What’s new in 7.16
editWhat’s new in 7.16
editHere are the highlights of what’s new and improved in Elastic Security!
For detailed information about this release, see the Release notes.
Other versions: 7.15 | 7.14 | 7.13 | 7.12 | 7.11 | 7.10 | 7.9
New features
editMemory threat protection added for Linux and macOS hosts
Memory threat protection, which detects and stops many of the techniques used for process injection, is now added to Linux and macOS hosts. It ships with preventions for shellcode (macOS and Linux), reflective ELF injection (Linux), and in-memory Mach-O execution (macOS), plus the preventions for Windows systems that were introduced in Elastic Stack version 7.15. Memory threat protection is available for customers with a Platinum or Enterprise license.
Expanded malicious behavior protection
Malicious behavior protection has been expanded to stop an advanced set of attack techniques. All analytics are mapped to the MITRE ATT&CK® framework and address methods related to initial access, privilege escalation, and defense evasion, including:
- Phishing with a spearphishing attachment, where an attacker drops an initial payload via a malicious document or shortcut.
- Signed binary proxy execution, comprised of commonly abused living off the land (LotL) binaries and scripts.
- Privilege escalation via UAC bypass, which allows adversaries to bypass Windows User Account Control to elevate privileges.
These new capabilities leverage the malicious behavior preventions introduced in Elastic Stack version 7.15 to stop various techniques for phishing, credential theft, living off the land (LotL), and achieving advanced persistence.
New integrations
Elastic Security ships the following new integrations in 7.16:
- AWS WAF
- Cisco Duo
- GitHub
- 1Password
ECS support for Osquery Manager integration
Host inspection is streamlined via the Osquery Manager integration for Elastic Agent. You can now map saved query results directly to ECS to return normalized data.
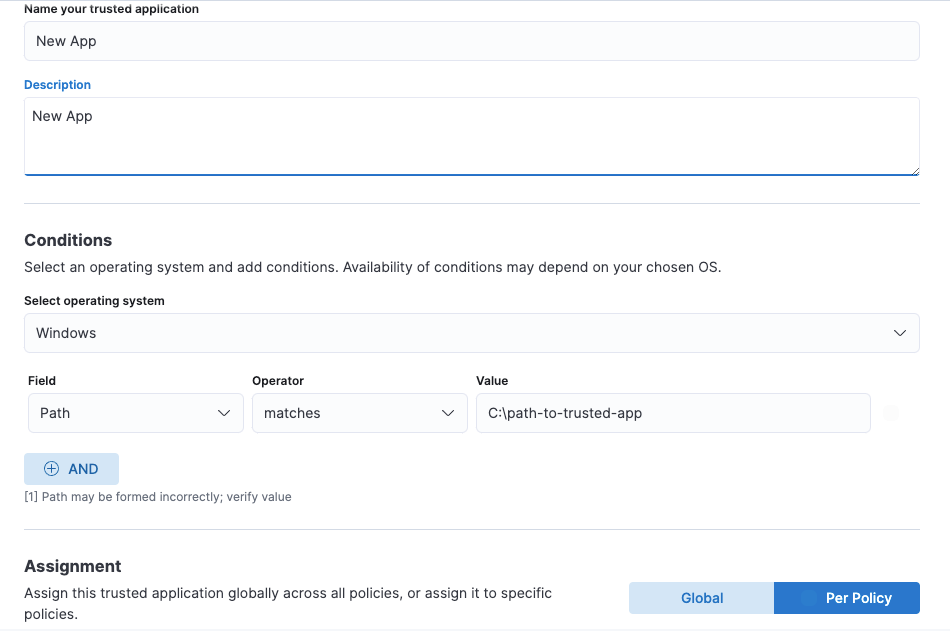
Trusted applications enhancements
You can now configure trusted applications per policy as well as globally, allowing you to configure hosts that may require unique settings. This feature requires a Platinum or Enterprise license. In addition, when configuring trusted applications, you can use the matches operator to include wildcards in file paths.
