Centralized pipeline management is an X-Pack feature that requires a paid X-Pack license. See the Elastic Subscriptions page for information about obtaining a license.
The pipeline management feature in X-Pack centralizes the creation and management of Logstash configuration pipelines. From within the pipeline management UI in Kibana, you can control multiple Logstash instances. You can add, edit, and delete pipeline configurations. On the Logstash side, you simply need to enable configuration management and register Logstash to use the centrally managed pipeline configurations.
The pipeline configurations, along with some metadata, are stored in Elasticsearch. Any changes that you make to a pipeline definition in the UI are picked up and loaded automatically by all Logstash instances registered to use the pipeline. The changes are applied immediately; you do not have to restart Logstash to pick up the changes, as long as Logtash is already registered to use the pipeline.
Before using the pipeline management UI, you must:
- Configure centralized pipeline management.
-
If Kibana is protected with basic authentication, make sure your Kibana user has
the
logstash_adminrole as well as thelogstash_writerrole that you created when you configured Logstash to use basic authentication.
To centrally manage Logstash pipelines:
-
Open Kibana in your browser and go to the Management tab. If you’ve set up configuration management correctly, you’ll see an area for managing Logstash. Click the Pipelines link.
-
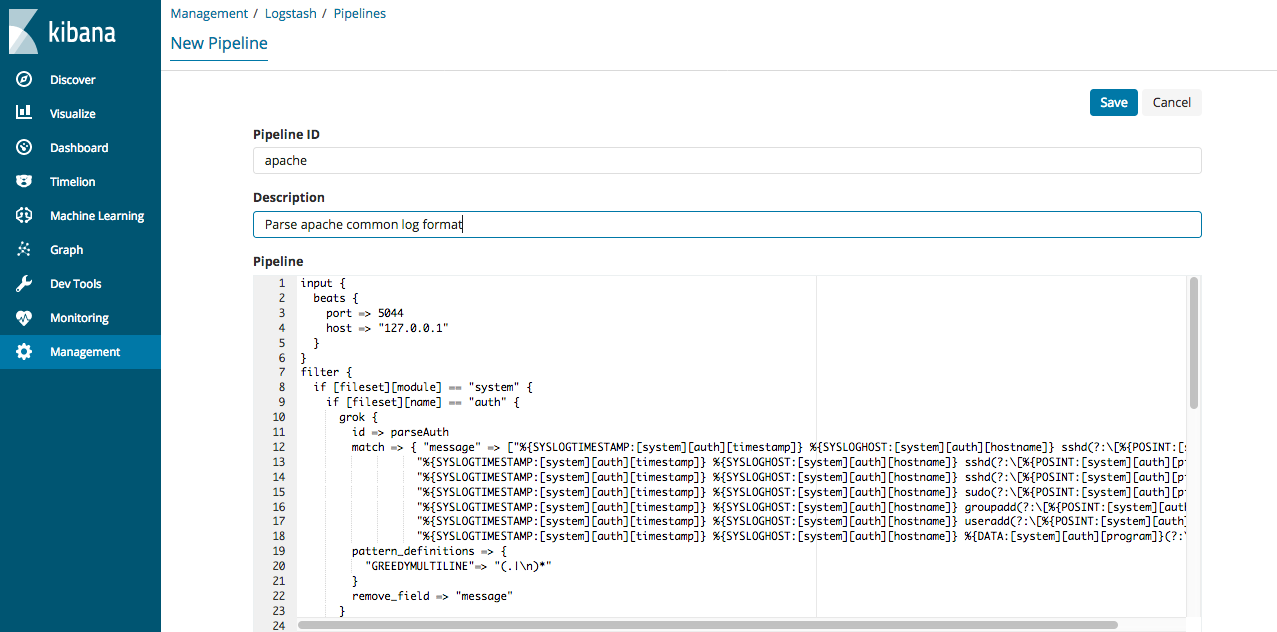
To add a new pipeline, click the Add button and specify values for the following fields:
Pipeline ID
A name that uniquely identifies the pipeline. This is the ID that you used when you configured centralized pipeline management and specified a list of pipeline IDs in the
xpack.management.pipeline.idsetting.Description
A description of the pipeline configuration. This information is for your use.
Pipeline
The pipeline configuration. You can treat the editor in the pipeline management UI like any other editor. You don’t have to worry about whitespace or indentation.
- Click Save.
The pipeline runs on all Logstash instances that are registered to use the pipeline. There is no validation done at the UI level. The UI will save the new configuration, and Logstash will attempt to load it. You need to check the local Logstash logs for configuration errors. If you’re using the Logstash monitoring feature in X-Pack, you can also navigate to the Monitoring tab to check the status of your Logstash nodes.
You can specify multiple pipeline configurations that run in parallel on the same Logstash node.
If you edit a pipeline configuration and save the changes, Logstash reloads the configuration in the background and continues processing events.
If you delete a pipeline (for example, apache) from the UI, Logstash will
attempt to stop the pipeline if it’s running. Logstash will wait until all
events have been fully processed by the pipeline. Before deleting a pipeline,
make sure you understand your data sources because stopping a pipeline may
lead to data loss.