Managing Indices
editManaging Indices
editIndex Management enables you to view index settings, mappings, and statistics and perform index-level operations. These include refreshing, flushing, clearing the cache, force merging segments, freezing indices, and more. Index Management provides a convenient way to perform bulk operations on multiple indices.
To access this feature, go to Management > Elasticsearch > Index Management.
If security is enabled,
you must have the monitor cluster privilege and the view_index_metadata
and manage index privileges to view the data. See
Security privileges for more
information.
Index Management uses badges to make users aware when an index is frozen, a follower index, or a rollup index. Clicking a badge filters for all indices of that type.
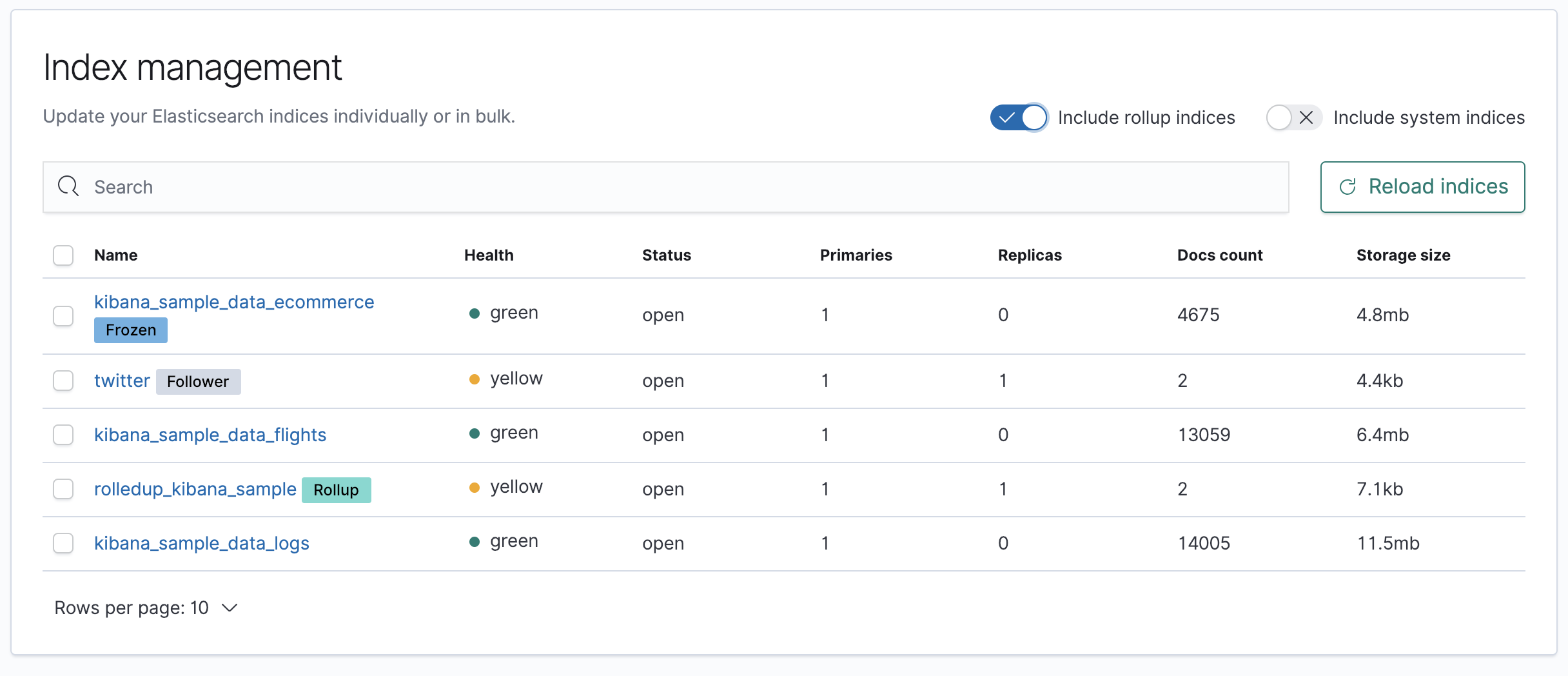
Clicking the name of an index displays the index summary and provides access to the index settings, mapping, and statistics.
From the Manage menu, you can perform these index-level operations on either a single or multiple indices:
- Close the index. Blocks the index from read/write operations. A closed index exists in the cluster, but doesn’t consume resources other than disk space. If you reopen a closed index, it goes through the normal recovery process.
- Force merge the index. Reduces the number of segments in your shard by merging smaller files and clearing deleted ones. Only force merge a read-only index.
- Refresh the index. Writes the operations in the indexing buffer to the filesystem cache. This is automatically done once per second. Forcing a manual refresh is useful during testing, but should not be routinely done in production because it has a performance impact.
- Clear the index cache. Clears all caches associated with the index.
- Flush the index. Frees memory by syncing the filesystem cache to disk and clearing the cache. Once the sync is complete, the internal transaction log is reset.
- Freeze the index. Makes the index read-only and reduces its memory footprint by moving shards to disk. Frozen indices remain searchable, but queries take longer.
- Delete the index. Permanently removes the index and all of it’s documents.
- Add an lifecycle policy. Specifies a policy for managing the lifecycle of the index.
For information about the available management operations, see Indices APIs.