Configure and install Elastic Endpoint integration
editConfigure and install Elastic Endpoint integration
editLike other Elastic integrations, Endpoint Security can be integrated into the Elastic Agent through Fleet. Upon configuration, the integration allows the Elastic Agent to monitor for events on your host and send data to the Elastic Security app.
To configure the Endpoint integration on the Elastic Agent, you must have permission to use Fleet in Kibana.
Before you begin
editDepending on the macOS version you’re using, macOS requires that you give full disk access to different kernels, system extensions, or files. See Enable Full Disk Access for more information.
Add Elastic Endpoint integration
edit-
In Kibana, select Security > Administration. If this is not your first time using Elastic Security, select Fleet > Integrations and search for "Endpoint Security".
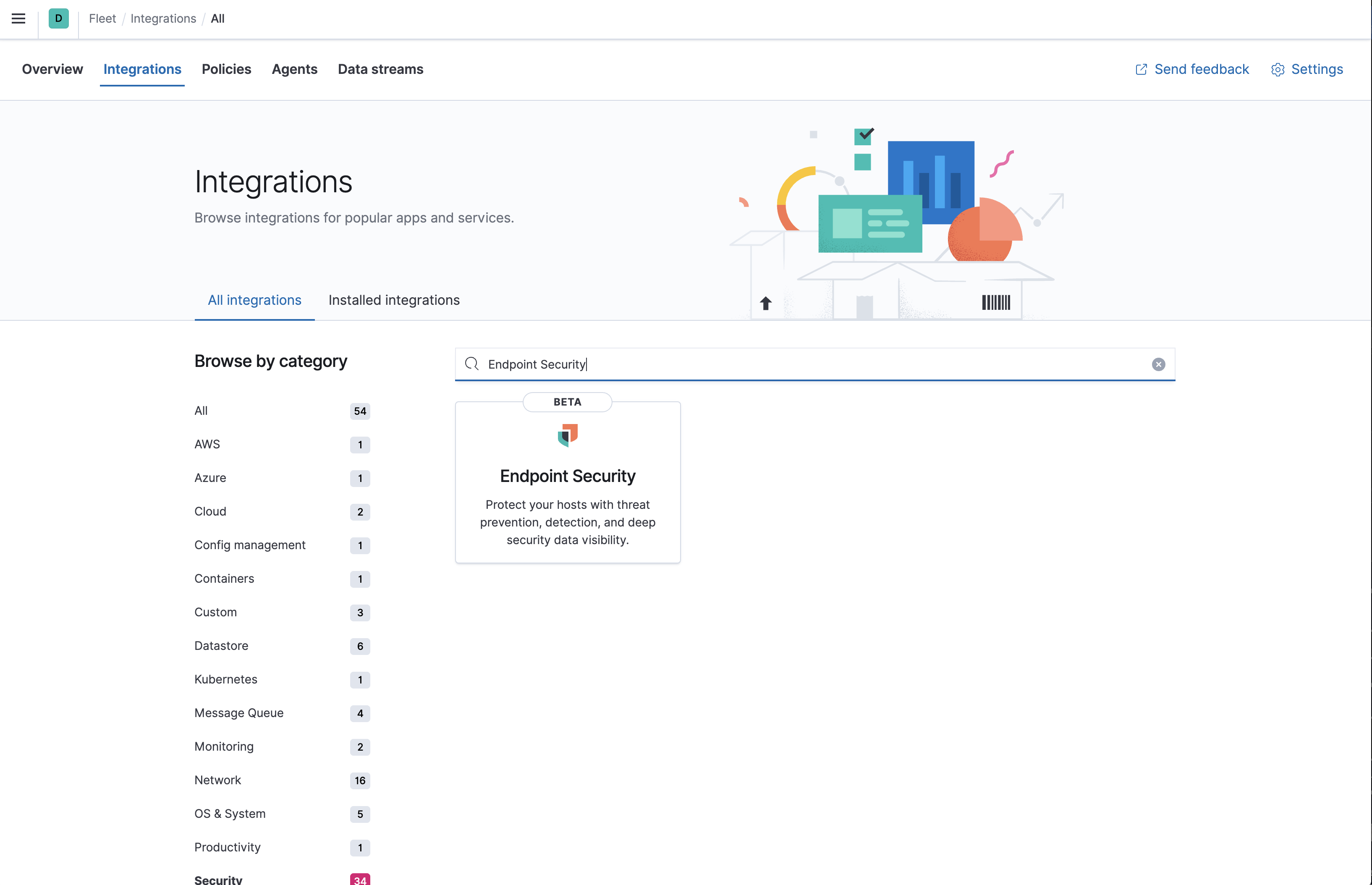
- On the Administration page of the Elastic Security app or the Endpoint Security integration page in Fleet, select Add Endpoint Security. The integration configuration page appears.
- Select a configuration for the Elastic Agent. You can use either the Default config, or add security integration to a custom or existing configuration. For more details on Elastic Agent configuration settings, see Configuration settings.
-
Configure the Endpoint Security integration with a name and optional description. When the configuration is complete, select Save integration. Kibana redirects you back to the administration section of the Elastic Security app.
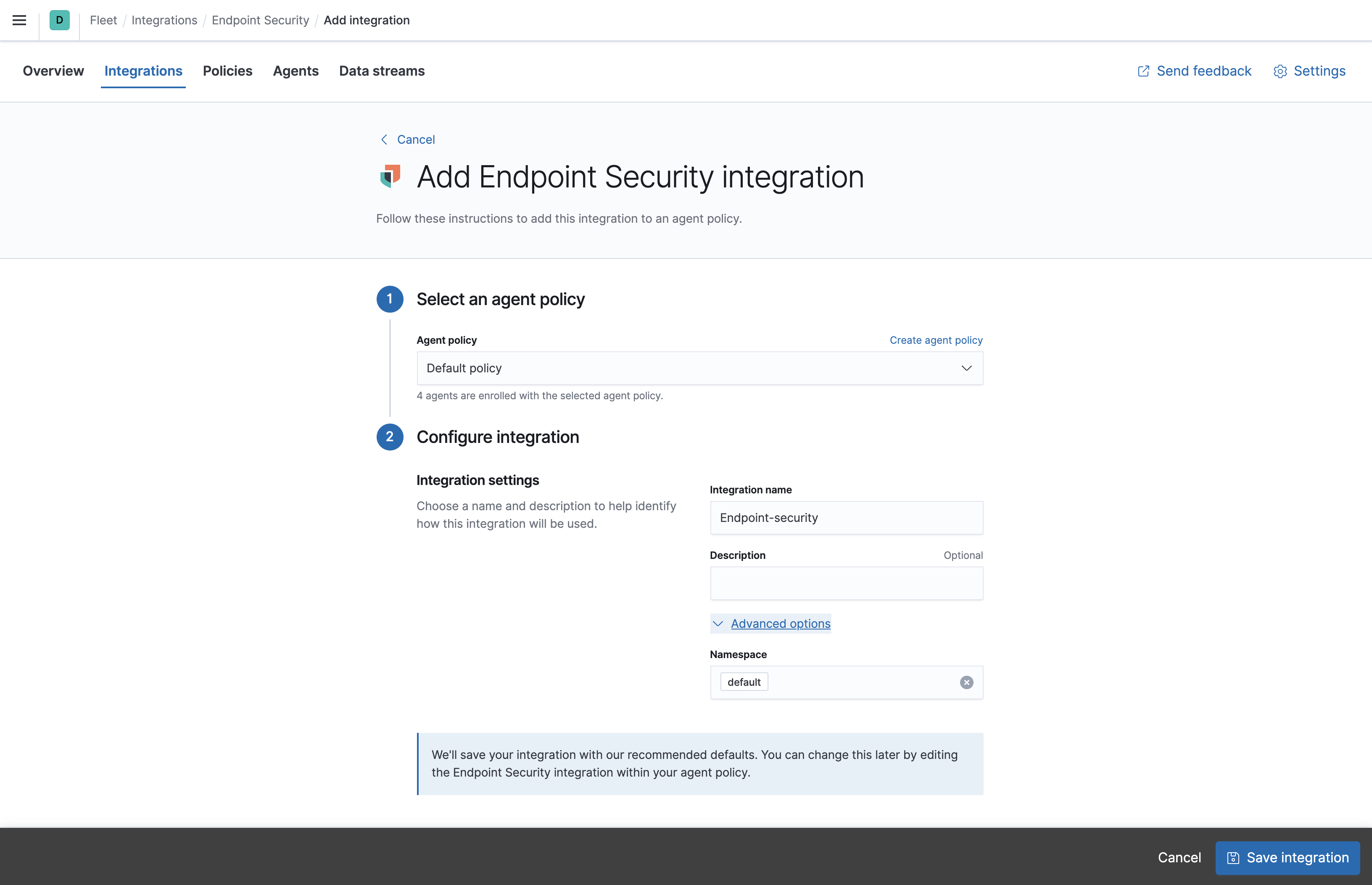
- On the "Enable Endpoint Security" on your Agent’s page, select the name of your new integration. To enroll your agents with Endpoint Security, select Enroll Agent.
- Kibana redirects you back to Fleet to add the Elastic Agent to your host.
Configure and enroll the Elastic Agent
editWhen integrating with the Elastic Agent, Endpoint Security requires enrollment through Fleet to enable the integration.
