Adding a choropleth layer
editAdding a choropleth layer
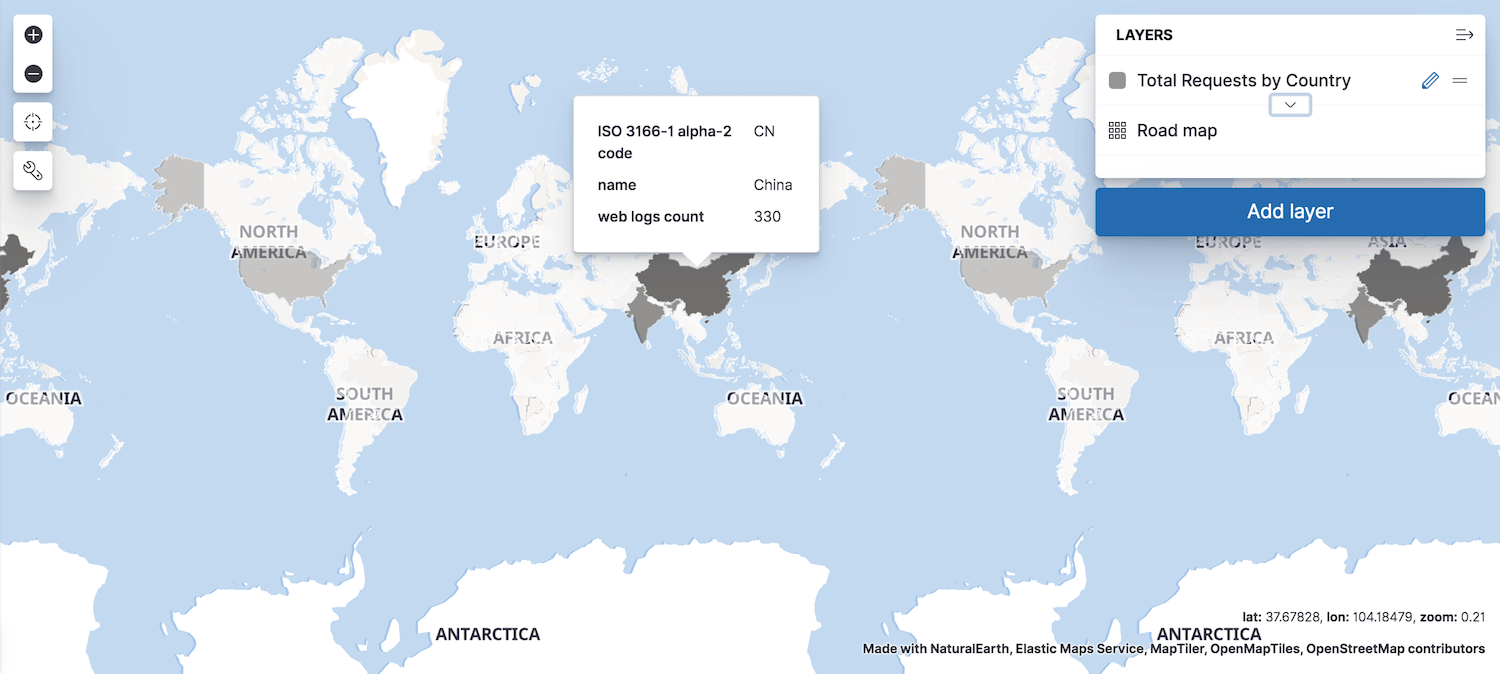
editNow that you have a map, you’ll want to add layers to it. The first layer you’ll add is a choropleth layer to shade world countries by web log traffic. Darker shades symbolize countries with more web log traffic, and lighter shades symbolize countries with less traffic.
Add a vector layer from the Elastic Maps Service source
edit- In the map legend, click Add layer.
- Click the EMS Boundaries data source.
- From the Layer dropdown menu, select World Countries.
- Click the Add layer button.
-
Set Name to
Total Requests by Country. - Set Opacity to 50%.
- Click Add under Tooltip fields.
- In the popover, select ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code and name and click Add.
Join the vector layer with the sample web log index
editYou now have a vector layer containing the world countries.
To symbolize countries by web traffic, you’ll need to augment the world country features with the count of Elasticsearch weblog documents originating from each country.
To do this, you’ll create a term join to link the vector source World Countries to
the Elasticsearch index kibana_sample_data_logs on the shared key iso2 = geo.src.
-
Click plus
 next to the Term Joins label.
next to the Term Joins label.
- Click Join --select--
- Set Left field to ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code.
- Set Right source to kibana_sample_data_logs.
- Set Right field to geo.src.
- Click and use metric count.
- Set Custom label to web logs count.
Set the layer style
editAll of the world countries are still a single color because the layer is using static styling. To shade the world countries based on which country is sending the most requests, you’ll need to use data driven styling.
- Under Fill color, change the selected value from Solid to By value.
- In the field select input, select web logs count.
- Select the grey color ramp.
- Under Border color, change the selected color to white.
-
Click Save & close.
Your map now looks like this: