IMPORTANT: No additional bug fixes or documentation updates
will be released for this version. For the latest information, see the
current release documentation.
Fleet
edit
IMPORTANT: This documentation is no longer updated. Refer to Elastic's version policy and the latest documentation.
Fleet
editFleet in Kibana enables you to add and manage integrations for popular services and platforms, as well as manage Elastic Agent installations in standalone or Fleet mode.
Standalone mode requires you to manually configure and manage the agent locally.
Fleet mode offers several advantages:
- A central place to configure and monitor your Elastic Agents.
- An overview of the data ingest in your Elasticsearch cluster.
- Multiple integrations to collect and transform data.
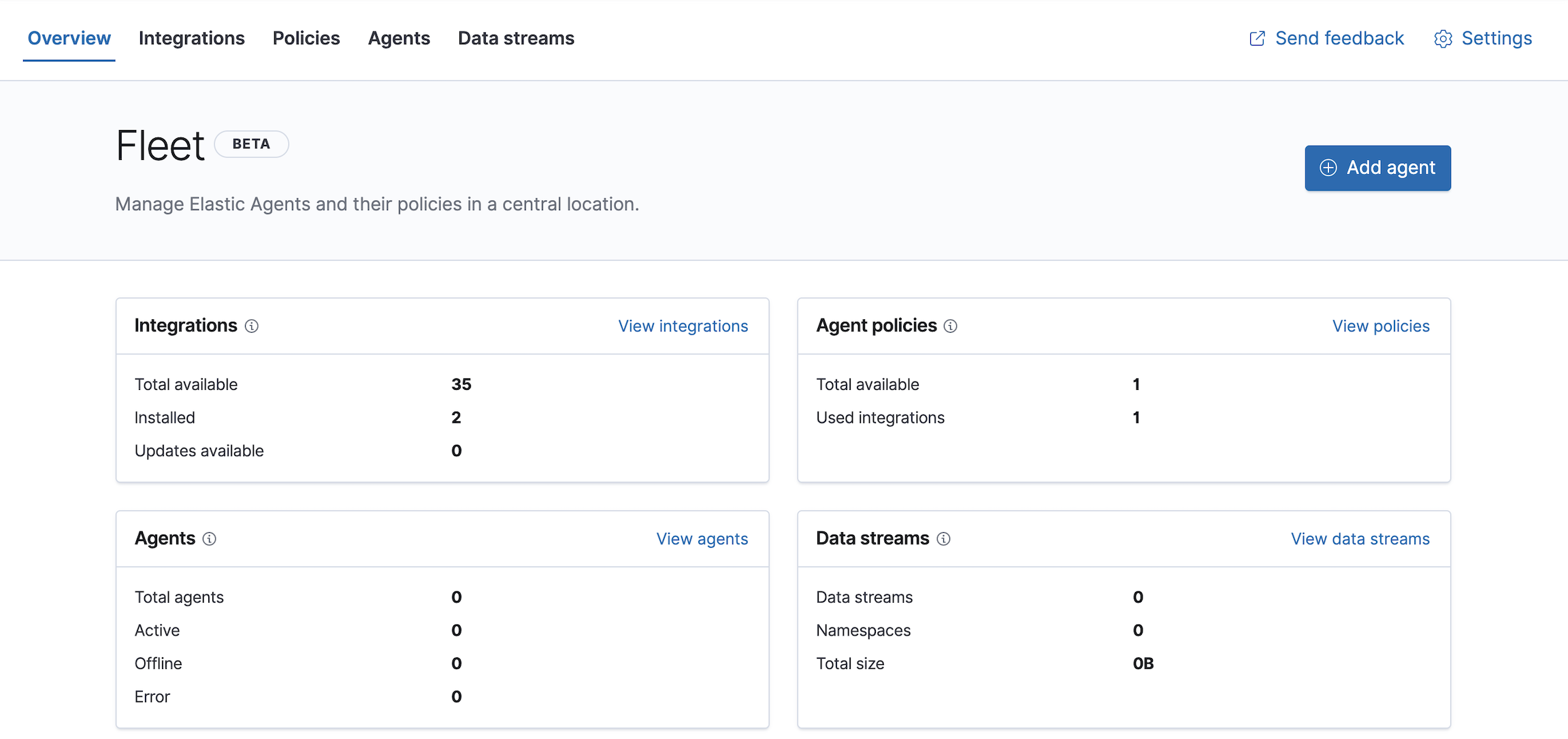
Get started
editTo get started with Fleet, refer to the Fleet docs.