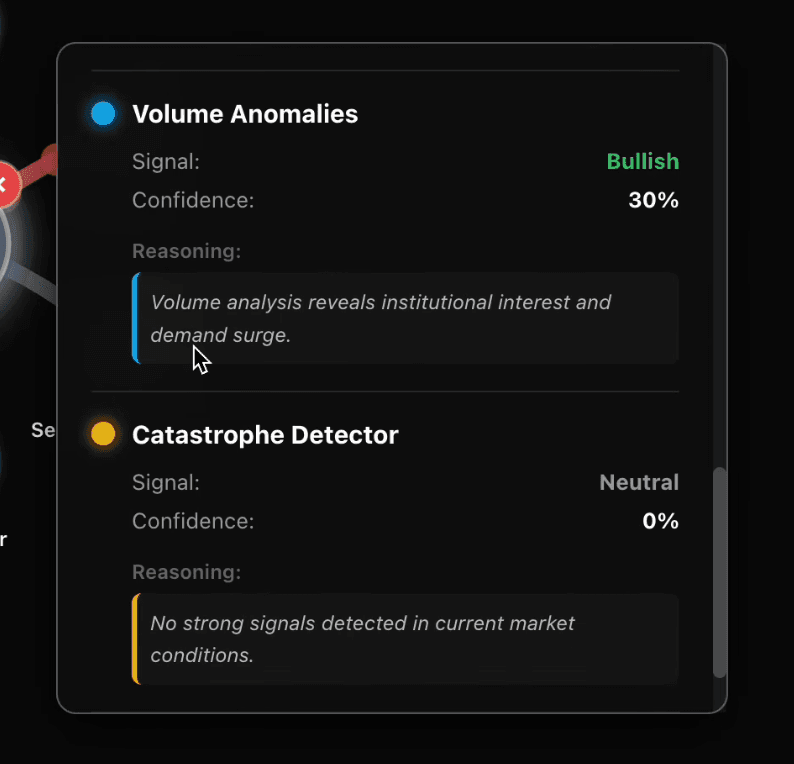
3. Aggregate signals into a unified “market energy” model
The combined outputs appear as glowing pulses around each stock, illustrating whether momentum is building, risk is rising, or sentiment is shifting.
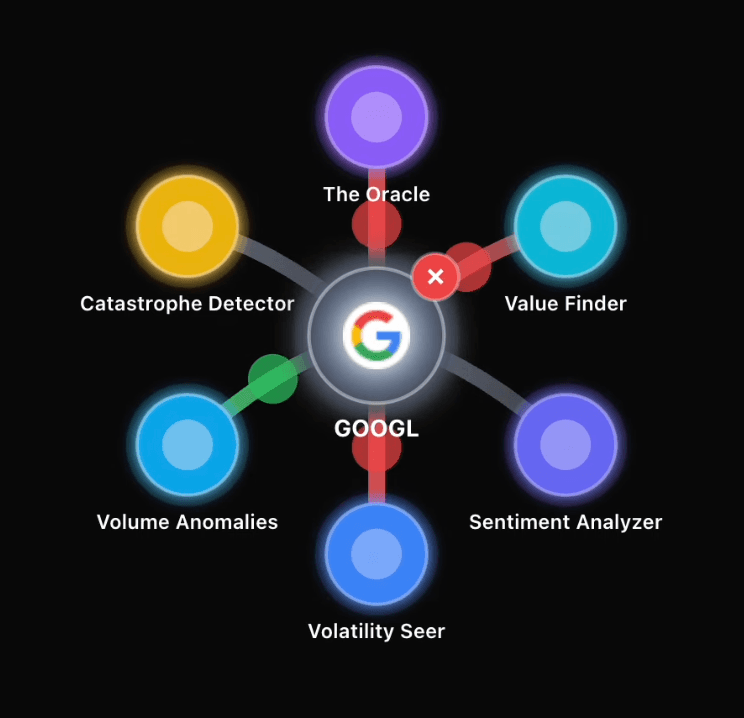
4. Visualize insights
The frontend was built with React and Next.js, using TypeScript, SVG physics-based visuals, and Chart.js for live candlestick charts. This turns raw analysis into real-time actionable feedback.