Endpoint Security cannot be integrated with an Elastic Agent in Standalone mode.
-
Go to Fleet. Select Overview > Add agent.
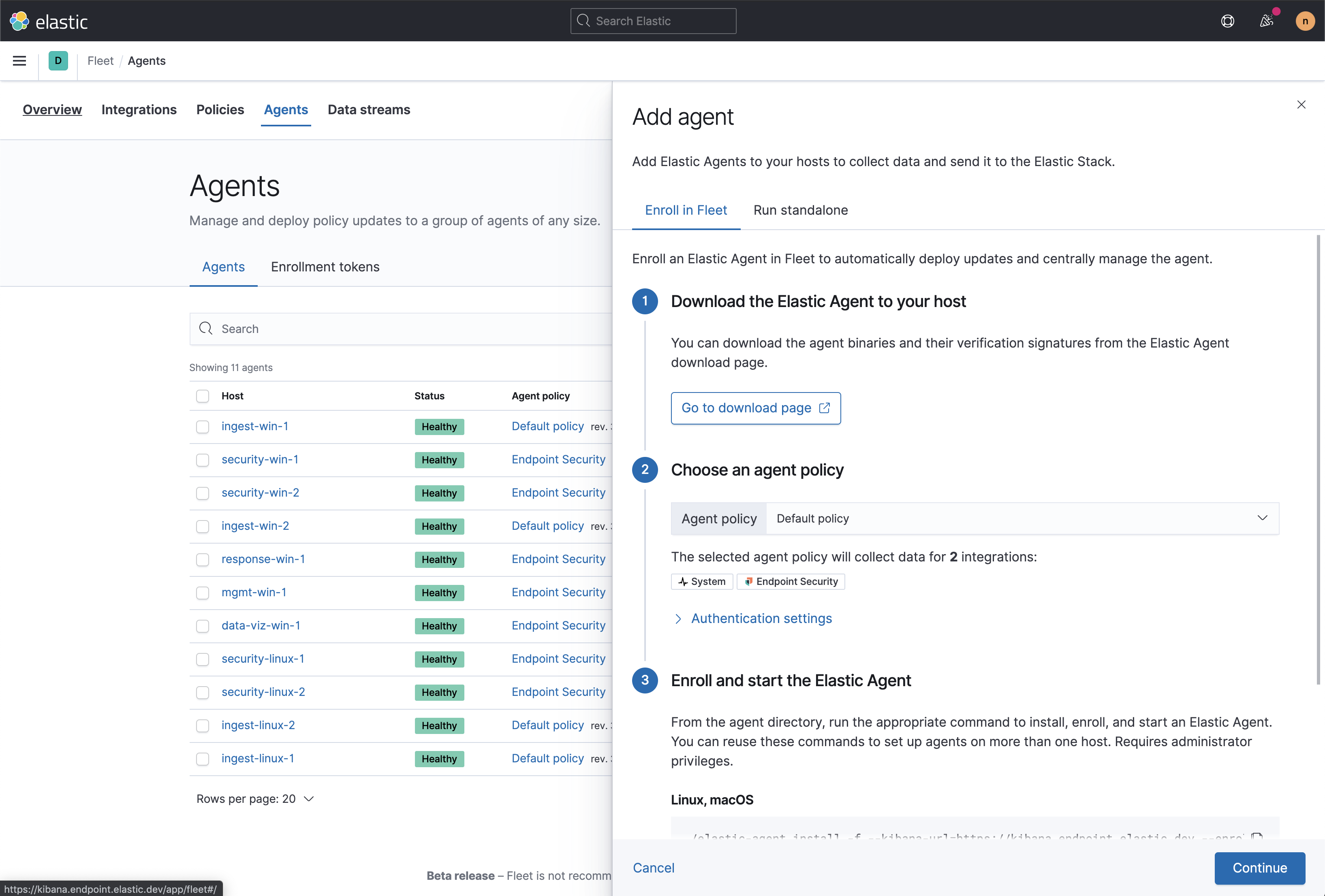
- In the Add agent pane of the Configurations section, download the Elastic Agent on your host’s machine.
-
After the download is complete, select an agent configuration. The selected integrations should include Endpoint Security.