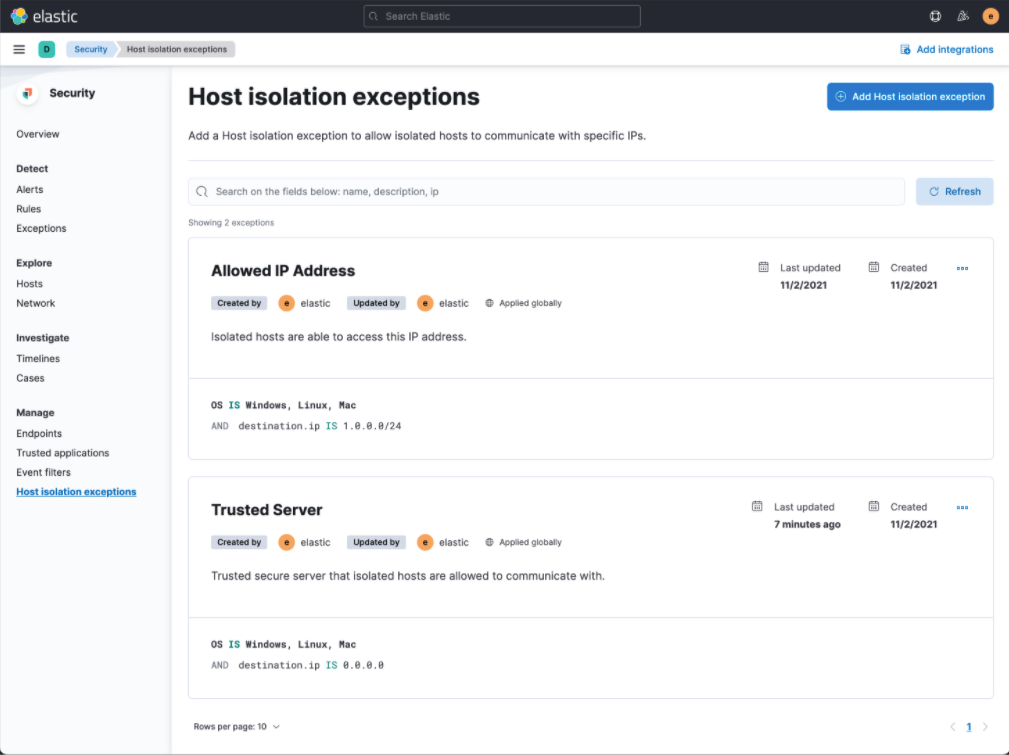
Host isolation exceptions
You can add host isolation exceptions for specific IP addresses that isolated hosts are still allowed to communicate with, even when blocked from the rest of your network.
Detection rule enhancements
- When exporting or importing detection rules, actions are now included.
