WARNING: Version 6.2 of APM Server has passed its EOL date.
This documentation is no longer being maintained and may be removed. If you are running this version, we strongly advise you to upgrade. For the latest information, see the current release documentation.
Install and run Elastic APMedit
To get started using Elastic APM, you need to have:
- an Elasticsearch cluster and Kibana (version 5.6 or above)
- a running APM Server process
- APM agents installed in your services
For information about setting up an Elasticsearch cluster, see the Elasticsearch Getting Started. To view the collected data, you need Kibana.
The following sections show how to get started quickly with Elastic APM on a local machine.
Install and run APM Serveredit
First, download APM Server for your operating system and extract the package.
In a production environment, you would put APM Server on it’s own machines, similar to how you run Elasticsearch. You can run it on the same machines as Elasticsearch, but this is not recommended, as the processes will be competing for resources.
To start APM Server, run:
./apm-server -e
You should see APM Server start up. It will try to connect to Elasticsearch on localhost port 9200 and expose an API to agents on port 8200. You can change the defaults by supplying a different addresses on the command line:
./apm-server -e -E output.elasticsearch.hosts=ElasticsearchAddress:9200 -E apm-server.host=localhost:8200
Or you can update the apm-server.yml configuration file to change the defaults.
apm-server:
host: localhost:8200
output:
elasticsearch:
hosts: ElasticsearchAddress:9200
If you are using an X-Pack secured version of Elastic Stack, you need to specify credentials in the config file before you run the commands that set up and start APM Server. For example:
output.elasticsearch: hosts: ["ElasticsearchAddress:9200"] username: "elastic" password: "elastic"
Secure access to the APIedit
The HTTP API exposed by APM Server listens on localhost and port 8200 by default.
If you change the listen address from localhost to something that is accessible from outside of the machine,
we recommend setting up firewall rules to ensure that only your own systems can access the API.
Alternatively,
you can use the secret token and TLS to secure access to APM Server API.
Install the Kibana dashboardsedit
APM Server comes with predefined Kibana dashboards and index templates for the APM data. To install those run the following command:
./apm-server setup
Due to a bug in Kibana 6.0.0.-rc2 the dashboards don’t work in Kibana 6.0.0-rc2.