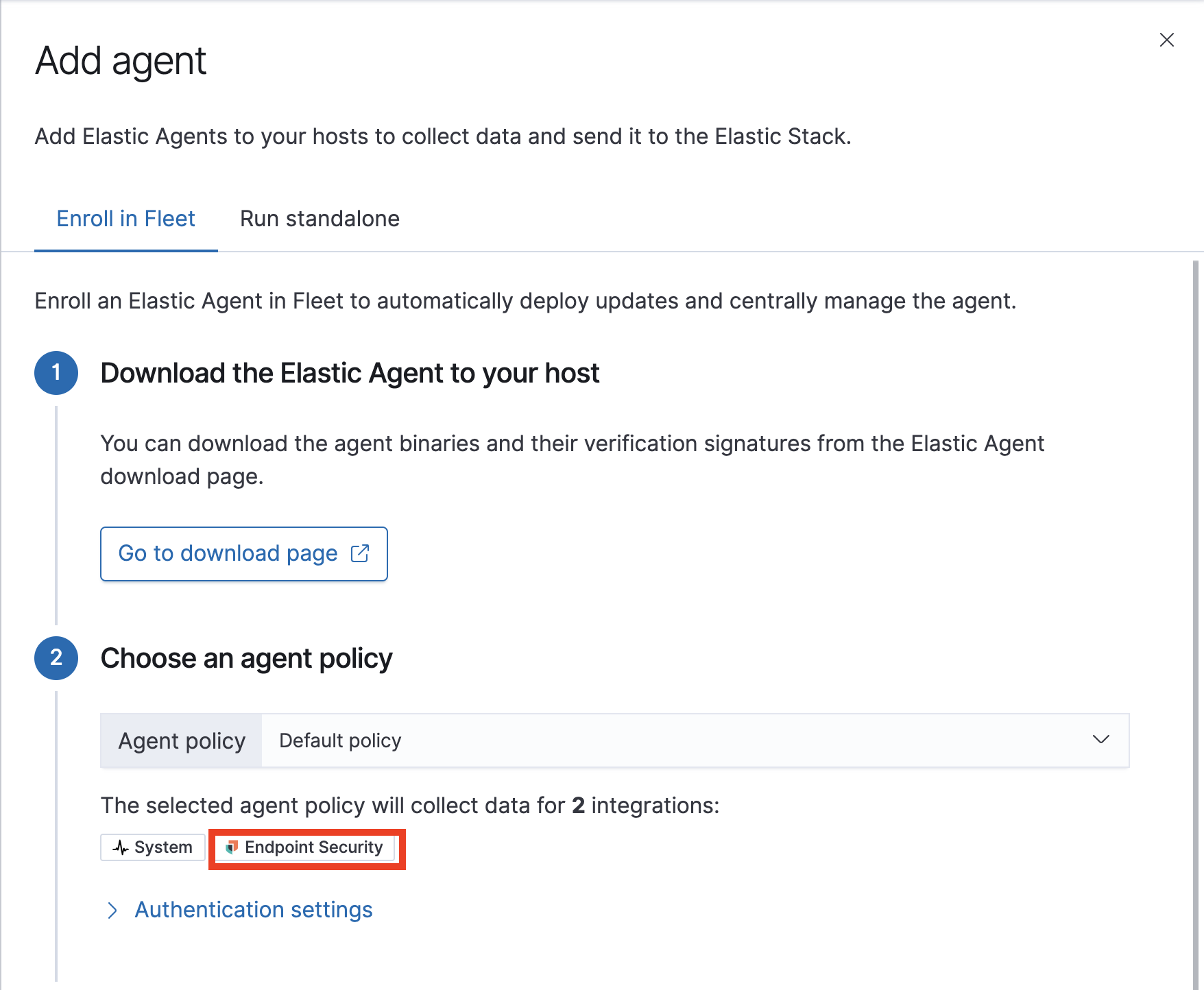
- After the Elastic Agent is installed on your host machine, open a command-line interface, and navigate to your Agent’s directory. Copy the commands from Fleet for your OS to enroll and run the Agent.
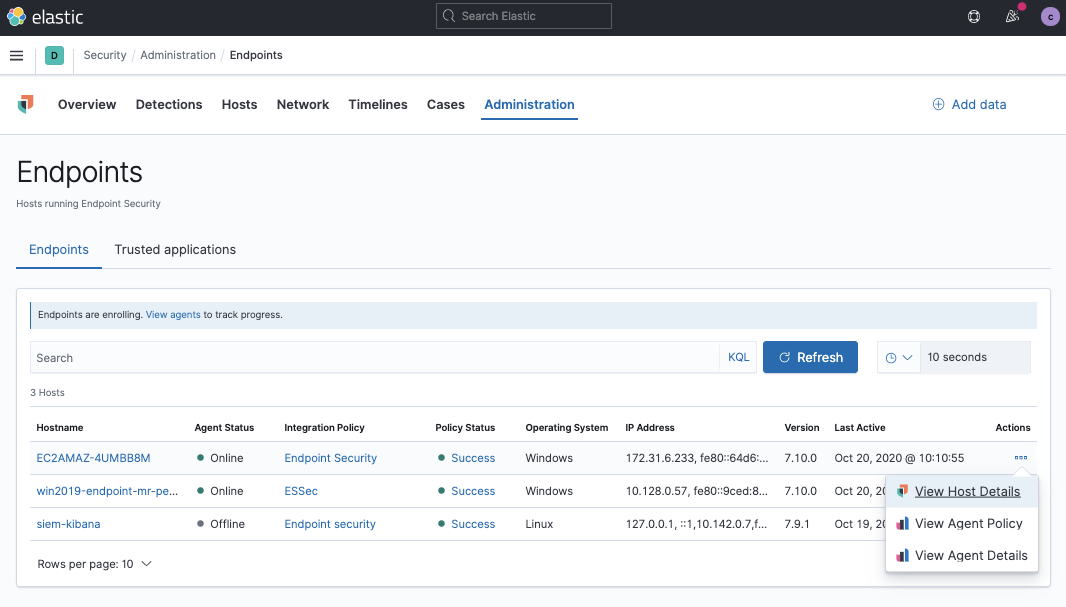
After you have enrolled the Elastic Agent on your host, select Continue. The host now appears in the Endpoints list, located on the Administration page in the Elastic Security app.
