Quickstart: Monitor your Kubernetes cluster with Elastic Agent
Serverless Stack
In this quickstart guide, you'll learn how to create the Kubernetes resources required to monitor your cluster infrastructure by using a single command to download, install, and configure Elastic Agent in your Kubernetes cluster.
We recommend using the Elastic Distribution of OpenTelemetry (EDOT) Collector as the preferred way to collect Kubernetes logs, metrics, and application traces using OpenTelemetry.
In Elastic Stack versions 9.0 and 9.1, the quickstart uses Kubectl to install Elastic Agent in a Kubernetes cluster. However, these versions also support using Helm charts, which is now the preferred method for installing Elastic Agent on Kubernetes. If your cluster is on version 9.0 or 9.1, we recommend that you follow the Install Elastic Agent on Kubernetes using Helm guide to deploy Elastic Agent.
- An Elastic Observability Serverless project. To learn more, refer to Create an Observability project.
- A user with the Admin role or higher (required to onboard system logs and metrics). To learn more, refer to Assign user roles and privileges.
- A running Kubernetes cluster with internet access
- Helm version 3.9+ up to and including 3.19.3.
- A running Elastic Stack deployment, either self-managed or orchestrated by platforms like Elastic Cloud Hosted, Elastic Cloud Enterprise, or Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes, with internet access. To get started quickly, try out Elastic Cloud.
- A user with the
superuserbuilt-in role or the privileges required to onboard data.
Expand to view required privileges
- A running Kubernetes cluster with internet access
- Helm version 3.9+ up to and including 3.19.3.
- A running Elastic Stack deployment, either self-managed or orchestrated by platforms like Elastic Cloud Hosted, Elastic Cloud Enterprise, or Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes, with internet access. To get started quickly, try out Elastic Cloud.
- A user with the
superuserbuilt-in role or the privileges required to onboard data.
Expand to view required privileges
- A running Kubernetes cluster with internet access
- Kubectl or Helm version 3.9+ up to and including 3.19.3
The installation command provided by the UI during the quickstart cannot be used as-is to install Elastic Agent in an air-gapped environment. For an air-gapped environment with a self-managed Elastic Stack deployment or orchestrator such as Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes, refer to the following resources:
- Install Elastic Agent air-gapped
- Install Elastic Agent on Kubernetes using Helm
- Deploy Elastic Agent in standalone mode with ECK
- Run Elastic Agent in an air-gapped environment
Go to your Elastic Observability Serverless project, then go to Add data.
In the What do you want to monitor? section, select Kubernetes, and then select Elastic Agent: Logs & Metrics.
To install Elastic Agent on your host, copy and run the install command.
By running this command, you use the Helm package manager to install and configure an instance of the Elastic Agent Helm chart with additional deployment-specific data such as the API key generated by Kibana for the acting user.
The Helm chart also includes a default installation of
kube-state-metrics(KSM), which is required by the Kubernetes integration to collect cluster-level metrics.If you encounter an error during the installation, refer to Troubleshooting.
Details about the install commandThe install command provided by the UI may be similar to:
helm repo add elastic https://helm.elastic.co/ && helm install elastic-agent elastic/elastic-agent --version 9.2.3 -n kube-system --set outputs.default.url=https:<elasticsearch-url>:443 --set kubernetes.onboardingID=<internal-id> --set kubernetes.enabled=true --set outputs.default.type=ESPlainAuthAPI --set outputs.default.api_key=$(echo "<api-key>" | base64 -d)Where:
elastic-agentis the name of the specific installation of the Helm chart, known as release name.elastic/elastic-agentdefines the name of the chart to install, using the format<repository>/<chart-name>.9.2.3 is the version of the Elastic Agent Helm chart to be installed.
kube-systemis the namespace where Elastic Agent is to be installed.--setparameters add configuration values specific to the serverless project, the acting user, and the deployment method of the Helm chart.Refer to Install standalone Elastic Agent on Kubernetes using Helm for a more detailed explanation of the configuration options used.
Go back to the Kubernetes: Logs & Metrics page in Kibana.
There might be a slight delay before data is ingested. When ready, you will see the message We are monitoring your cluster.