- The default query for indicator match rules has been updated to check the indicator index patterns for matched indicators that have occurred within the past 30 days.
- 38 new prebuilt rules.
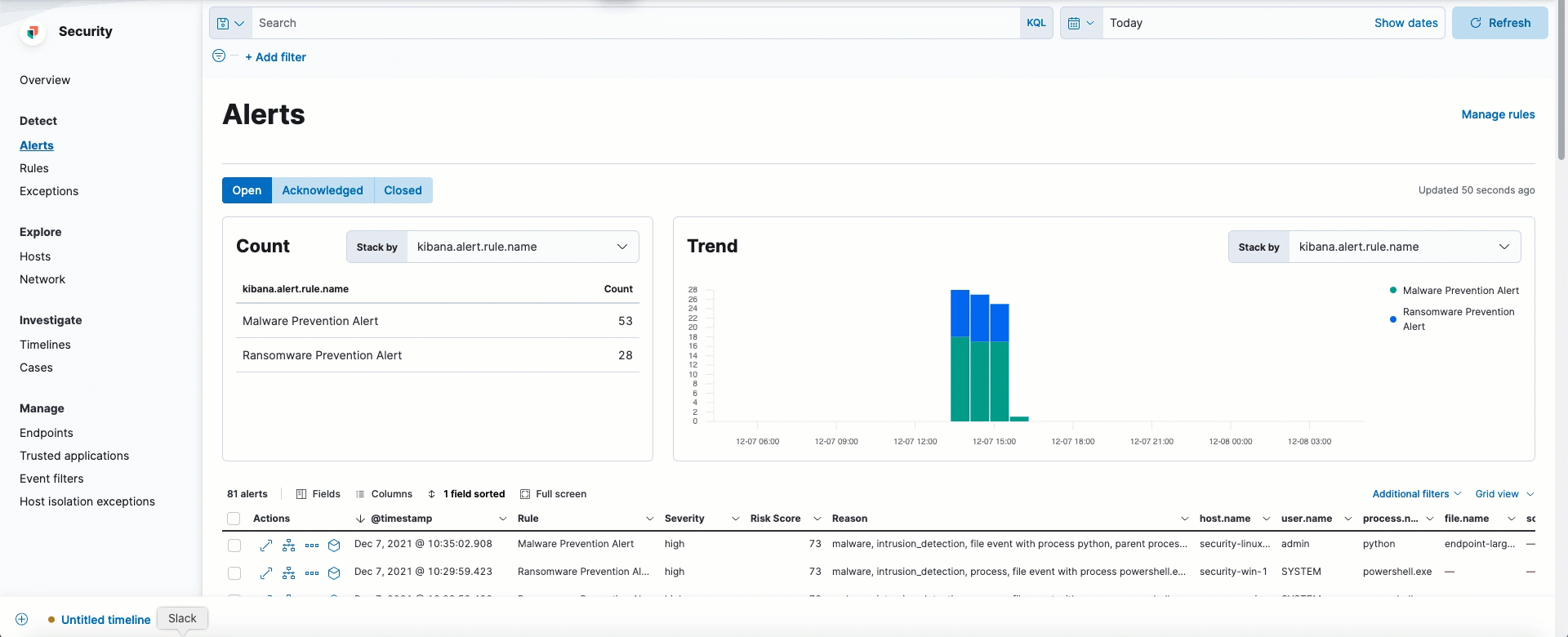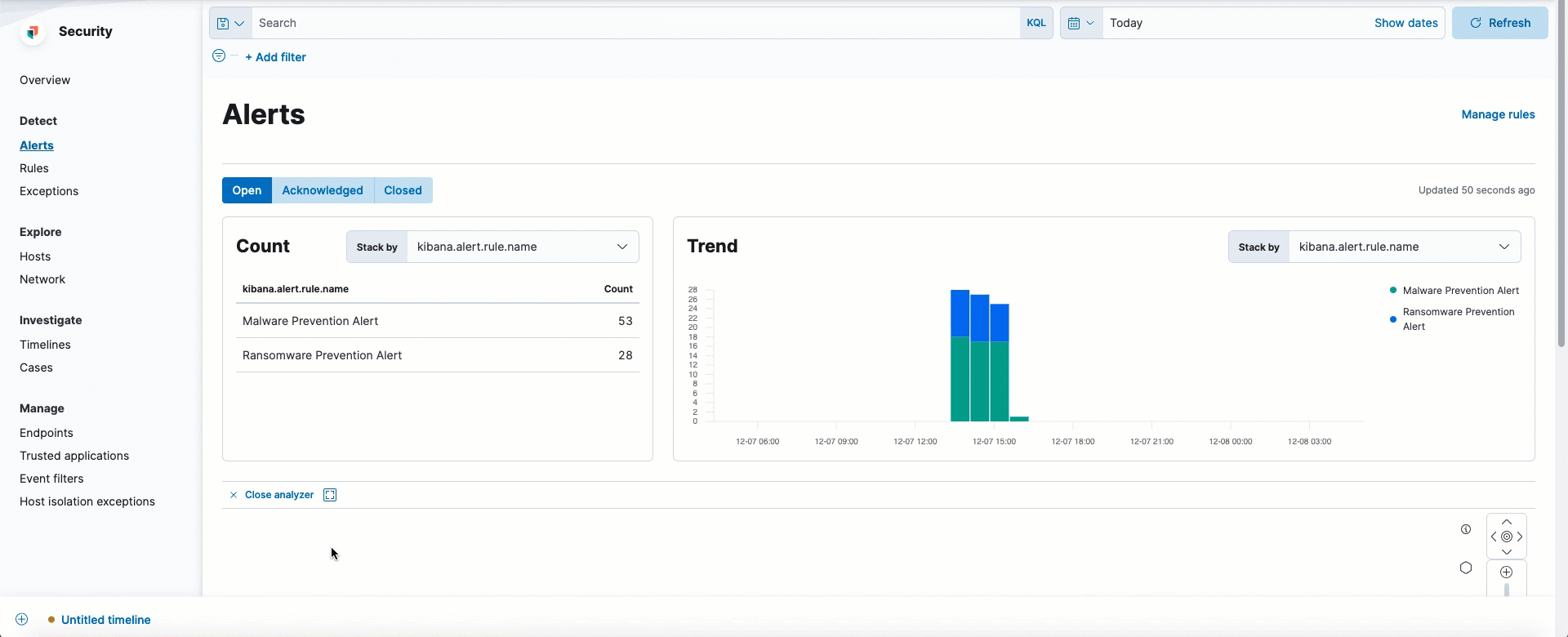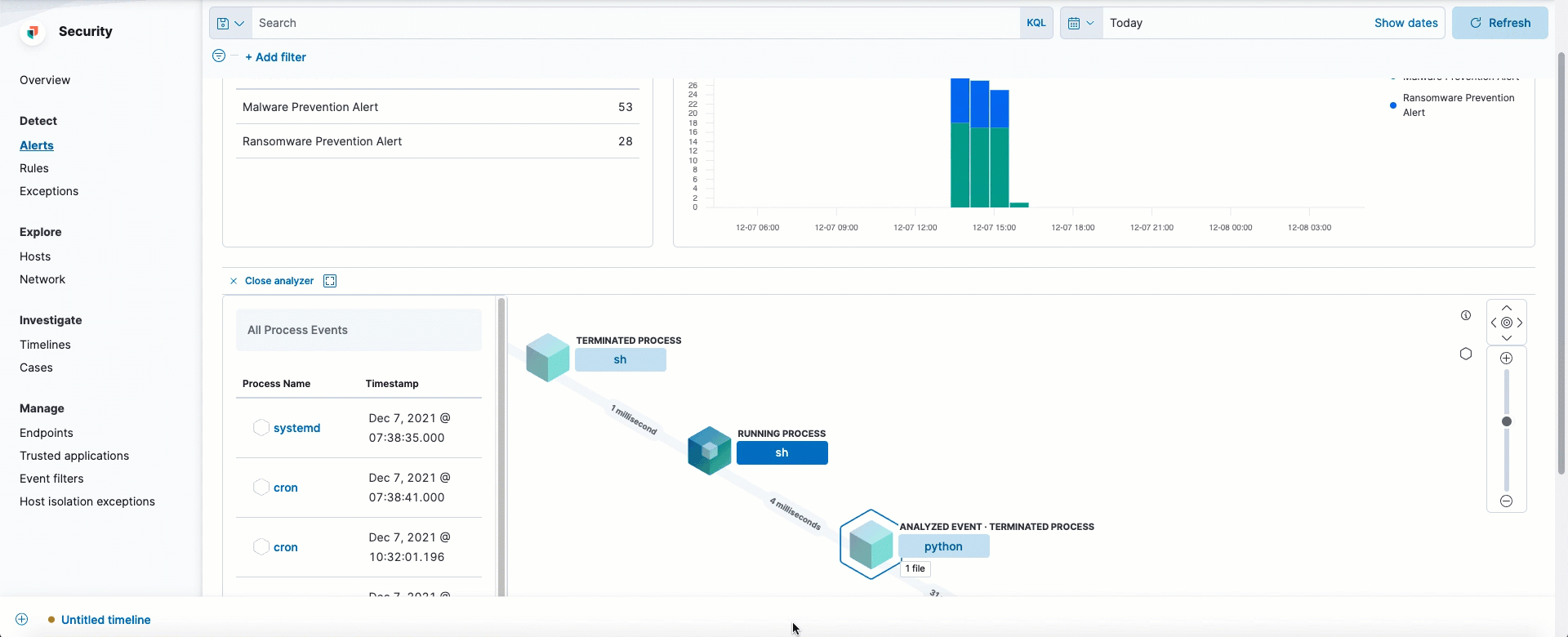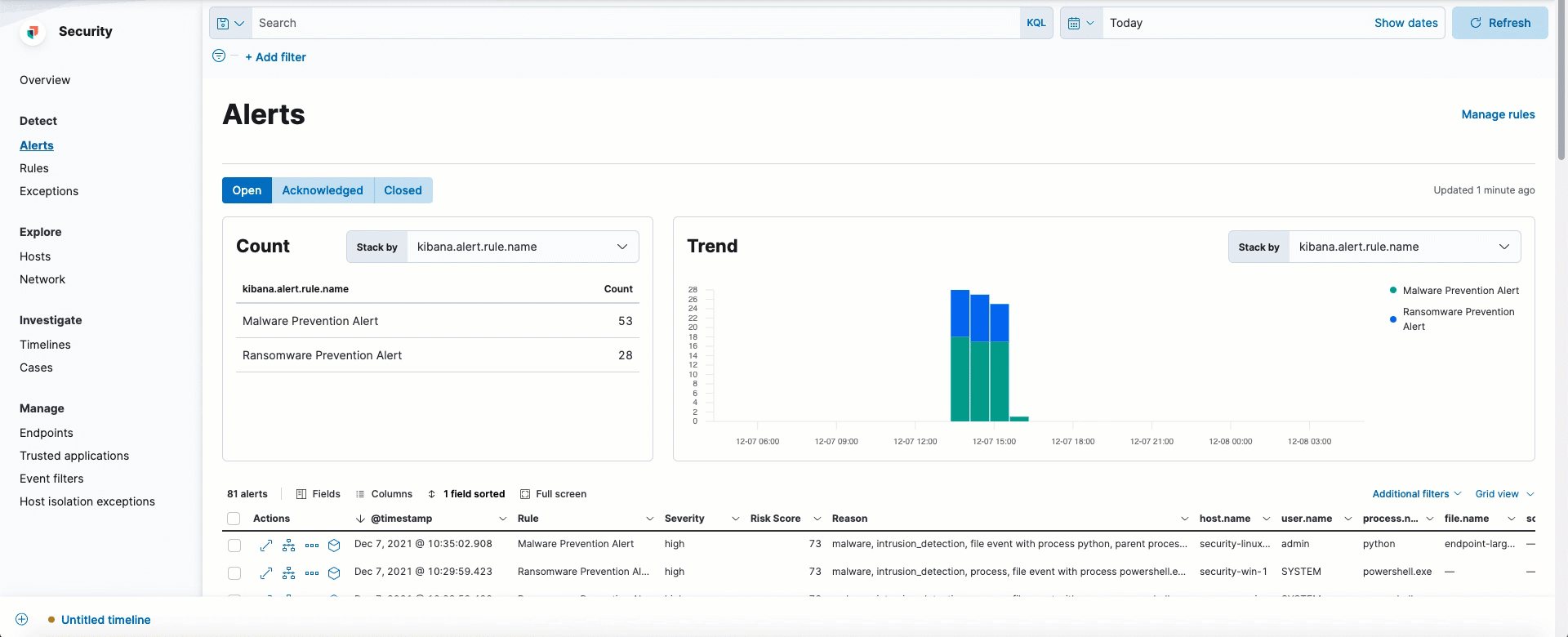
Easily view events that can be analyzed in the Alerts table
Alerts that can be opened in the visual event analyzer are denoted by the Analyze event button.

This option now appears as a visible inline action, whereas previously it was only accessible from the overflow menu.
New ServiceNow integrations
This release delivers certified applications for ServiceNow Security Operations (SecOps) and ServiceNow IT Service Management (ITSM), plus a new connector for ServiceNow IT Operations Management (ITOM).
- Elastic + ServiceNow SecOps maximizes practitioner efficiency with security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR).
- Elastic + ServiceNow ITSM coordinates the workload and processes of modern IT teams.
- Elastic + ServiceNow ITOM maximizes uptime by powering proactive IT operations with machine learning.
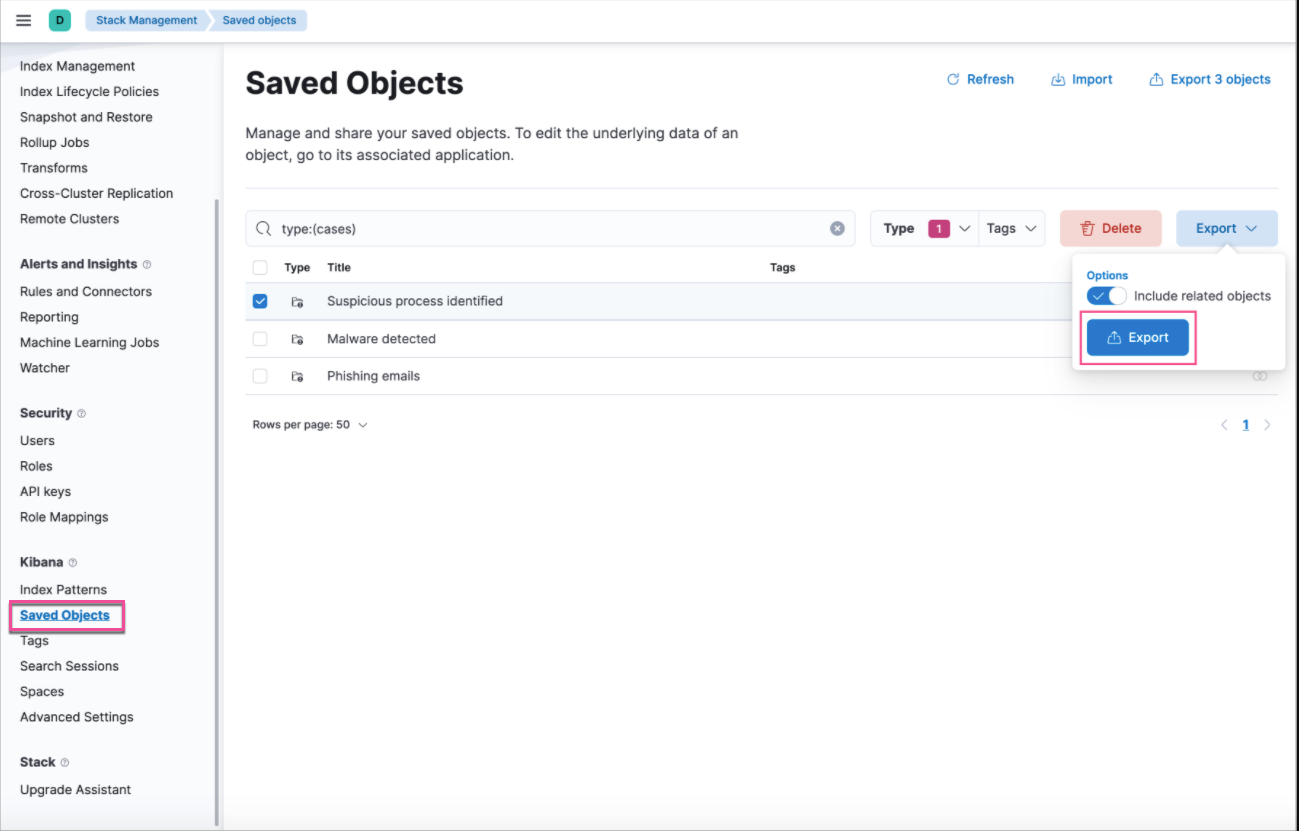
Exporting and importing cases as saved objects
You can now export and import cases as saved objects using the Kibana Saved Objects UI.