To unenroll an agent from your host, see Unenroll Elastic Agent.
Enable Elastic Endpoint kernel
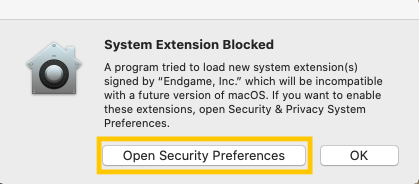
editWhen running the Elastic Agent with endpoint integrated on macOS 10.13, 10.14 and 10.15, you will be prompted to approve a kernel extension from "Endgame, Inc". To approve the extension:
Endgame Sensor users can approve the kernel the same way for the Elastic Endgame app.
-
Select Open Security Preferences. The Security and Privacy window opens.
-
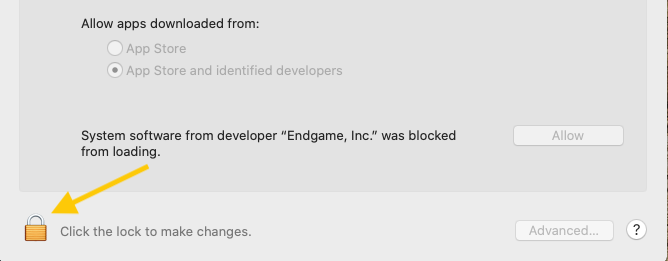
Select the Lock icon at the bottom left of the window to make changes to your security settings.
-
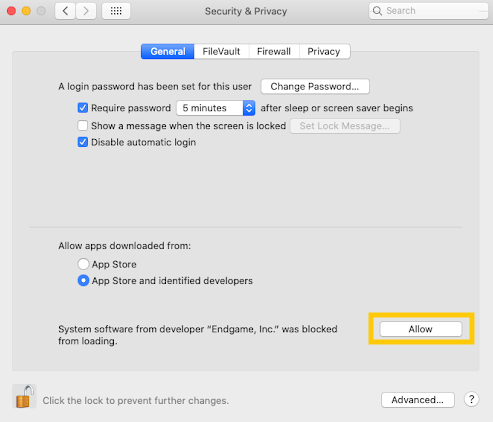
Allow "Endgame, Inc" by selecting the Allow button.
If the prompt does not appear because you’re using a version earlier than macOS Big Sur (11.0), enable the extension by doing the following:
- Open a Terminal application.
-
Enter
kextload /Library/Extension/kendpoint.kext. Prepend the command withsudoif necessary. -
To confirm the kernel extension has loaded, enter
kextstat | grep co.elastic.kendpoint. -
You should receive an output similar to
149 0 0xffffff7f82e7b000 0x21000 0x21000 co.elastic.kendpoint (7.11.0) BD152A57-ABD3-370A-BBE8-D15A0FCBD19A <6 5 2 1>. If you receive this output, the kernel extension is enabled.
Configure an Integration Policy (optional)
editAfter the Elastic Agent is installed successfully, malware prevention and ransomware prevention (a Platinum+ license feature) are automatically enabled on protected hosts. If needed, you can update the Integration Policy to configure malware protection, ransomware protection, event collection, and antivirus settings to meet your company’s security needs.
To access the Integration Policy:
- In the Elastic Security app, select the Administration tab to view the Endpoints list. Remember that you must have admin permissions in Kibana to access this page.
- From the Integration Policy column, select the Policy you want to configure. The Integration Policy Configuration page appears.
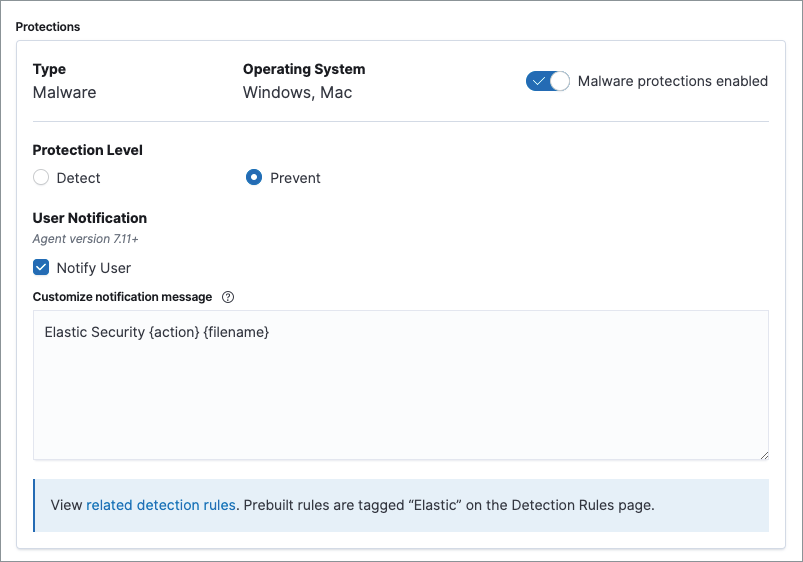
Malware protection
editMalware prevention on the Elastic Agent detects and stops malicious attacks by using a machine learning model that looks for static attributes to determine if a file is malicious or benign.
By default, malware protection is enabled on Windows and macOS hosts. To disable malware protection, switch the Malware protections enabled toggle off. Malware protection levels are as follows:
- Detect: Detects malware on the host and generates an alert. The agent will not block malware. You must pay attention to and analyze any malware alerts that are generated. Notifications do not appear by default. Select the Notify User option to enable them.
-
Prevent (Default): Detects malware on the host, blocks it from executing, and generates an alert. Notifications appear by default. Deselect the Notify User option to disable them.
Platinum and Enterprise customers can customize these notifications using the
Elastic Security {action} {filename}syntax.
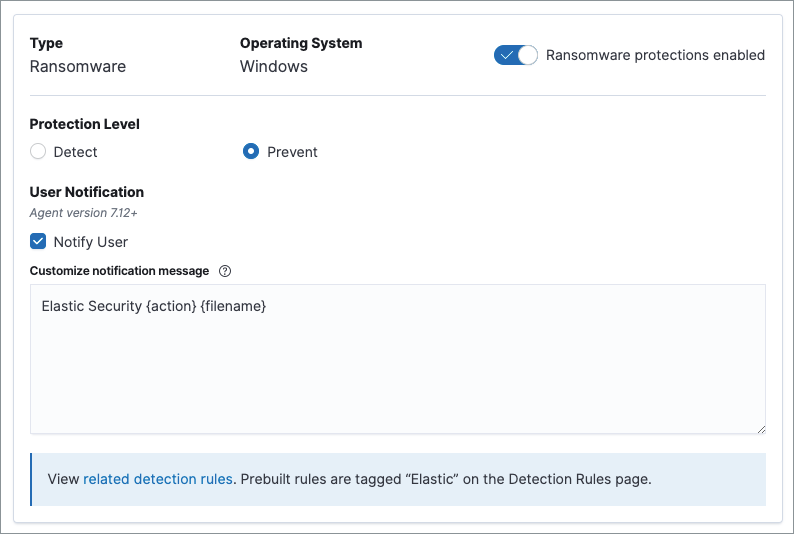
Ransomware protection
editBehavioral ransomware prevention on the Elastic Agent detects and stops ransomware attacks on Windows systems by analyzing data from low-level system processes, and is effective across an array of widespread ransomware families — including those targeting the system’s master boot record.
Ransomware protection is a paid feature and is enabled by default if you have a Platinum or Enterprise license. If you upgrade to a Platinum+ license from Basic or Gold, ransomware protection will be disabled by default.
Ransomware protection levels are as follows:
- Detect: Detects ransomware on the host and generates an alert. The Elastic Agent will not block malware. Select the Notify User option to enable user notifications.
-
Prevent (Default): Detects ransomware on the host, blocks it from executing, and generates an alert. User notifications are enabled by default. Deselect the Notify User option to disable them.
Platinum and Enterprise customers can customize these notifications using the
Elastic Security {action} {filename}syntax.