Click Explore Kubernetes cluster to navigate to dashboards and explore your data.
In Kibana, go to the Observability overview page, and click Add Data.
In the What do you want to monitor? section, select Kubernetes, and then select Elastic Agent: Logs & Metrics.
To install Elastic Agent on your host, copy and run the install command.
By running this command, you use the Helm package manager to install and configure an instance of the Elastic Agent Helm chart with additional deployment-specific data such as the API key generated by Kibana for the acting user.
The Helm chart also includes a default installation of
kube-state-metrics(KSM), which is required by the Kubernetes integration to collect cluster-level metrics.If you encounter an error during the installation, refer to Troubleshooting.
Details about the install commandThe install command provided by the UI may be similar to:
helm repo add elastic https://helm.elastic.co/ && helm install elastic-agent elastic/elastic-agent --version 9.2.3 -n kube-system --set outputs.default.url=https:<elasticsearch-url>:443 --set kubernetes.onboardingID=<internal-id> --set kubernetes.enabled=true --set outputs.default.type=ESPlainAuthAPI --set outputs.default.api_key=$(echo "<api-key>" | base64 -d)Where:
elastic-agentis the name of the specific installation of the Helm chart, known as release name.elastic/elastic-agentdefines the name of the chart to install, using the format<repository>/<chart-name>.9.2.3 is the version of the Elastic Agent Helm chart to be installed.
kube-systemis the namespace where Elastic Agent is to be installed.--setparameters add configuration values specific to the serverless project, the acting user, and the deployment method of the Helm chart.Refer to Install standalone Elastic Agent on Kubernetes using Helm for a more detailed explanation of the configuration options used.
Go back to the Kubernetes: Logs & Metrics page in Kibana.
There might be a slight delay before data is ingested. When ready, you will see the message We are monitoring your cluster.
Click Explore Kubernetes cluster to navigate to dashboards and explore your data.
In Kibana, go to the Observability UI and click Add Data.
In the What do you want to monitor? section, select Kubernetes, and then select Elastic Agent: Logs & Metrics.
To install Elastic Agent on your host, copy and run the install command.
By running this command, you use
kubectl kustomizeto download a manifest file, inject deployment-specific data such as the API key generated by Kibana for the acting user, and create the Kubernetes resources for Elastic Agent.Go back to the Kubernetes: Logs & Metrics page in Kibana.