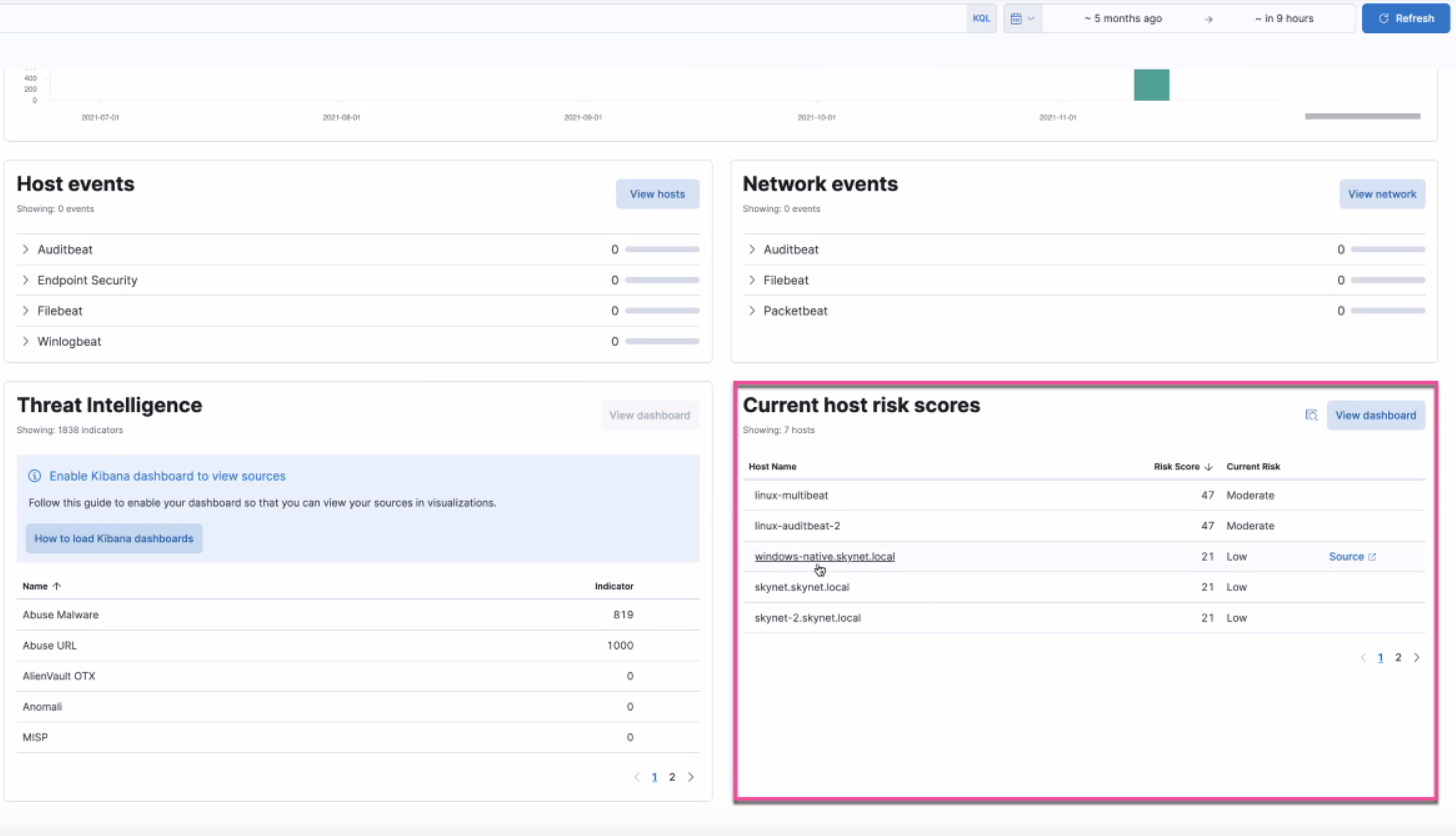
Experimental feature: Host Risk Score data
editThe Host Risk Score feature highlights risky hosts from within your environment. It utilizes a transform with a scripted metric aggregation to calculate host risk scores based on detection rule alerts with an "open" status within a 5-day window. The transform runs hourly to update the score as new detection rule alerts are generated. Each host risk score is normalized to a scale of 0 to 100.