See an example screenshot of a Kibana dashboard:
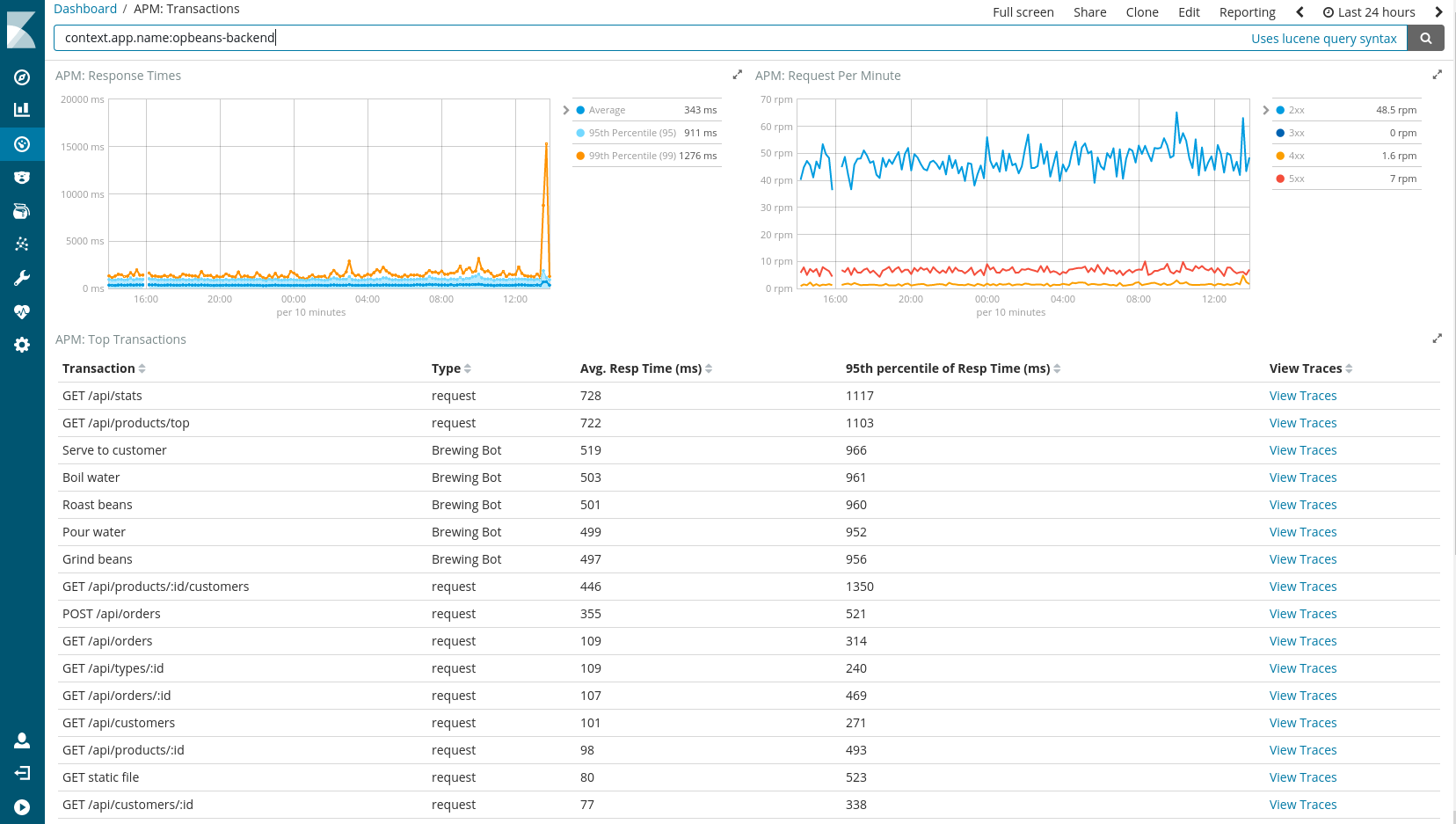
More informationFor detailed instructions on how to install and secure APM Server in your server environment, including details on how to run APM Server in a highly available environment, please see APM Server documentation.
Once APM Server is up and running, you need to install an agent in your service.
Install and configure APM agentsedit
Agents are written in the same language as your service. Currently, Elastic APM has agents for Node.js and for Python.
Setting up a new service to be monitored requires installing the agent in the service, coming up with a good name for the service, and then configuring the agents so they know the address of your APM Server and the service name.
Choose a service nameedit
The service name is used by Elastic APM to differentiate between data coming from different services and to group data coming from the same services. When configuring an agent, you need to supply a service name.
Elastic APM includes the service name field on every document that it saves in Elasticsearch. This has the implication that if you change the service name after using Elastic APM for some time, you will see the old service name and the new service name as two separate services. Make sure you choose a good service name before you get started.
The service name can only contain alphanumeric characters, spaces, underscores, and dashes (must match ^[a-zA-Z0-9 _-]+$).
Install the Node.js agentedit
To install the Node.js agent, simply install the elastic-apm-node module from npm in your service:
npm install elastic-apm-node --save
Then configure the elastic-apm-node module inside your service by adding the following lines to the very top of your code:
// Add this to the VERY top of the first file loaded in your app
var apm = require('elastic-apm-node').start({
// Set required service name (allowed characters: a-z, A-Z, 0-9, -, _, and space)
serviceName: '',
// Use if APM Server requires a token
secretToken: '',
// Set custom APM Server URL (default: http://localhost:8200)
serverUrl: ''
})
The Node.js agent supports Express, hapi, and Koa out of the box. See the APM Node.js Agent documentation for more details.
Install the Python agentedit
To install the Python agent, install the Elastic APM module from pypi:
pip install elastic-apm
The Python agent supports Django and Flask out of the box. See the APM Python Agent documentation for more details.
Set up Kibanaedit
You can use the dashboards that are packaged with APM Server,
as mentioned above.