There might be a slight delay before data is ingested. When ready, you will see the message We are monitoring your cluster.
Click Explore Kubernetes cluster to navigate to dashboards and explore your data.
After installation is complete and all relevant data is flowing into Elastic, the Visualize your data section allows you to access the Kubernetes Cluster Overview dashboard that can be used to monitor the health of the cluster.
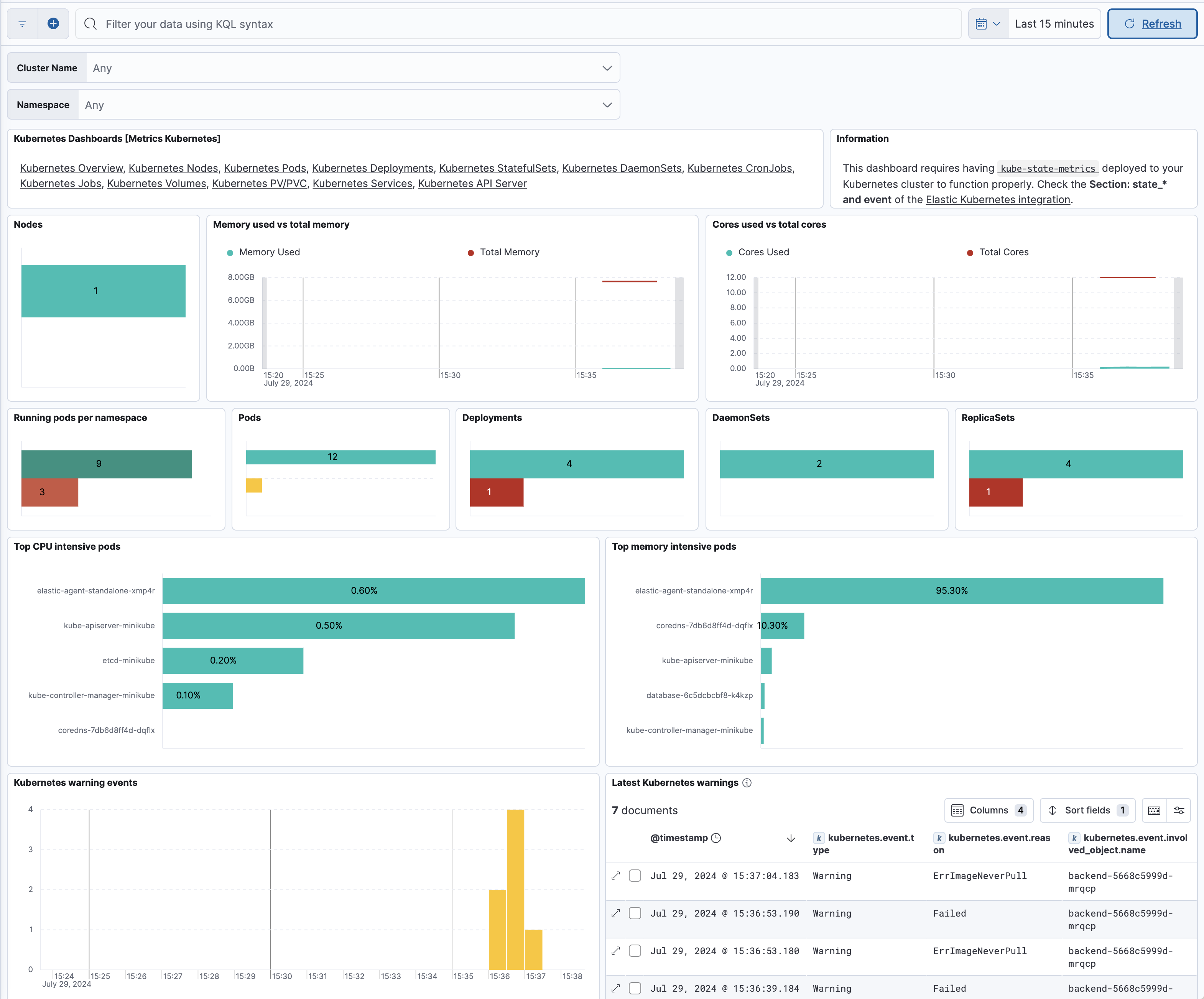
Furthermore, you can access other useful prebuilt dashboards for monitoring Kubernetes resources, for example running pods per namespace, as well as the resources they consume, like CPU and memory.
Refer to Observability overview for a description of other useful features.
To uninstall Elastic Agent and the Kubernetes resources installed with Helm, run:
helm uninstall <release-name> -n <namespace>
- Substitute
<release-name>with the release name and<namespace>with the namespace used in the quickstart command described in the Collect your data section.
If you used the default values from the quickstart, the command would be:
helm uninstall elastic-agent -n kube-system
To uninstall Elastic Agent and the Kubernetes resources installed with Helm, run:
helm uninstall <release-name> -n <namespace>
- Substitute
<release-name>with the release name and<namespace>with the namespace used in the quickstart command described in the Collect your data section.
If you used the default values from the quickstart, the command would be:
helm uninstall elastic-agent -n kube-system
To uninstall Elastic Agent and the Kubernetes resources installed with kubectl:
- Copy the
kubectlquickstart command for installing Elastic Agent described in the Collect your data section. - Replace
| kubectl apply -f-with| kubectl delete -f-, then run the command.
If you're using helm to install Elastic Agent in your Kubernetes cluster, you may encounter an error if kube-state-metrics is already installed in the same namespace where Elastic Agent is to be installed. In this case, add the option --set kube-state-metrics.enabled=false to the install command provided by the UI to skip the installation of kube-state-metrics.
If you're using helm to install Elastic Agent in your Kubernetes cluster and the elastic repository is already configured on your host, replace the helm repo add elastic https://helm.elastic.co/ part of the command provided by the UI with helm repo update elastic to ensure the repository is updated with the latest package information.