Other interesting projects:
Here are some other strong contenders that used Elastic in different parts of their stack:
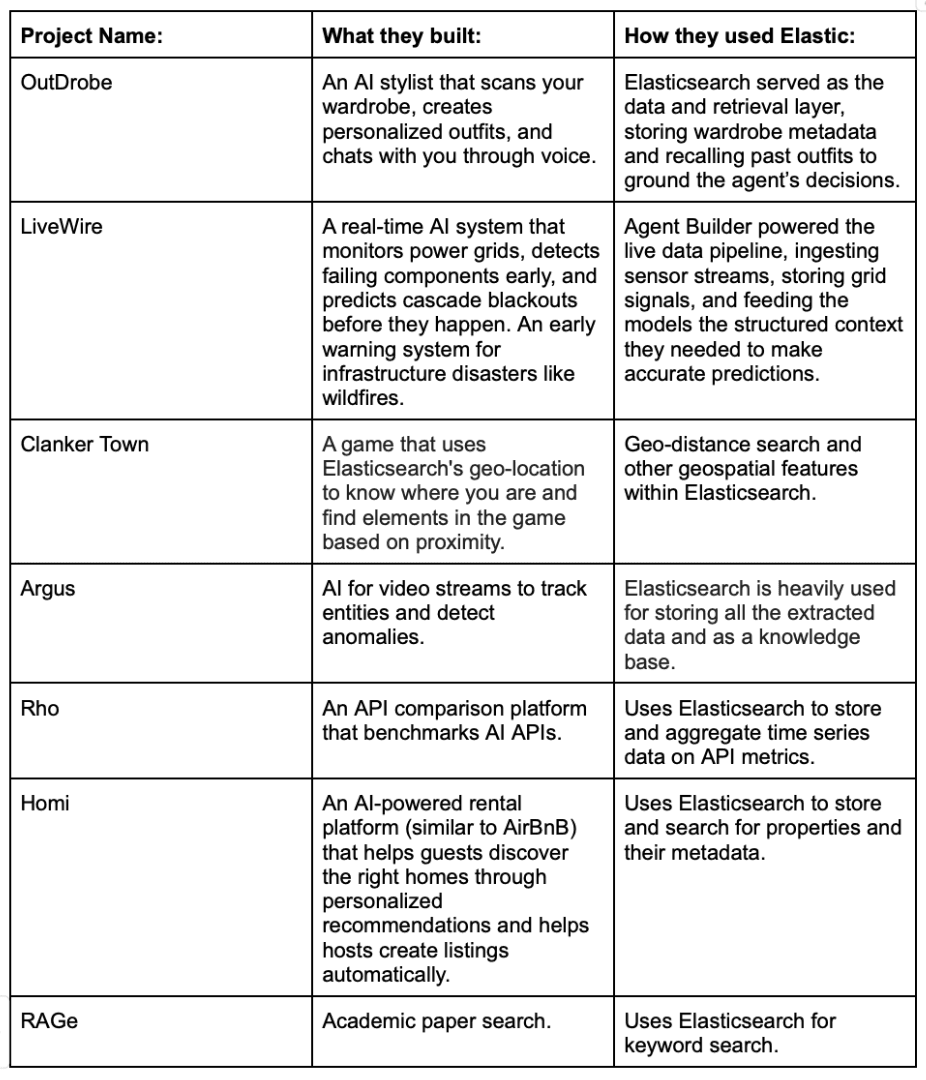
Find the full list of projects that were submitted to our track here.
What we learned from developers
- Agent Builder is user-friendly:
Most teams had never used Elastic before and were still able to build agents quickly with little support. We held a workshop for those who needed more guidance, but most were able to ingest their data and build an agent to perform actions on that data.
- LLMs excel at
kNNqueries, but still need guidance in generating ES|QL:
Asking ChatGPT-5 to generate ES|QL queries returned incorrect information, often mixing ES|QL and SQL. Feeding the LLM the docs in a markdown file seemed to be a workable fix.
- Snapshot-only ES|QL functions leaked into docs:
The upcoming FIRST and LAST aggregation functions had unintentionally slipped into our ES|QL docs. Because we fed those docs to ChatGPT, the model dutifully used these functions, even though they aren't available in Serverless yet. Thanks to the feedback from the group, engineering quickly opened and merged a fix to remove the functions from the published docs (PR #137341).
- Missing Serverless-specific guidance:
A team tried enabling LOOKUP JOIN on an index that wasn’t created in lookup mode. The error message sent them chasing commands that don’t exist on Serverless. We relayed this to the product team, who immediately opened a fix for a Serverless-specific, actionable message. Longer term, the vision is to hide the reindexing complexity entirely (Issue #4838).
- Value of in-person events:
Online hackathons are great, but nothing matches the rapid feedback loop you get when you're debugging shoulder-to-shoulder with builders. We watched teams integrate Agent Builder across different use cases, spotted where the developer experience with ES|QL could be improved, and fixed issues much quicker than trying to do so over asynchronous channels.
Conclusion
Cal Hacks 12.0 gave us more than a weekend of cool demos; it also gave us insight into how new developers are interacting with the Elastic Stack. In just 36 hours, we saw teams pick up Agent Builder, ingest data into Elasticsearch, design multi-agent systems, and test our features in a variety of ways. The event also reminded us why in-person events matter. The rapid feedback loops, real conversations, and hands-on debugging helped us understand current developer needs. We’re excited to bring back what we learned to the engineering team. We’ll see you at the next hackathon.