WARNING: Version 6.2 of Kibana has passed its EOL date.
This documentation is no longer being maintained and may be removed. If you are running this version, we strongly advise you to upgrade. For the latest information, see the current release documentation.
Viewing Monitoring Data in Kibana
editViewing Monitoring Data in Kibana
editMonitoring is automatically enabled when you install X-Pack into Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana. You can also enable monitoring in Beats. By default, the monitoring agents on Elasticsearch index data within the same cluster.
If you have a dedicated monitoring cluster, the information is accessible even if the Elasticsearch cluster you’re monitoring is not. You can send data from multiple clusters to the same monitoring cluster and view them all through the same instance of Kibana. For more information, see
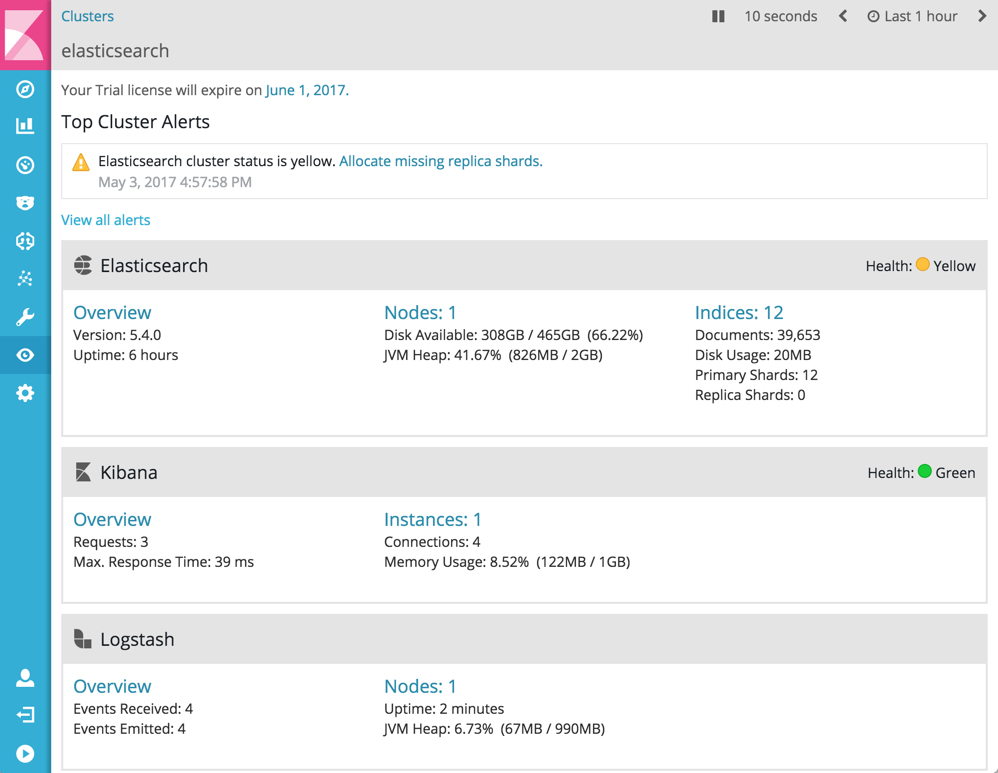
To view and analyze the health and performance of Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, and Beats:
- Install X-Pack in Elasticsearch. If you want to use a separate monitoring cluster, see Monitoring in a Production Environment.
- Install X-Pack in Kibana and configure monitoring.
- Install X-Pack in Logstash and configure monitoring.
- Configure monitoring in Auditbeat, Filebeat, Heartbeat, Metricbeat, Packetbeat, and Winlogbeat.
-
Open Kibana in your web browser and log in. If you are running Kibana
locally, go to
http://localhost:5601/. To access Kibana and view the monitoring dashboards, you must log in as a user who has thekibana_userandmonitoring_userroles. - Click Monitoring in the side navigation. This displays any cluster alerts that require your attention and a summary of the available monitoring metrics for Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, and Beats. To view additional information, click the Overview, Nodes, Indices, or Instances links.
Watcher must be enabled to view cluster alerts. If you have a Basic license, Top Cluster Alerts are not displayed.