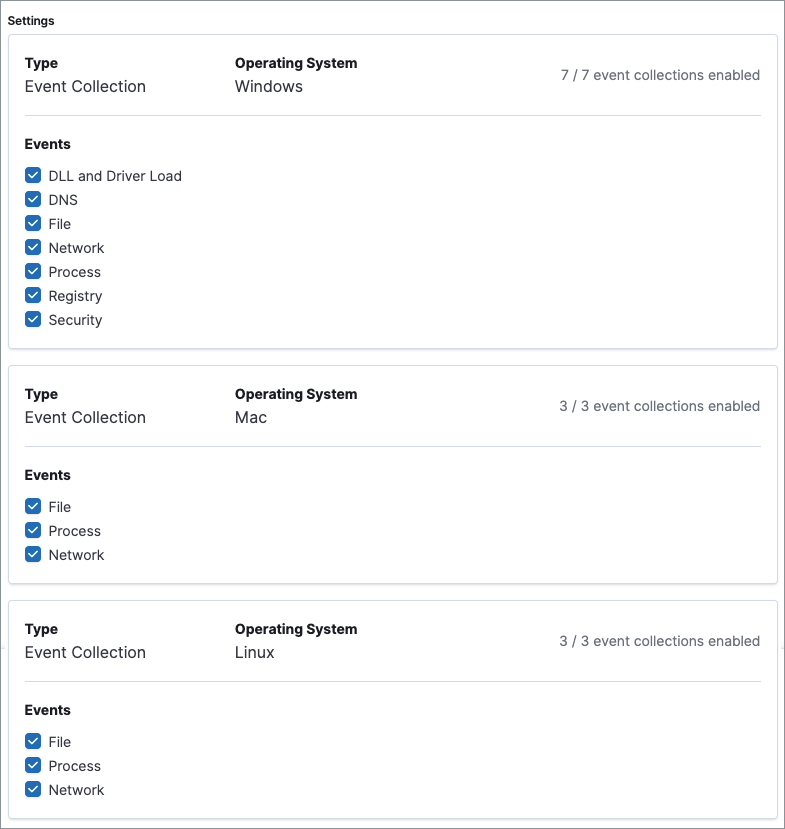
Event collection
editIn the Settings section, review the events that collect data on each operating system. By default, all event data is collected. If you no longer want a specific event to collect data, deselect it.
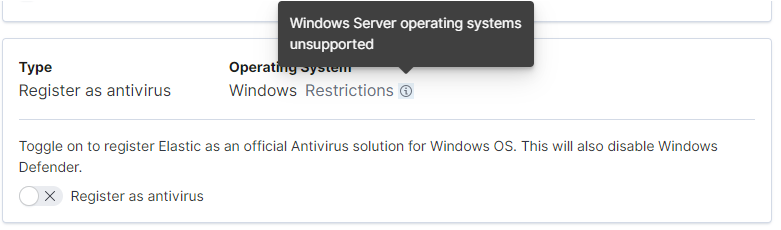
Register Elastic Security as antivirus (optional)
editIf you download the Elastic Agent version 7.10 or later on Windows 7 or above, you can configure Elastic Security as your antivirus software switching the Register as antivirus toggle on.
Advanced Policy settings (optional)
editUsers who have unique configuration and security requirements can select Show Advanced Settings to configure the Policy to support advanced use cases. Hover over each setting to view its description.
Advanced settings are not recommended for most users.
Save the integration
edit- After you have customized your desired Policy settings, click Save.
- On the dialog that appears, click Save and Deploy changes. If successful, a "Success" confirmation appears in the lower-right corner.
Verify Endpoint enrollment
editAfter installing the Elastic Agent, there’s a lag time of several hours between when the Elastic Endpoint begins detecting and sending alerts to Kibana. To ensure that the installation of Elastic Endpoint on your host was successful, go to Administration > Endpoints. A message appears that says, "Endpoints are enrolling. View agents to track progress". Select View agents to check the status of your endpoint enrollment.